Chemical Burns: First Aid Treatment and Prevention Tips
Chemical burns must be treated as a medical emergency. This is because many chemicals commonly used at home, school, or work can cause severe burns to the skin and may cause deeper burns than they look
The severity of burns will depend on the type of chemical, how long it is in contact with the skin, and how strong the chemical is.
If you see someone having a chemical burn, washing the chemical off as quickly as possible with large amounts of water is vital.
Here are other things that you should know about chemical burns.
What is Chemical Burn?
Chemical burns are tissue damage due to a harsh or corrosive substance.
Usually, most people are aware of such a burn and its cause.
But sometimes, you may not immediately recognize it if a milder chemical substance causes it.
Unlike heat burns, chemical toxins can continue causing tissue damage even after you come into contact with them.
Therefore, immediate medical attention is essential to prevent scarring or complications.
The damage may develop hours after exposure.
Major chemical burns need emergency medical help, while you can usually treat minor chemical burns with first aid.
Who Are at Risk of Chemical Burns?
Workers exposed to chemicals for their jobs, such as construction and factory workers, farmers, laboratory technicians, mechanics, and plumbers, are at high risk of chemical burns.
Infants and children are also at risk of chemical burns since they may accidentally touch or swallow chemicals in the house like detergents, bleach, or cleaning products.
Burns from chemicals often happen by accident at home or in the workplace, but sometimes, they can also result from an assault or self-harm.
They are most likely to affect the eye surface, face, limbs, hands, or feet. For instances of self-harm, chemicals can also burn you inside if swallowed.
FIRST AID: VISIT THE DMC DINAS MEDICAL CONSULTANTS BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
What Causes Chemical Burn?
Most chemical burns are caused by strong acids such as sulfuric acid, muriatic acid, or strong bases, which you can find in products such as:
- Petrol
- Concrete mix
- Pool chlorinators
- Phosphorous (found in fireworks and fertilizers)
- Drain or toilet bowl cleaners
- Metal cleaners
- Bleach
What Are the Symptoms of Chemical Burn?
The symptoms of a chemical burn are similar to a burn caused by sunburn or heat.
A burn to the eye can cause vision problems, and a burn to the lungs can cause coughing or shortness of breath.
Other common symptoms include:
- Redness and burning in the skin
- Pain or numbness
- Blisters
- Blackened skin
For Severe Chemical Injury, the Symptoms Are:
- Irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness and faintness
- Headache
- Seizure
- Low blood pressure
- Heart attack
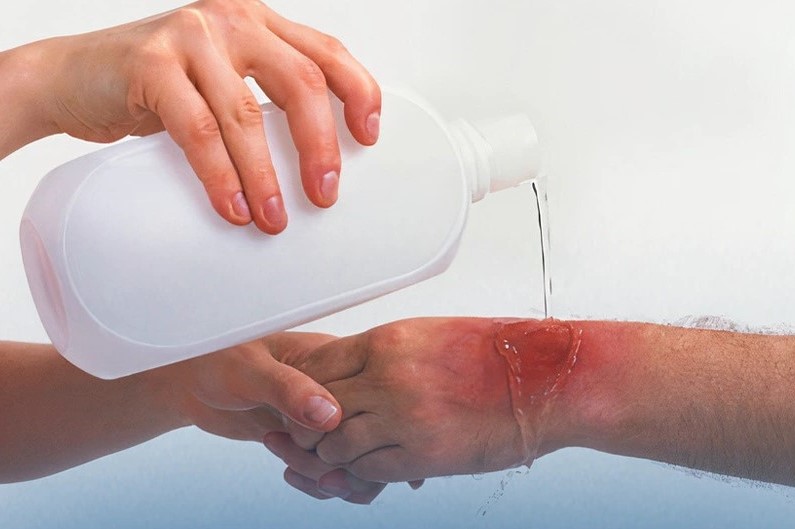
First Aid for Chemical Burns
You probably won’t be admitted to the hospital if you have a minor chemical burn.
However, you should follow your doctor’s instructions to keep the wound clean and prevent it from drying.
In addition, your doctor will advise you on appropriate pain relief and what creams and dressings should be applied.
If you have a burn injury caused by chemicals, take these steps immediately:
- Dial Emergency Number
- Put on gloves and brush off any remaining dry chemicals. Avoid exposing yourself to chemicals.
- Remove contaminated clothing or jewelry and rinse the area with cool water for at least 20 minutes. Flood area or until help from the emergency department arrives.
- Don’t use a strong stream of water, if possible; make sure water doesn’t flow onto another part of the person’s body or you.
- After flushing the burn, follow instructions on the label of the chemical product, if available.
- Don’t try to neutralize the burn with acid or alkali because it could cause a chemical reaction that worsens the burn.
- Don’t put antibiotic ointment on the burn.
- Cover the burn with a clean cloth or bandage. Do not wrap it tightly to avoid putting pressure on the damaged skin.
- If you feel more burning, rinse it again with large amounts of water for several more minutes.
RESCUERS’ RADIO IN THE WORLD? VISIT THE EMS RADIO BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
When to Seek Emergency Medical Care?
The severe chemical injury will need medical attention and emergency treatment in the hospital to control the pain and prevent infection.
Healthcare providers also need to manage any problems with breathing or circulation caused by the burn.
For example, they will ask you about the type of chemical, how much there was, how long was the contact with the skin, and what medical treatment has been done.
It’s crucial to seek immediate medical treatment for severe chemical burns, which are deep, involving all layers of the skin, more extensive than 3 inches in diameter, and if the burn covers the hands, feet, face, or a major joint or encircles an arm or leg.
It might cause shock, with symptoms such as cool, clammy skin, weak pulse, and shallow breathing.
In some cases of severe burns, patients may need surgery to remove the burned portion of their skin.
In addition, some may need a skin graft, where a surgeon takes healthy skin on your body and attaches it to the burned area.
This surgery can also repair perforations in your gastrointestinal tract.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Head Trauma And Brain Injuries In Childhood: A General Overview
Stroke Action First Aid: Actions To Recognise And Help
Neonatal/Pediatric Endotracheal Suctioning: General Characteristics Of The Procedure
Food Poisoning: Know The Symptoms And First Aid Treatment
War In Ukraine, Doctors In Kiev Receive WHO Training On Chemical Weapons Damage
FDA Warns On Methanol Contamination Using Hand Sanitizers And Expands The List Of Poisonous Products
Poison Mushroom Poisoning: What To Do? How Does Poisoning Manifest Itself?
Identifying And Treating Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Emergency Burn Treatment: Rescuing A Burn Patient
First Aid For Scalding: How To Treat Hot Water Burn Injury
6 Facts About Burn Care That Trauma Nurses Should Know
Blast Injuries: How To Intervene On The Patient’s Trauma
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Ukraine Under Attack, Ministry Of Health Advises Citizens About First Aid For Thermal Burn
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
Electric Shock First Aid And Treatment
RICE Treatment For Soft Tissue Injuries
How To Carry Out Primary Survey Using The DRABC In First Aid
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
The Patient Complains Of Blurred Vision: What Pathologies Can Be Associated With It?
A Tourniquet Is One Of The Most Important Pieces Of Medical Equipment In Your First Aid Kit
12 Essential Items To Have In Your DIY First Aid Kit
First Aid For Burns: Classification And Treatment
Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible Shock: What They Are And What They Determine
Burns, First Aid: How To Intervene, What To Do
First Aid, Treatment For Burns And Scalds
Wound Infections: What Causes Them, What Diseases They Are Associated With
Patrick Hardison, The Story Of A Transplanted Face On A Firefighter With Burns
Eye Burns: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Burn Blister: What To Do And What Not To Do


