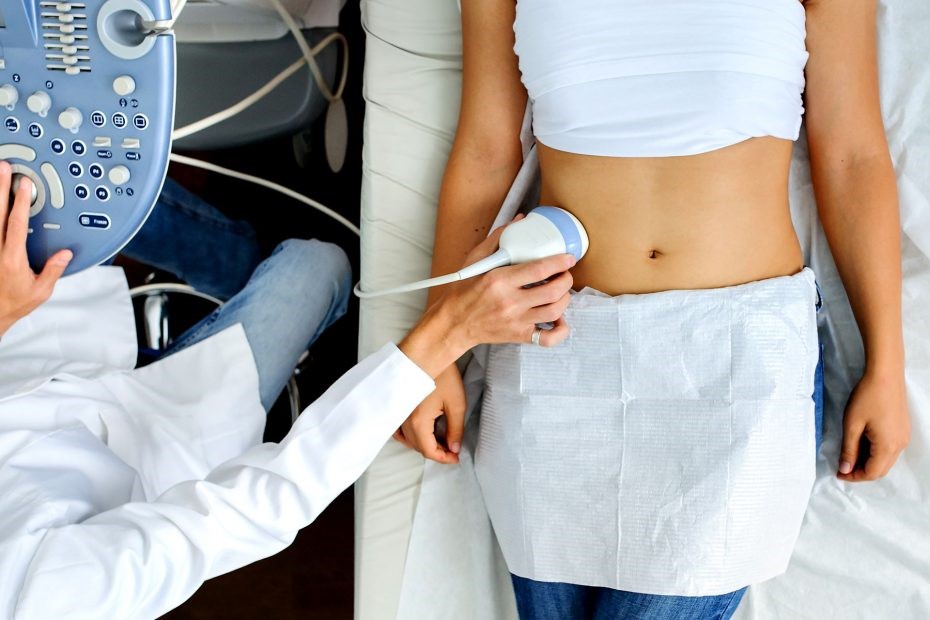
Diagnostic tests: what is ultrasound?
Ultrasound scanning is a simple diagnostic imaging technique used by many specialists who turn to the sonographer for a more in-depth examination to aid diagnosis
Ultrasound makes use of ultrasound to obtain a precise image of the organs under investigation
While originally ultrasound was mainly used in the internist and gynaecologist fields, today it is a fundamental routine test often used in the diagnostic field (internist, surgical, gynaecologist, endocrinologist, urologist, obstetrician, orthopaedist).
What is ultrasound used for?
The field of application of ultrasound is vast; it is a test that allows images of the organs being observed to be acquired.
Apart from bones, for example, which are not visible, everything else is clearly observable: ultrasound shows everything that is parenchymal (the liver, kidneys) and everything that is liquid (bladder, cysts, haematomas).
Ultrasound has not only a diagnostic purpose, it is in fact used a great deal as a guide for interventional manoeuvres: biopsies, drainage of abscesses, placement of catheters.
These interventions are performed by the sonographer with the collaboration of the surgeon, the hepatologist or the specialist who sends the patient for surgery.
Who can perform ultrasound?
There are no limitations or contraindications to undergoing this test.
Is ultrasound painful or dangerous?
It is well established that ultrasound is harmless for the body; there are therefore no limitations or contraindications to undergoing this type of test.
How does ultrasound work?
Using a probe that sends ultrasound (placed on the patient’s body or, in certain ultrasound scans, inserted into the vagina or anus, for example), the sonographer is able to ‘see’ inside the human body.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
What Is The Resting Cardiac Echocolordoppler (Or Echocardiogram)?
What Is Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
Echocardiogram: What It Is And When It Is Required
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
What Is The Loop Recorder? Discovering Home Telemetry
Cardiac Holter, The Characteristics Of The 24-Hour Electrocardiogram
Peripheral Arteriopathy: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Endocavitary Electrophysiological Study: What Does This Examination Consist Of?
Cardiac Catheterisation, What Is This Examination?
Echo Doppler: What It Is And What It Is For
Transesophageal Echocardiogram: What Does It Consist Of?
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Echotomography Of Carotid Axes
Echo- And CT-Guided Biopsy: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Echodoppler: What It Is And When To Perform It
What Is 3D Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
Congenital Heart Disease: Tricuspid Atresia
What Is Stress Echocardiography And What Is It Used For?


