Electroencephalogram: what is the EEG for?
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is an instrumental test that allows the electrical activity of the brain to be recorded and monitored
Brain activity gives rise to electrical waves. Under normal conditions, brain waves in a resting adult have a frequency of 8-13 cycles per second (alpha rhythm).
In the case of brain diseases, this rhythm is altered and the EEG results allow a preliminary diagnosis to be made, which can then be further investigated through other tests.
What the EEG is used for
The EEG is used to diagnose diseases of the nervous system such as brain infections, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, sleep and memory disorders.
It is often used following head injuries, while it is of little use in cases of headaches.
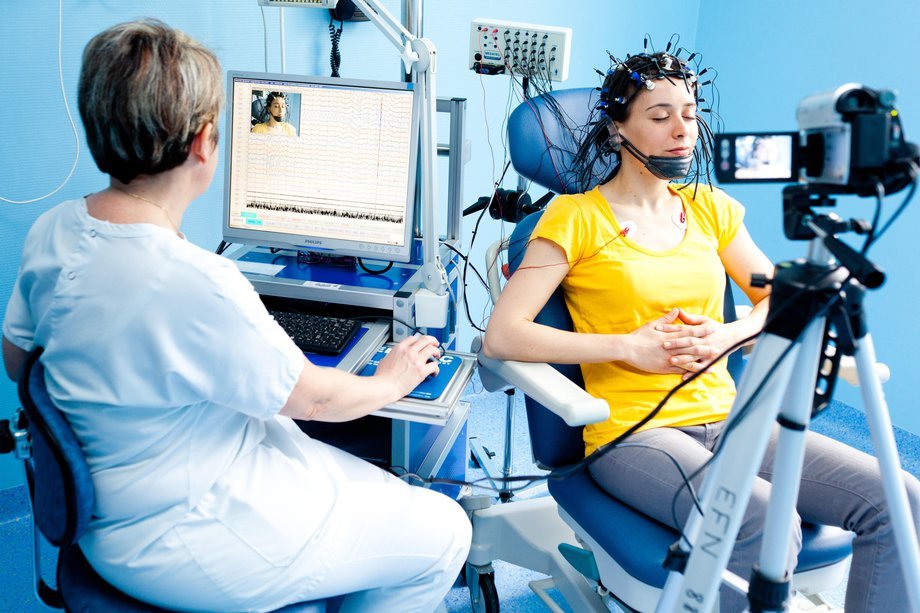
Electroencephalogram: how it is performed
The patient lies in a supine position, with eyes closed and in a resting position.
Small metal electrodes (similar to those used in electrocardiograms) are attached to the scalp at different areas of the cerebral cortex.
The electrodes, which are connected to an amplifier, collect electrical impulses from the brain and send them to a recorder and to equipment capable of translating them into a graph.
The ‘waking’ test takes about half an hour, while the ‘sleeping’ test varies from two hours for daytime recordings to an entire night for night-time ones.
EEG with the Holter method involves continuous recording over the course of 24 hours.
EEG results are available approximately two days after the test.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Seizures In The Neonate: An Emergency That Needs To Be Addressed
Epileptic Seizures: How To Recognise Them And What To Do
Epilepsy Surgery: Routes To Remove Or Isolate Brain Areas Responsible For Seizures
European Resuscitation Council (ERC), The 2021 Guidelines: BLS – Basic Life Support
First Aid And Medical Intervention In Epileptic Seizures: Convulsive Emergencies
Pre-Hospital Seizure Management In Paediatric Patients: Guidelines Using GRADE Methodology / PDF
New Epilepsy Warning Device Could Save Thousands Of Lives
Understanding Seizures And Epilepsy
First Aid And Epilepsy: How To Recognise A Seizure And Help A Patient
Childhood Epilepsy: How To Deal With Your Child?
Spinal Immobilisation Of The Patient: When Should The Spine Board Be Put Aside?
Who Can Use The Defibrillator? Some Information For Citizens
Schanz Collar: Application, Indications And Contraindications
AMBU: The Impact Of Mechanical Ventilation On The Effectiveness Of CPR
Pulmonary Ventilation In Ambulances: Increasing Patient Stay Times, Essential Excellence Responses
Microbial Contamination On Ambulance Surfaces: Published Data And Studies
Is Applying Or Removing A Cervical Collar Dangerous?
Cervical Collars : 1-Piece Or 2-Piece Device?
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
Ambu Bag: Characteristics And How To Use The Self-Expanding Balloon
Manual Ventilation, 5 Things To Keep In Mind
Ambulance: What Is An Emergency Aspirator And When Should It Be Used?
What Is Intravenous Cannulation (IV)? The 15 Steps Of The Procedure
Nasal Cannula For Oxygen Therapy: What It Is, How It Is Made, When To Use It
Ambu Bag, Salvation For Patients With Lack Of Breathing
Supplemental Oxygen: Cylinders And Ventilation Supports In The USA
What Is Intravenous Cannulation (IV)? The 15 Steps Of The Procedure
Nasal Cannula For Oxygen Therapy: What It Is, How It Is Made, When To Use It
Nasal Probe For Oxygen Therapy: What It Is, How It Is Made, When To Use It
Oxygen Reducer: Principle Of Operation, Application
How To Choose Medical Suction Device?
Holter Monitor: How Does It Work And When Is It Needed?
What Is Patient Pressure Management? An Overview
Head Up Tilt Test, How The Test That Investigates The Causes Of Vagal Syncope Works
Suction Unit For Emergency Care, The Solution In A Nutshell: Spencer JET
Airway Management After A Road Accident: An Overview
Ambulance: Common Causes Of EMS Equipment Failures — And How To Avoid Them


