Eczema: causes and symptoms
Eczema (or dermatitis) is a non-contagious inflammatory skin disease. It is the most common of skin diseases and can affect people at any age, even those with no particular health problems
Why does eczema occur?
Eczema is caused by an abnormal reaction of the skin to certain factors, both internal and external to the body, that lead to the appearance of inflammation.
Usually, eczema manifests itself most frequently in the form of:
- Atopic dermatitis, characterised by an exaggerated response in the skin due to exposure to various environmental stimuli (food, pollen, mites) often related to allergic diseases;
- Contact dermatitis, which appears following contact with irritants such as cosmetics, detergents, solvents, substances in flowers, vegetables, medicines, etc.
How to recognise eczema
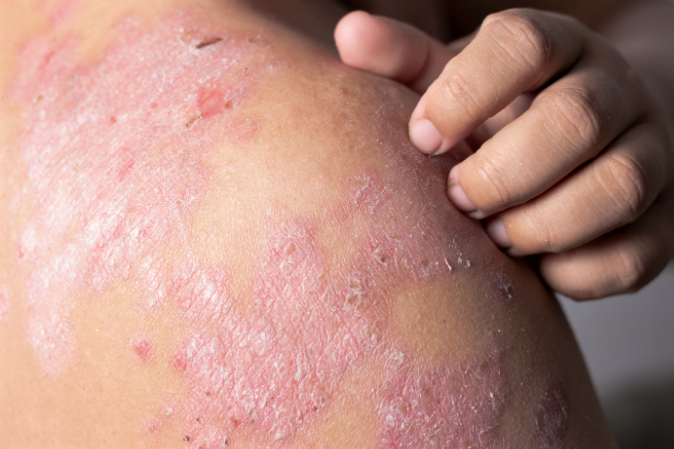
Eczema generally manifests itself with itching and skin rashes: the disease usually begins with a small redness that tends to expand into a series of red patches, plaques and moist blisters that over time, partly due to rubbing, tend to break up and become scabs or flakes, until the skin becomes dry and thick.
In atopic dermatitis, the body parts most affected are the face, neck, elbows, knees, wrists and ankles
In contact dermatitis, lesions appear on the parts of the body that have touched irritants, such as the hands.
Eczema causes intense itching that can also be very debilitating, but one must avoid scratching in order not to worsen the situation and not to cause wounds on the skin that would risk becoming infected.
How to treat eczema
Therapy consists of controlling the disease rather than treating the eczema.
In fact, the aim is to reduce redness, inflammation and itching, which involves taking antihistamines, emollients and cortisone ointments.
Eczema should therefore be prevented in the first place: in contact dermatitis, it is advisable to stay away from substances that are harmful to the skin; in the case of atopic dermatitis, on the other hand, the offending allergen must be identified and avoided.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Atopic Dermatitis: Treatment And Cure
Psoriasis, A Disease That Affects The Mind As Well As The Skin
Allergic Contact Dermatitis And Atopic Dermatitis: The Differences
Adverse Drug Reactions: What They Are And How To Manage Adverse Effects
Symptoms And Remedies Of Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Conjunctivitis: Causes, Symptoms And Prevention
What Is And How To Read The Allergy Patch Test
Eczema Or Cold Dermatitis: Here’s What To Do
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Clinical Manifestations Of Atopic Dermatitis
Pemphigus: Discovering This Rare Autoimmune Skin Disease


