CT scan of the chest in smokers: what it is used for and why it is essential
CT scan of the chest in smokers: the lung and cardiovascular diseases that are most frequent in patients at high risk due to persistent exposure to cigarette smoke require early diagnosis and careful follow-up
Early diagnosis is the only way to intervene in these diseases when they are still in their early stages, thus enabling timely treatment that will impact on the clinical history of these patients.
The need for regular and constant follow-up in high-risk patients should be considered a priority: for this reason it is essential that both patients who are already undergoing screening, and those who would be accessing screening for the first time, never miss their scheduled appointments.
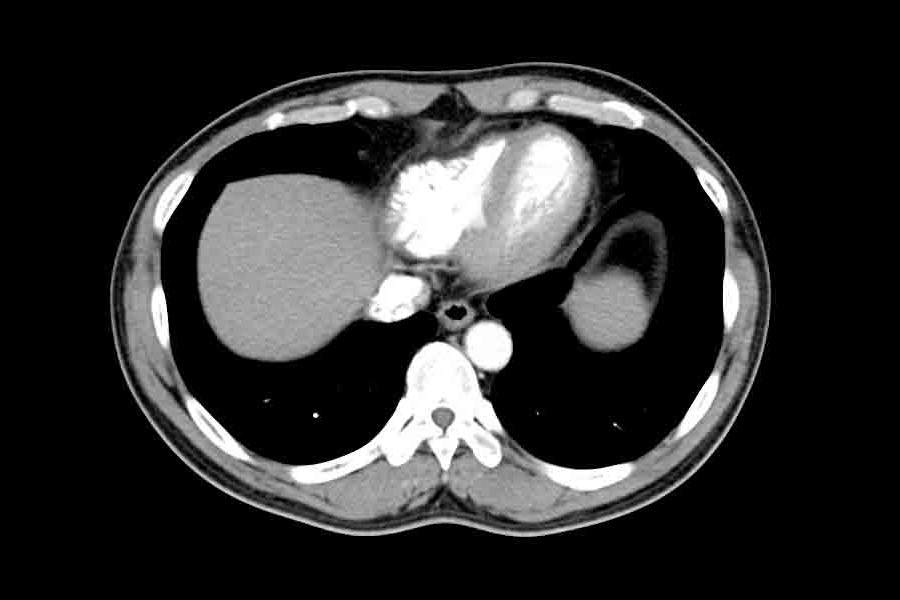
The reference examination, which should not be postponed under any circumstances, for detecting lung cancer at an early stage is the low-dose CT scan without contrast medium, which all high-risk patients (heavy smokers and workers exposed to other known risk factors) over 50 years of age should have at least once every two years.
Chest CT: an ally against lung cancer
Computed Axial Tomography (CT) is a diagnostic method based on the use of X-rays (ionising radiation).
The Humanitas Group has 15 CT scans, all with advanced “multi-layer” technology and optimised to obtain high quality examinations with a particularly low dose of radiation, slightly higher than that of a standard chest X-ray study.
Among the major risk factors for lung cancer is exposure to cigarette smoke.
Thanks to low-dose CT scans without contrast medium, lung nodules can be detected even when they are less than a centimetre in size and therefore still in an early stage, i.e. when the patient has not yet usually developed any symptoms of the disease.
It is very important to detect lung cancer at this stage, because at a more advanced stage the chances of recovery decrease dramatically.
Screening also allows minimally invasive, robotic and personalised surgery techniques to be used to detect very small tumours: a type of approach that allows less invasive operations, with less painful and faster recovery for the patient and a shorter hospital stay.
Low-dose thoracic CT scan without contrast medium is also used clinically in cardiology
It can be used to assess the level of calcification of the coronary arteries, an important risk factor for diseases such as heart attack and coronary artery stenosis.
Screening with chest CT, therefore, also helps to assess cardiovascular risk, directing patients to more invasive second-line procedures only when necessary.
Read Also:
Psychosis Is Not Psychopathy: Differences In Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
PET: What It Is For And How To Take The Exam


