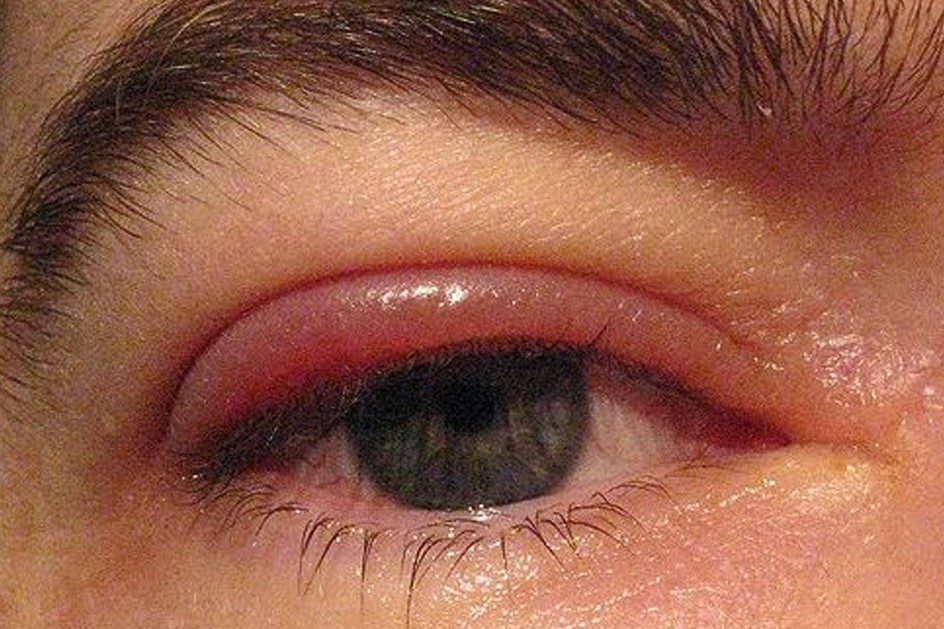
Blepharitis: the inflammation of the eyelids
Blepharitis consists of an inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelid, which is quite common. The condition often tends to become chronic, favoured by polluted environments, poor hygiene and familiarity
Symptoms of blepharitis
Symptoms are characterised by burning and a sensation of heat on the eyelid edge.
Itching is also very common, due to which there is a tendency to rub the eyelid with the hand.
This latter behaviour should be avoided, however, as it promotes inflammation, causing micro-lesions of the eyelid skin over time.
In addition to this symptomatology typical of mild forms, in severe blepharitis there is eyelid swelling, localised pain that is accentuated by blinking and, finally, photophobia, i.e. intolerance to light.
The causes of blepharitis
The causes of blepharitis can be:
- an altered secretion of the eyelid meibomian glands (sebaceous secretion rich in lipids)
- uncorrected refractive defects (especially astigmatism and hypermetropia);
- skin diseases (such as seborrhoeic eczema);
- eating disorders (avitaminosis and dyspepsia);
- general pathologies such as diabetes or increased blood fats (cholesterol, triglycerides);
- allergic and environmental factors (smoke, dust).
Certain bacteria, such as staphylococci or streptococci, can be the main cause or complicate blepharitis
Small white dandruff-like scales, small crusts and, in more severe forms, the formation of actual ulcers can occur on the eyelid margin.
Diagnosis: how is it made?
The diagnosis is based on the presence of the above-mentioned eyelid signs and symptoms and on the objective examination, which is carried out by the ophthalmologist using a slit lamp or biomicroscope, which allows better observation thanks to a magnification of the anatomical structures of the eye.
How to prevent blepharitis
Given the tendency for recurrence, chronicity and the considerable difficulty in healing, general rules of hygiene and behaviour must be followed to prevent blepharitis.
Compliance with normal rules of hygiene is essential to minimise the risk of any type of infection, including blepharitis.
It is therefore recommended to always wash one’s hands thoroughly, especially before touching the eyes, trying to minimise this habit.
When a family member or cohabitant complains of symptoms of probable blepharitis, as well as any other eye infection, it is advisable to avoid the promiscuous use of personal care items, bed linen, clothing or pillowcases, so that contamination does not occur.
Women are also advised to avoid using eye cosmetics during the entire treatment.
It is important to follow a proper diet rich in fruit, fresh vegetables and lean proteins, such as chicken and fish, which are always good for eye health.
You should limit sugar and caffeinated drinks, which can contribute to eye irritation and worsen blepharitis symptoms.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Ophthalmology: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment Of Astigmatism
Pupillary Reflex To Light: Mechanism And Clinical Significance
Cataract: Symptoms, Causes And Intervention
Inflammations Of The Eye: Uveitis
Corneal Keratoconus, Corneal Cross-Linking UVA Treatment
Myopia: What It Is And How To Treat It
Presbyopia: What Are The Symptoms And How To Correct It
4 Reasons To Seek Emergency Care For Vision Symptoms
Autoimmune Diseases: The Sand In The Eyes Of Sjögren’s Syndrome
Blepharoptosis: Getting To Know Eyelid Drooping
Corneal Abrasions And Foreign Bodies In The Eye: What To Do? Diagnosis And Treatment
Corneal Abrasions And Foreign Bodies In The Eye: What To Do? Diagnosis And Treatment
Wound Care Guideline (Part 2) – Dressing Abrasions And Lacerations
Contusions And Lacerations Of The Eye And Eyelids: Diagnosis And Treatment
Macular Degeneration: Faricimab And The New Therapy For Eye Health
Blepharoptosis: Getting To Know Eyelid Drooping
Blepharitis: What Is It And What Are The Most Common Symptoms?
Essential Blepharospasm: What It Is And What It Can Be A Symptom Of


