Emergency Room, Emergency and Acceptance Department, Red Room: let's clarify
The Emergency Room (sometimes Emergency Department or Emergency Room, hence the acronyms ED and ER) is an operating unit of hospitals expressly equipped to accommodate emergency cases, divide patients based on the seriousness of the situation, quickly provide diagnosis and treatment , send the most serious patients to special areas equipped to manage them and have some patients stop in special spaces dedicated to brief observation
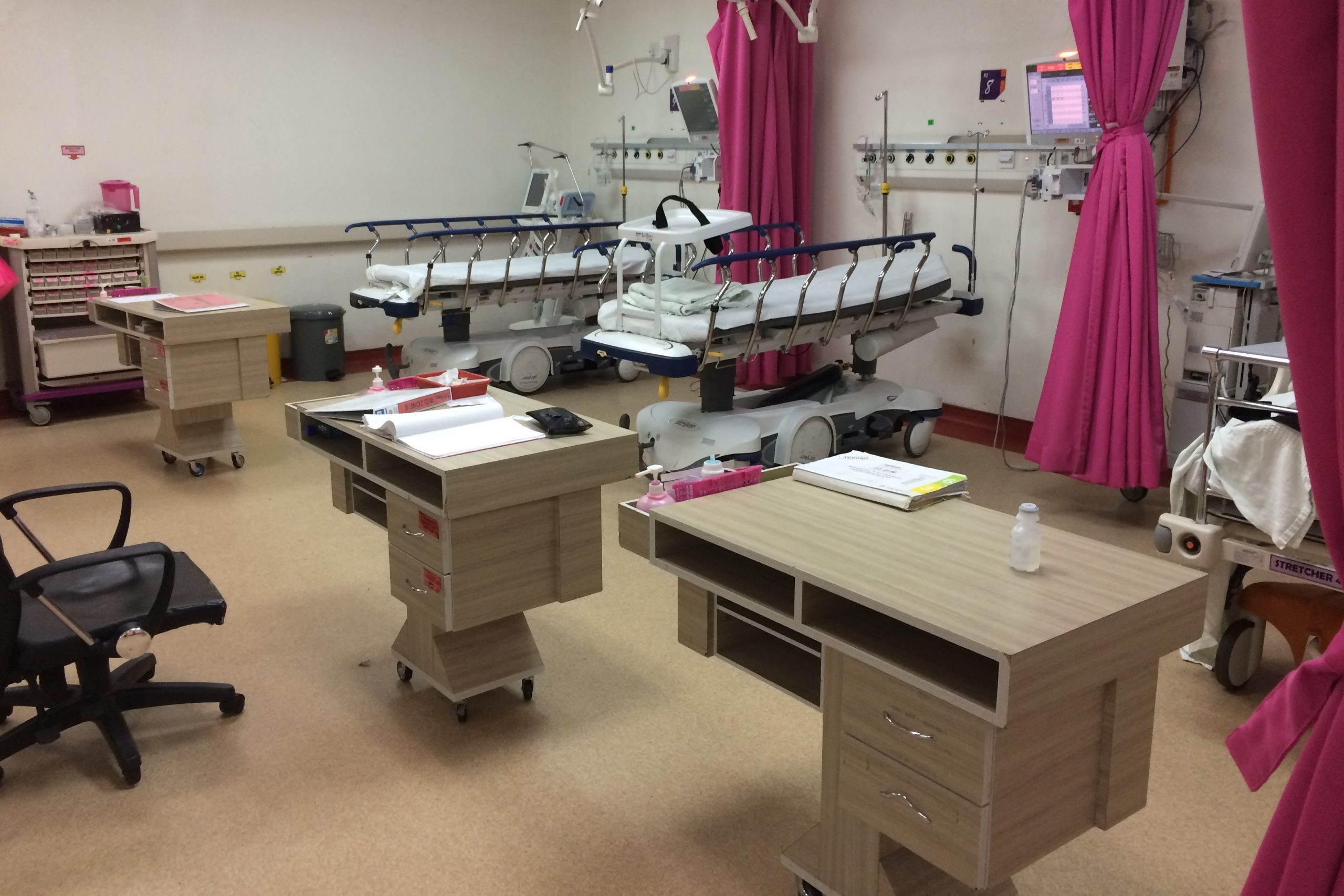
Red Room of the Emergency Department, what does it consist of?
In the Emergency Department of many Western countries, first aid is provided in all cases of urgency and emergency, such as major trauma, heart attacks, haemorrhages, cerebral strokes, in simple words all those cases in which the patient’s life is put at risk and c ‘very rapid intervention is required, for this reason the Emergency Room is accessed in “urgent hospitalization” mode, or arriving by one’s own means or by ambulance after calling the Single Number for Emergencies.
In some countries instead of “red room” “red zone” or similar is used, but the concept remains substantially unchanged.
In some hospitals, the Emergency Room has been replaced by the “DEA”, although often the latter is still called “Emergency Room” for convenience.
Nurses and doctors specialized in internal medicine, general surgery and emergency medicine (and equivalent) work in the Emergency Department.
DEA (Emergency and Admissions Department)
In Italy, the concept of first aid has now been superseded by the wider Emergency and Admissions Department (DEA), however there are still, in smaller hospitals, some first aid services which do not configure the assistance complexity of the DEA but are able to provide emergency and urgency services.
It is a new formulation modeled on the US model, and it also concerns many other Western countries.
Some less complex services are called First Aid Points (PPI) and differ from Emergency Departments in that patients can only access them independently and not accompanied by an emergency/urgency service ambulance and can also provide a service only on 12 hours instead of 24 hours.
THE RADIO FOR RESCUERS IN THE WORLD? VISIT THE EMS RADIO BOOTH AT THE EMERGENCY EXPO
Triage
Access to emergency room care obviously does not take place on the basis of the order of arrival of patients, but on the severity of their conditions assessed through “triage”
A previously trained nurse assigns each patient, upon her arrival, a degree of urgency represented by a “color code”:
- red code or “emergency”: with immediate access to medical intervention;
- yellow code or “urgency”: with access to the room within 10-15 minutes;
- green code or “deferrable urgency”: without signs of imminent danger to life;
- white code or “non-emergency”: patient who can contact his general practitioner. In some cases the white code is made to coincide with “improper access” and then submitted to the payment of the ticket.
- main environments
The structure of a hospital Emergency Department varies according to many factors, such as the size of the hospital, however it is generally equipped with:
- a red room for the most serious cases;
- one or more emergency rooms;
- one or more visiting rooms;
- one or more rooms for brief observation (astanteria);
- one or more waiting rooms for non-urgent patients and for friends and relatives;
- reception desks.
Red Room (Red Area or Red Zone)
The red room (sometimes called “red area” or “shock room”) is an area of the DEA or Emergency Department, equipped with technologically advanced equipment and dedicated to the treatment of patients in particularly critical conditions (the “red codes”).
This environment accommodates all patients with significant alterations of vital signs, such as polytrauma, myocardial infarction, stroke, respiratory failure, cardiac arrest or severe internal bleeding.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Emergency Room Red Area: What Is It, What Is It For, When Is It Needed?
Code Black In The Emergency Room: What Does It Mean In Different Countries Of The World?
Emergency Medicine: Objectives, Exams, Techniques, Important Concepts
Chest Trauma: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Management Of The Patient With Severe Chest Injury
Dog Bite, Basic First Aid Tips For The Victim
Choking, What To Do In First Aid: Some Guidance To The Citizen
Cuts And Wounds: When To Call An Ambulance Or Go To The Emergency Room?
Notions Of First Aid: What A Defibrillator Is And How It Works
How Is Triage Carried Out In The Emergency Department? The START And CESIRA Methods
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Does The Recovery Position In First Aid Actually Work?
What To Expect In The Emergency Room (ER)
Basket Stretchers. Increasingly Important, Increasingly Indispensable
Nigeria, Which Are The Most Used Stretchers And Why
Self-Loading Stretcher Cinco Mas: When Spencer Decides To Improve Perfection
Ambulance In Asia: What Are The Most Commonly Used Stretchers In Pakistan?
Stretcher: What Are The Most Used Types In Bangladesh?
Travel And Rescue, USA: Urgent Care Vs. Emergency Room, What Is The Difference?


