Echo Doppler: what it is and what it is for
Echo Doppler is used to diagnose congenital heart disease, narrowing and aneurysms of blood vessels
Doppler ultrasound or echo Doppler or echocolordoppler (see below) is based on a physical principle postulated in 1842 by Christian Doppler: the frequency of a sound varies as a result of the relative movement between the sound wave transmitter and the receiver.
If the transmitter is an ambulance siren and the receiver is our ear, we can tell if the ambulance is approaching or receding by perceiving the changes in frequency of the sound emitted by the siren.
Ultrasound scanning uses high-frequency sound waves: the ultrasound is emitted by a probe and passes through the tissues and returns, allowing the image of the region under examination to be formed.
The ultrasound reflected by red blood cells and other corpuscular blood components within arteries and veins changes frequency as the reflectors – e.g. red blood cells – move closer to or further away from the probe.
Thus, using this instrument, blood flow can be detected.
With the emergence of more powerful processors, it was possible to take multiple simultaneous measurements, represent them in space and merge them with the two-dimensional (moving, real-time) image.
This is how Echo-Doppler is created: due to variations in ultrasound frequency, blood flowing towards the probe is conventionally represented in red while blood moving away from the probe appears blue on the screen.
What is Echo-Doppler used for?
Echo Doppler has many indications in paediatrics and medicine in general.
In cardiology, it can be used to study the structure and function of the heart and heart valves in congenital heart disease and thus to make a diagnosis in most cases without invasive investigations.
It can be used to assess blood flow in large vessels and within organs.
The technique makes it possible to directly and indirectly assess the presence of narrowing (stenosis) or complete obstruction of blood vessels, to detect collateral circuits, aneurysms, to analyse the state of organs on the basis of the resistance they offer to blood flow.
The limitations of Echo Doppler, which is operator dependent, are related to the equipment of probes, the characteristics of the organs and subjects to be investigated, the depth of the vessel, the speed of the flow.
The passage of ultrasound is impeded by air and bone. Slow flow in an obese patient is the biggest challenge.
How is an Echo Doppler performed?
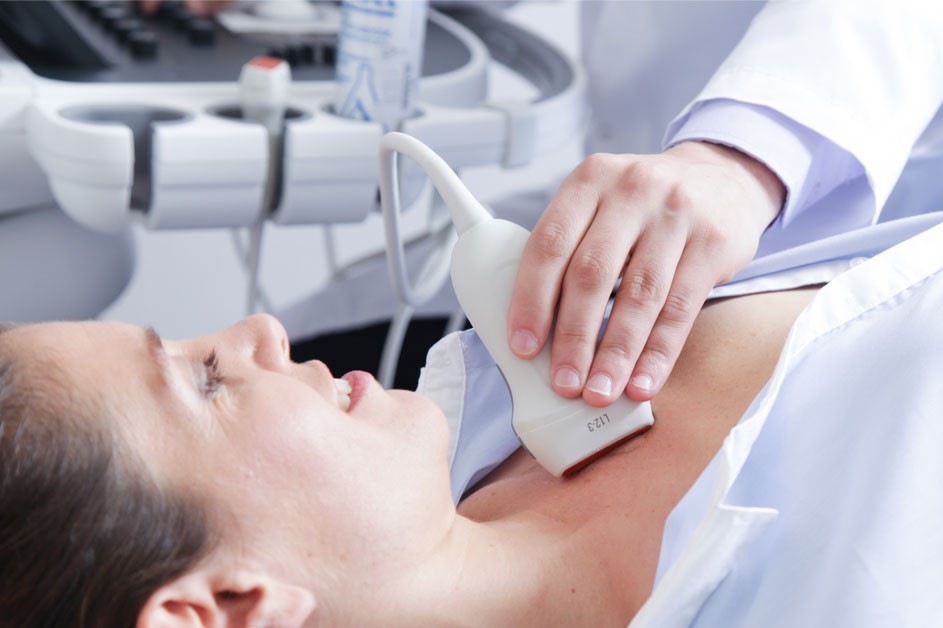
The Echo Doppler needs no preparation, it is performed like an ultrasound scan.
With the patient lying on a couch, the doctor runs a probe coated with gel over the skin.
The examination lasts about 10-20 minutes.
Echo Doppler has no contraindications.
It is non-invasive, painless and not dangerous.
Read Also:
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Heart Murmur: What Is It And What Are The Symptoms?
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Manoeuvres: Management Of The LUCAS Chest Compressor


