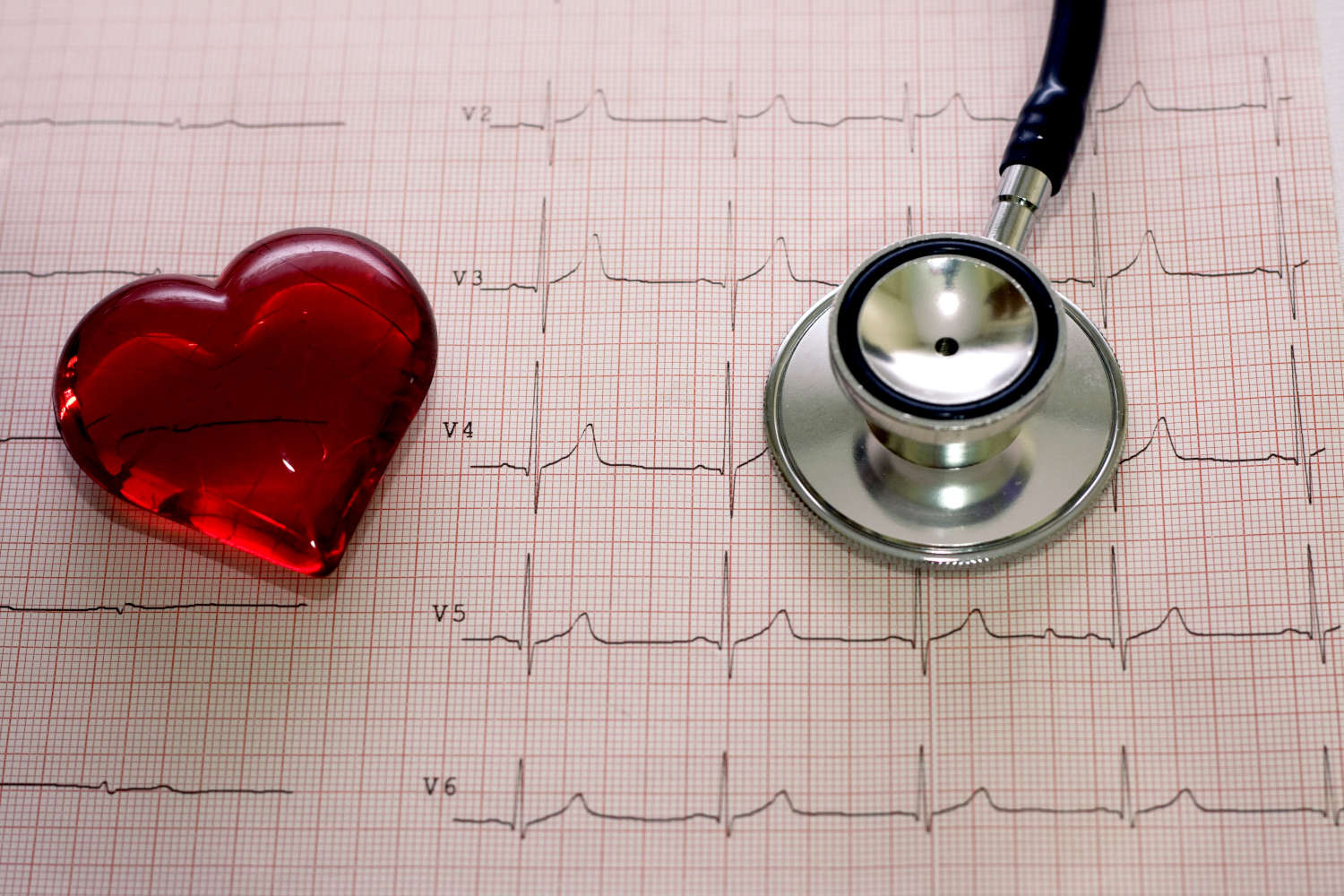
Electrocardiogram (ECG): what it is for, when it is needed
The electrocardiogram or ECG is a diagnostic test designed to record the electrical activity of the heart in order to assess its health status and detect various cardiac abnormalities, pathologies or arrhythmias
There are three types of ECG, which can meet different needs depending on the specific case: resting ECG, dynamic ECG according to Holter, and exercise ECG.
What is the purpose of the electrocardiogram?
The ECG can record the heart rhythm and electrical activity of the heart, and through this examination, a cardiologist can detect:
- cardiac arrhythmias: normally, the heart beats at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute, but alterations in rhythm can occur, even asymptomatic ones, which can be potentially dangerous to the patient;
- ischemia or myocardial infarction;
- functional alterations of the heart muscle (the myocardium), such as cardiomyopathy, dilation of atria or ventricles, wall hypertrophy, and enlarged heart;
In addition, the electrocardiogram makes it possible to examine damage from previous heart attacks, assess the function of pacemakers and similar devices, or analyze the effects that certain drugs may have on the heart.
How should I prepare for an electrocardiogram?
An EKG is a noninvasive test that poses no risk to the patient and requires no special preparation.
In general, it is advisable to wear comfortable clothes and shoes such as sneakers or “trainers,” particularly in the case of an EKG under stress, and to inform the physician if you are taking any drug therapies or if you have any pacemakers.
*This is indicative information; therefore, it is necessary to contact the facility where the examination is being performed to obtain specific information on the preparation procedure.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Head Up Tilt Test, How The Test That Investigates The Causes Of Vagal Syncope Works
Aslanger Pattern: Another OMI?
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Epidemiology And Diagnosis
What Is Ischaemic Heart Disease And Possible Treatments
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): What Is It?
Ischaemic Heart Disease: What Is It?
EMS: Pediatric SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia) Vs Sinus Tachycardia
Paediatric Toxicological Emergencies: Medical Intervention In Cases Of Paediatric Poisoning
Valvulopathies: Examining Heart Valve Problems
What Is The Difference Between Pacemaker And Subcutaneous Defibrillator?
Heart Disease: What Is Cardiomyopathy?
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Heart Murmurs: What It Is And When To Be Concerned
Clinical Review: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Botallo’s Ductus Arteriosus: Interventional Therapy
Heart Valve Diseases: An Overview
Cardiomyopathies: Types, Diagnosis And Treatment
First Aid And Emergency Interventions: Syncope
Tilt Test: What Does This Test Consist Of?
Cardiac Syncope: What It Is, How It Is Diagnosed And Who It Affects
New Epilepsy Warning Device Could Save Thousands Of Lives
Understanding Seizures And Epilepsy
First Aid And Epilepsy: How To Recognise A Seizure And Help A Patient
Neurology, Difference Between Epilepsy And Syncope
Positive And Negative Lasègue Sign In Semeiotics
Wasserman’s Sign (Inverse Lasègue) Positive In Semeiotics
Positive And Negative Kernig’s Sign: Semeiotics In Meningitis
Lithotomy Position: What It Is, When It Is Used And What Advantages It Brings To Patient Care
Trendelenburg (Anti-Shock) Position: What It Is And When It Is Recommended
Prone, Supine, Lateral Decubitus: Meaning, Position And Injuries
Stretchers In The UK: Which Are The Most Used?
Does The Recovery Position In First Aid Actually Work?
Reverse Trendelenburg Position: What It Is And When It Is Recommended
Drug Therapy For Typical Arrhythmias In Emergency Patients
Canadian Syncope Risk Score – In Case Of Syncope, Patients Are Really In Danger Or Not?


