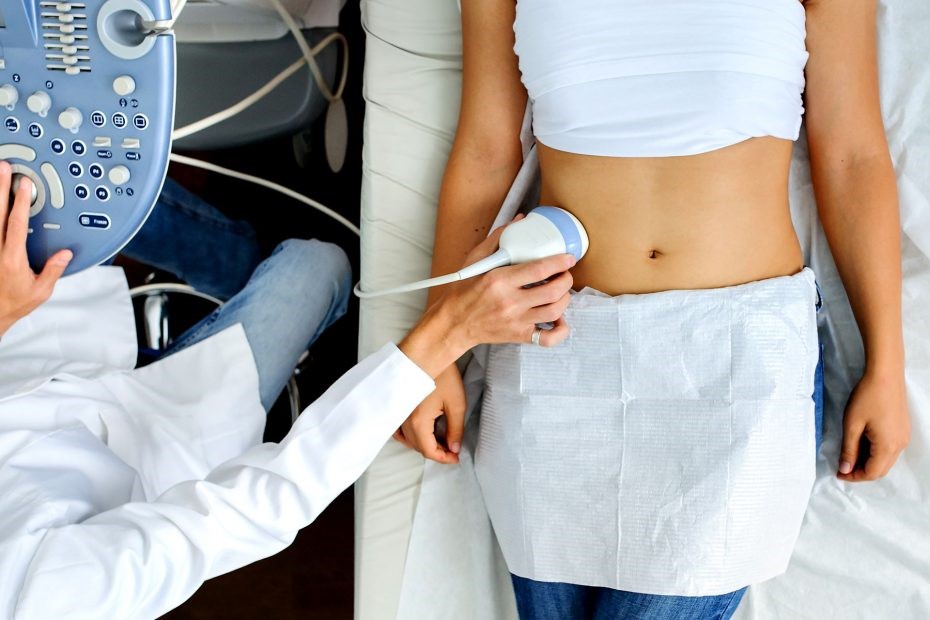
Abdominal ultrasound: how to prepare for the exam?
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys
The blood vessels that lead to some of these organs, such as the inferior vena cava and aorta, can also be examined with ultrasound.
An ultrasound machine makes images of organs and structures inside the body
The machine sends out high-frequency sound waves that reflect off body structures.
A computer receives these waves and uses them to create a picture.
Unlike with x-rays or CT scans, this test does not expose you to ionizing radiation.
You will be lying down for the procedure.
A clear, water-based conducting gel is applied to the skin over the abdomen.
This helps with the transmission of the sound waves.
A handheld probe called a transducer is then moved over the abdomen.
You may need to change position so that the health care provider can look at different areas.
You may also need to hold your breath for short periods during the exam.
Most of the time, the test takes less than 30 minutes.
How to Prepare for an abdominal ultrasound
How you will prepare for the test depends on the problem.
You will likely be asked not to eat or drink for several hours before the exam.
Your health care provider will go over what you need to do.
How the Test will Feel
There is little discomfort.
The conducting gel may feel a little cold and wet.
The sonographer may press the probe against your abdomen.
Why an abdominal ultrasound is Performed
You may have this test to:
- Find the cause of abdominal pain
- Find the cause of kidney infections
- Diagnose or monitor tumors and cancers
- Diagnose or treat ascites
- Learn why there is swelling of an abdominal organ
- Look for damage after an injury
- Look for stones in the gallbladder or kidney
- Look for the cause of abnormal blood tests such as liver function tests or kidney tests
- Look for the cause of a fever
The reason for the test will depend on your symptoms.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The meaning of abnormal results depends on the organ being examined and the type of problem.
Talk to your provider if you have any questions or concerns.
An abdominal ultrasound can indicate conditions such as
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Abscess
- Appendicitis
- Cholecystitis
- Gallstones
- Hydronephrosis
- Kidney stones
- Pancreatitis (inflammation in pancreas)
- Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
- Portal hypertension
- Liver tumors
- Obstruction of bile ducts
- Cirrhosis
Risks
There is no known risk.
You are not exposed to ionizing radiation.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Abdominal Health Emergencies, Warning Signs And Symptoms
Abdominal Ultrasound: How It Is Performed And What It Is Used For
Abdominal Pain: ‘Should I Go To The Emergency Room?
Diagnostic Tests: What Is Ecoendoscopy?
What Is Ultrasound Of The Complete Abdomen?
Acute Abdomen: Causes And Cures
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck): What It Is And When It Is Performed
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Abdominal Trauma: A General Overview Of Management And Trauma Areas
Abdominal Distension (Distended Abdomen): What It Is And What It Is Caused By
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Symptoms, Evaluation And Treatment
What Is The Resting Cardiac Echocolordoppler (Or Echocardiogram)?
Echo- And CT-Guided Biopsy: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Echodoppler: What It Is And When To Perform It
What Is 3D Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
What Is Stress Echocardiography And What Is It Used For?
What Is Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
Echocardiogram: What It Is And When It Is Required
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
What Is The Loop Recorder? Discovering Home Telemetry
Cardiac Holter, The Characteristics Of The 24-Hour Electrocardiogram
Peripheral Arteriopathy: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Endocavitary Electrophysiological Study: What Does This Examination Consist Of?
Cardiac Catheterisation, What Is This Examination?
Echo Doppler: What It Is And What It Is For
Transesophageal Echocardiogram: What Does It Consist Of?
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Echotomography Of Carotid Axes


