Abdominal Health Emergencies, warning signs and symptoms
It can be easy to blame your abdominal pain on indigestion or stress. But sometimes the pain is more serious, and you’ll need to see a doctor to diagnose appendicitis or any other more serious abdominal conditions
Learn which symptoms to watch out for and when you should get medical help.
Did you know that stomach pain is the most common reason for emergency room visits? When a person is unsure about what to do, it may be best to call a doctor to decide if an ER visit is necessary.
What Causes Stomach Pain?
Common Causes – Harmless abdominal pain usually subsides or goes away within two hours. (WebMD – March 2019)
Gas: Formed in the stomach and intestines as your body breaks down food, this can cause general stomach pain and cramps. This often can be indicated by belching or flatulence.
Bloating: Related to gas, this occurs when excessive gas builds up in your digestive tract. Your stomach will usually feel full, and you may experience cramps.
Constipation: This occurs when you are having difficulty making bowel movements. If you are having two or fewer bowel movements a week, constipation is the likely cause. In addition to feeling bloated and nauseous, you may experience cramping and pain in your rectum.
Indigestion: You typically experience this as an upset stomach, burning, or belly pain after eating.
Stomach flu: Your stomach may hurt before each episode of vomiting or diarrhea.
Severe Pain Causes – In serious cases, the stomach pain gets worse
This may be an indication of a more severe condition, such as:
- Appendicitis: This happens when the appendix, which is part of the large intestine, becomes infected and inflamed. If the appendix ruptures, it can become life-threatening. Surgery to remove the appendix, an appendectomy, is the usual treatment.
- Stomach (peptic) ulcers: crater-like sores in the lining of the stomach and small intestine. These can bleed or burst and be life-threatening if not treated. Medication to reduce your stomach acid can help treat them.
- Gallstones: Hardstones, made up of cholesterol and other materials, that form in the gallbladder, which is just below the liver. They can cause inflammation of the gallbladder, which can lead to inflammation – known as acute cholecystitis. Treatment for these problems includes the removal of the gallbladder.
- Kidney stones: Crystals of varying sizes that form in your urine and build up in your kidneys. The pain can be severe. You can pass some on your own through urination, or doctors may remove them surgically.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): A chronic inflammation in the digestive tract that can cause severe abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, and rectal bleeding. Examples of IBD include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Pancreatitis: The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon – the two hormones that manage how your body processes sugar – and aids in digestion. Inflammation of the pancreas, which can affect its performance and cause severe stomach pain.
- Hernia: Tissue from inside the abdomen that bulges out through a weak point in the abdominal wall. There are several different types depending on where the bulge appears.
(Medicine Net, 2019)
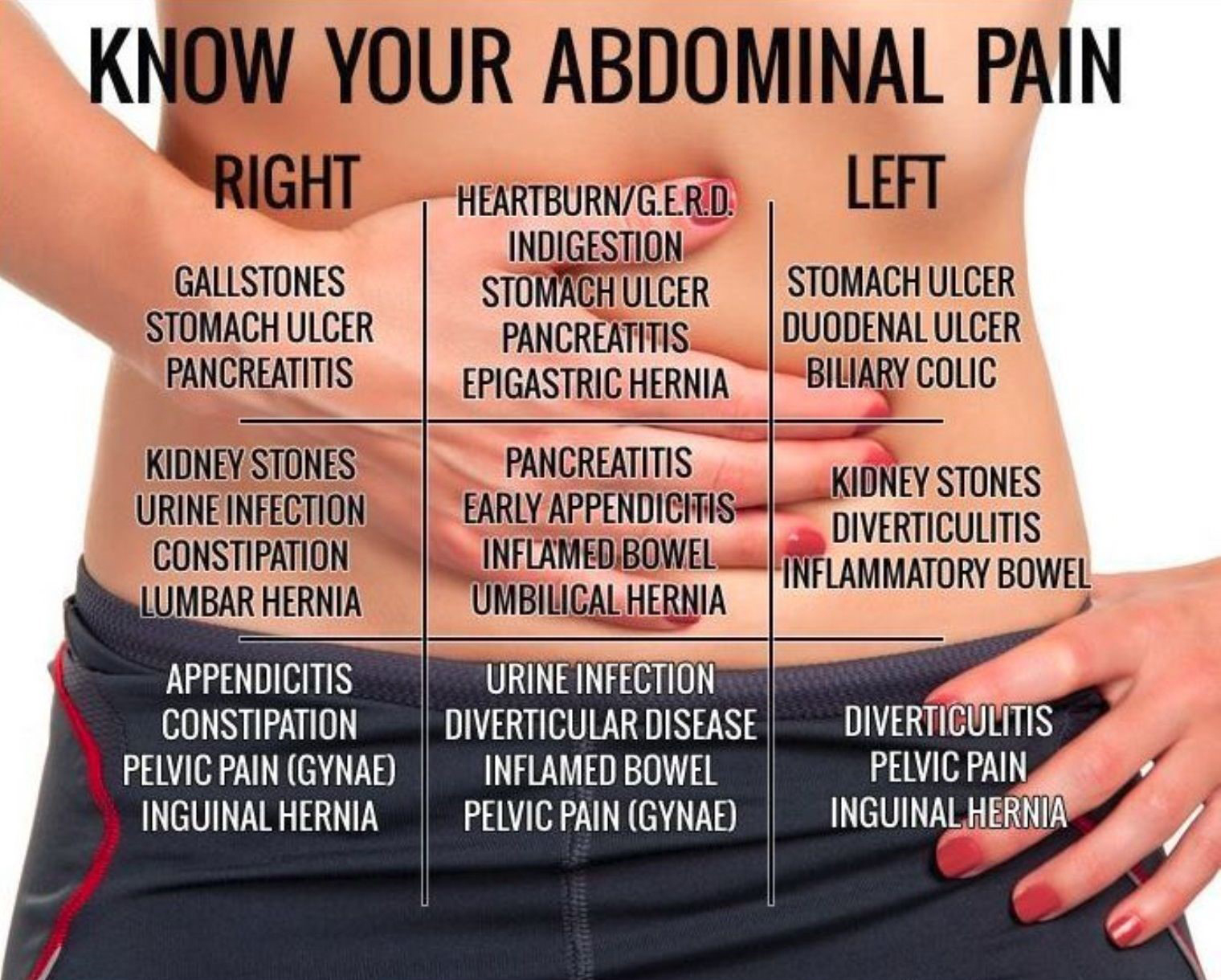
Identify the Abdominal Pain Location
Many times the location of the pain in your stomach can determine the potential cause:
- Upper right: Gallstones, cholecystitis, stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, hepatitis
- Upper center: Heartburn/indigestion, hiatal hernia, epigastric hernia, stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, hepatitis
- Upper left: Functional dyspepsia, stomach ulcer, gastritis, pancreatitis
- Middle right: Kidney stones, kidney infection, inflammatory bowel disease, constipation
- Middle center: Umbilical hernia, appendicitis, stomach ulcer, inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis
- Middle left: Kidney stones, kidney infection, inflammatory bowel disease, constipation
- Lower right: Appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, constipation, pelvic pain
- Lower center: Bladder infection, prostatitis, inflammatory bowel disease, inguinal hernia, pelvic pain
- Lower left: Constipation, diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, pelvic pain, inguinal hernia
When Should You Contact Your Doctor?
If your abdominal pain is severe, doesn’t go away, or keeps coming back, talk to your doctor.
Ideally, mild abdominal pain normally goes away without treatment.
However, in some cases, abdominal pain may need an urgent visit to the ER.
Call Emergency Number if your abdominal pain is severe and associated with trauma (from an accident or injury) or pressure or pain in your chest, or experiencing any of the following:
- Bloody stools
- High fever (greater than 101°F)
- Vomiting up blood (called hematemesis)
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
- Swelling or severe tenderness of the abdomen
- Difficulty breathing
- In case you’re pregnant or breastfeeding and you experience abdominal pain, we highly recommend visiting the ER without delay.
(Healthline, 2019)
At last, we can summarize that stomach pain can feel very uncomfortable, and can often signal a minor illness.
However, it is not possible to diagnose stomach pain based on symptoms alone.
The severity of a person’s stomach pain does not necessarily correlate with the severity of the illness.
For example, some gas pain can be severe but will pass without causing any lasting harm. (Medical News Today, 2019)
It is best to have a visit to the ER on the side of caution and see a doctor for any stomach pain that does not go away, or if the cause is unclear.
References
Marks, Jay W., and Charles Patrick Davis. “Abdominal Pain: Reasons for Stomach Aches, Cramps & Discomfort.” MedicineNet, MedicineNet, 12 July 2019, www.medicinenet.com/abdominal_pain_causes_remedies_treatment/article.html
Kahn, April. “Abdominal Pain: Causes, Types, and Prevention.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 8 May 2020, www.healthline.com/health/abdominal-pain
Khatri, Minesh. “Why Does My Stomach Hurt? 17 Possible Causes of Stomach Pain.” WebMD, WebMD, 30 May 2019, www.webmd.com/pain-management/guide/abdominal-pain-causes-treatments
“Severe Stomach Pain: When to Go to the Doctor.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325162
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Acute Abdomen: Causes And Cures
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck): What It Is And When It Is Performed
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Abdominal Trauma: A General Overview Of Management And Trauma Areas
Abdominal Distension (Distended Abdomen): What It Is And What It Is Caused By
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Symptoms, Evaluation And Treatment
Hypothermia Emergencies: How To Intervene On The Patient
Emergencies, How To Prepare Your First Aid Kit
Seizures In The Neonate: An Emergency That Needs To Be Addressed
First Aid, When Is It An Emergency? Some Information For Citizens
Precordial Chest Punch: Meaning, When To Do It, Guidelines
Ambu Bag, Salvation For Patients With Lack Of Breathing
Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD’s)
UK / Emergency Room, Paediatric Intubation: The Procedure With A Child In Serious Condition
How Long Does Brain Activity Last After Cardiac Arrest?
Quick And Dirty Guide To Chest Trauma
Cardiac Arrest: Why Is Airway Management Important During CPR?
Neurogenic Shock: What It Is, How To Diagnose It And How To Treat The Patient
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
6 Facts About Burn Care That Trauma Nurses Should Know
Blast Injuries: How To Intervene On The Patient’s Trauma
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Ukraine Under Attack, Ministry Of Health Advises Citizens About First Aid For Thermal Burn
Electric Shock First Aid And Treatment
RICE Treatment For Soft Tissue Injuries
How To Carry Out Primary Survey Using The DRABC In First Aid
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
The Patient Complains Of Blurred Vision: What Pathologies Can Be Associated With It?
A Tourniquet Is One Of The Most Important Pieces Of Medical Equipment In Your First Aid Kit
12 Essential Items To Have In Your DIY First Aid Kit
First Aid For Burns: Classification And Treatment
Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible Shock: What They Are And What They Determine
Burns, First Aid: How To Intervene, What To Do
First Aid, Treatment For Burns And Scalds
Wound Infections: What Causes Them, What Diseases They Are Associated With
Patrick Hardison, The Story Of A Transplanted Face On A Firefighter With Burns
Eye Burns: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Burn Blister: What To Do And What Not To Do
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
Emergency Burn Treatment: Rescuing A Burn Patient
Epileptic Aura: The Phase Before A Seizure
Seizures In Children: Types, Causes And Treatments Of Seizures
Spinal Immobilisation Of The Patient: When Should The Spine Board Be Put Aside?
First Aid And Medical Intervention In Epileptic Seizures: Convulsive Emergencies
Airway Management After A Road Accident: An Overview
Ambulance: Common Causes Of EMS Equipment Failures — And How To Avoid Them
Traumatic Injury Emergencies: What Protocol For Trauma Treatment?
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
What Is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Pathophysiology Of Thoracic Trauma: Injuries To The Heart, Great Vessels And Diaphragm
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Manoeuvres: Management Of The LUCAS Chest Compressor
Chest Trauma: Clinical Aspects, Therapy, Airway And Ventilatory Assistance
Abdominal Pain: ‘Should I Go To The Emergency Room?


