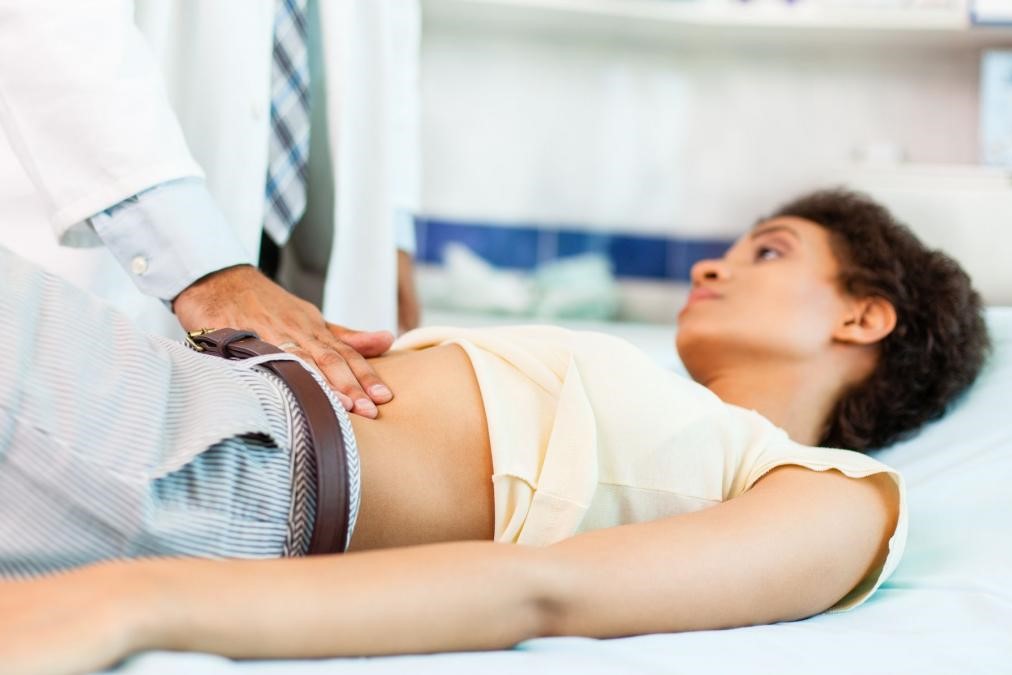
Abdominal pain: 'Should I go to the emergency room?
When is abdominal pain severe enough to warrant a trip to the emergency room? Very often patients come to the emergency room complaining of stomach pain
Sometimes the cause of this pain is severe enough to justify a visit, while at other times a doctor’s visit could have been avoided.
Abdominal pain, when is it appropriate to go to the emergency room?
- If the pain is so severe that you cannot stand up, you should go to the emergency room.
- If the pain is new, it is possible that it is appendicitis. Normally appendicitis pain starts in the epigastric area or navel and over time migrates to the lower right side of the abdomen. If antibiotics and surgery are not used, or if treatment is significantly delayed, the risk of severe infection, sepsis or even death is high.
- Pain in the upper right abdomen could also be the result of gallstones. It usually occurs after eating, especially fatty or greasy food. But the result of this condition is the same: a trip to the emergency room for blood tests and imaging.
- When it comes to abdominal problems, you literally have to listen to your gut. If the pain is abnormally intense and you feel that you need immediate help, you should seek medical attention immediately.
EMERGENCY RADIO IN THE WORLD? VISIT THE EMS RADIO BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Other key indicators are the symptoms that accompany pain in the abdomen
Emergency symptoms
If any of the following symptoms occur in addition to pain, emergency assistance may be required:
- fever
- Inability to eat without vomiting
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain
- irregular heartbeat
- feeling light-headed or fainting
- Dark, black or bloody stools
- Vomiting blood
Another thing to keep in mind is that some people with certain conditions are at higher risk and should go to the emergency room.
For example:
- individuals who have recently undergone an endoscopy or abdominal surgery
- women who are pregnant or may be pregnant
- People over 45 years of age who experience pain in the upper abdomen or tightness in the chest (may indicate a heart attack)
- People who have undergone gastric bypass surgery.
Some signs that abdominal pain requires medical intervention in the emergency room
Intense pain
If the pain is so severe that you cannot stand up, go to the emergency room.
Another sign of possible severity is if the stomach is sensitive to touch or if it occurs suddenly or with fever.
Vomiting
If you find yourself in the unfortunate situation of vomiting and notice blood in your vomit, you should seek medical attention.
Recent surgery or pregnancy?
It is important to remember that if you are experiencing abdominal pain and have recently undergone surgery or are pregnant, a trip to us is definitely the right choice.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Acute Abdomen: Causes And Cures
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck): What It Is And When It Is Performed
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Abdominal Trauma: A General Overview Of Management And Trauma Areas
Abdominal Distension (Distended Abdomen): What It Is And What It Is Caused By
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Symptoms, Evaluation And Treatment
Hypothermia Emergencies: How To Intervene On The Patient
Emergencies, How To Prepare Your First Aid Kit
Seizures In The Neonate: An Emergency That Needs To Be Addressed
First Aid, When Is It An Emergency? Some Information For Citizens
Precordial Chest Punch: Meaning, When To Do It, Guidelines
Ambu Bag, Salvation For Patients With Lack Of Breathing
Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD’s)
UK / Emergency Room, Paediatric Intubation: The Procedure With A Child In Serious Condition
How Long Does Brain Activity Last After Cardiac Arrest?
Quick And Dirty Guide To Chest Trauma
Cardiac Arrest: Why Is Airway Management Important During CPR?
Neurogenic Shock: What It Is, How To Diagnose It And How To Treat The Patient
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
6 Facts About Burn Care That Trauma Nurses Should Know
Blast Injuries: How To Intervene On The Patient’s Trauma
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Ukraine Under Attack, Ministry Of Health Advises Citizens About First Aid For Thermal Burn
Electric Shock First Aid And Treatment
RICE Treatment For Soft Tissue Injuries
How To Carry Out Primary Survey Using The DRABC In First Aid
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
The Patient Complains Of Blurred Vision: What Pathologies Can Be Associated With It?
A Tourniquet Is One Of The Most Important Pieces Of Medical Equipment In Your First Aid Kit
12 Essential Items To Have In Your DIY First Aid Kit
First Aid For Burns: Classification And Treatment
Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible Shock: What They Are And What They Determine
Burns, First Aid: How To Intervene, What To Do
First Aid, Treatment For Burns And Scalds
Wound Infections: What Causes Them, What Diseases They Are Associated With
Patrick Hardison, The Story Of A Transplanted Face On A Firefighter With Burns
Eye Burns: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Burn Blister: What To Do And What Not To Do
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
Emergency Burn Treatment: Rescuing A Burn Patient
Epileptic Aura: The Phase Before A Seizure
Seizures In Children: Types, Causes And Treatments Of Seizures
Spinal Immobilisation Of The Patient: When Should The Spine Board Be Put Aside?
First Aid And Medical Intervention In Epileptic Seizures: Convulsive Emergencies
Airway Management After A Road Accident: An Overview
Ambulance: Common Causes Of EMS Equipment Failures — And How To Avoid Them
Traumatic Injury Emergencies: What Protocol For Trauma Treatment?
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
What Is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Pathophysiology Of Thoracic Trauma: Injuries To The Heart, Great Vessels And Diaphragm
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Manoeuvres: Management Of The LUCAS Chest Compressor
Chest Trauma: Clinical Aspects, Therapy, Airway And Ventilatory Assistance


