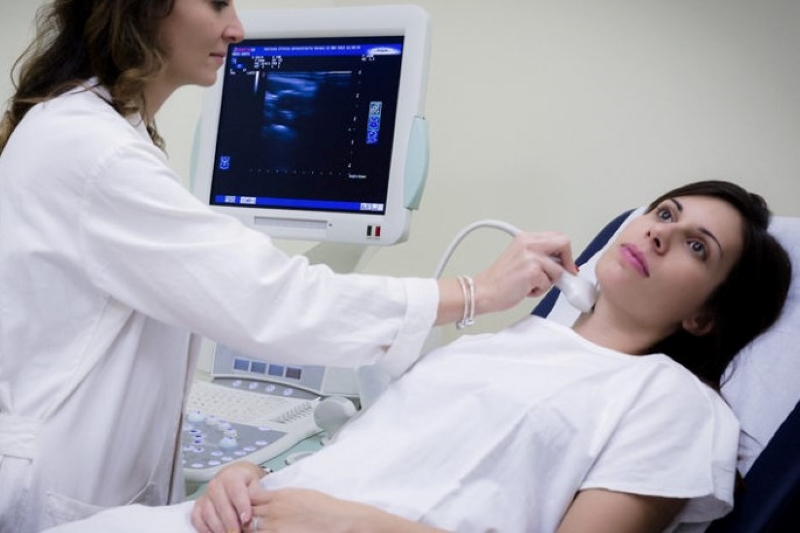
Echotomography of carotid axes
Echotomography of the carotid axes is an inexpensive, non-invasive and therefore easily repeatable test that allows the determination of carotid damage in the preclinical phase and with it a staging of the patient with arterial hypertension
Why use echotomography
With this method it is possible to make accurate measurements of the thickness of the intima media complex (IMT) of the carotid wall for a quantitative assessment of the extent of vascular damage.
The quantitative analysis is performed by taking 12 measurements at the distal third of the common carotid artery, the bulb and the proximal third of the internal carotid artery for both right and left carotids.
Accuracy in these measurements can be up to a tenth of a millimetre.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
What Is The Loop Recorder? Discovering Home Telemetry
Cardiac Holter, The Characteristics Of The 24-Hour Electrocardiogram
Peripheral Arteriopathy: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Endocavitary Electrophysiological Study: What Does This Examination Consist Of?
Cardiac Catheterisation, What Is This Examination?
Echo Doppler: What It Is And What It Is For
Transesophageal Echocardiogram: What Does It Consist Of?
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Heart Murmur: What Is It And What Are The Symptoms?
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Manoeuvres: Management Of The LUCAS Chest Compressor
Supraventricular Tachycardia: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Prognosis
Identifying Tachycardias: What It Is, What It Causes And How To Intervene On A Tachycardia
Tachycardia: Is There A Risk Of Arrhythmia? What Differences Exist Between The Two?
Do You Have Episodes Of Sudden Tachycardia? You May Suffer From Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
Transient Tachypnoea Of The Newborn: Overview Of Neonatal Wet Lung Syndrome
Paediatric Toxicological Emergencies: Medical Intervention In Cases Of Paediatric Poisoning
Valvulopathies: Examining Heart Valve Problems
What Is The Difference Between Pacemaker And Subcutaneous Defibrillator?
Heart Disease: What Is Cardiomyopathy?
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Heart Murmurs: What It Is And When To Be Concerned
Broken Heart Syndrome Is On The Rise: We Know Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathies: What They Are And What Are The Treatments
Alcoholic And Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Difference Between Spontaneous, Electrical And Pharmacological Cardioversion
What Is Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy (Broken Heart Syndrome)?
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: What It Is, What Causes It And How It Is Treated
Heart Pacemaker: How Does It Work?
Basic Airway Assessment: An Overview
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
Pain Assessment: Which Parameters And Scales To Use When Rescuing And Treating A Patient
Airway Management After A Road Accident: An Overview
Tracheal Intubation: When, How And Why To Create An Artificial Airway For The Patient
What Is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Poison Mushroom Poisoning: What To Do? How Does Poisoning Manifest Itself?
Chest Trauma: Clinical Aspects, Therapy, Airway And Ventilatory Assistance
The Quick And Dirty Guide To Pediatric Assessment
EMS: Pediatric SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia) Vs Sinus Tachycardia


