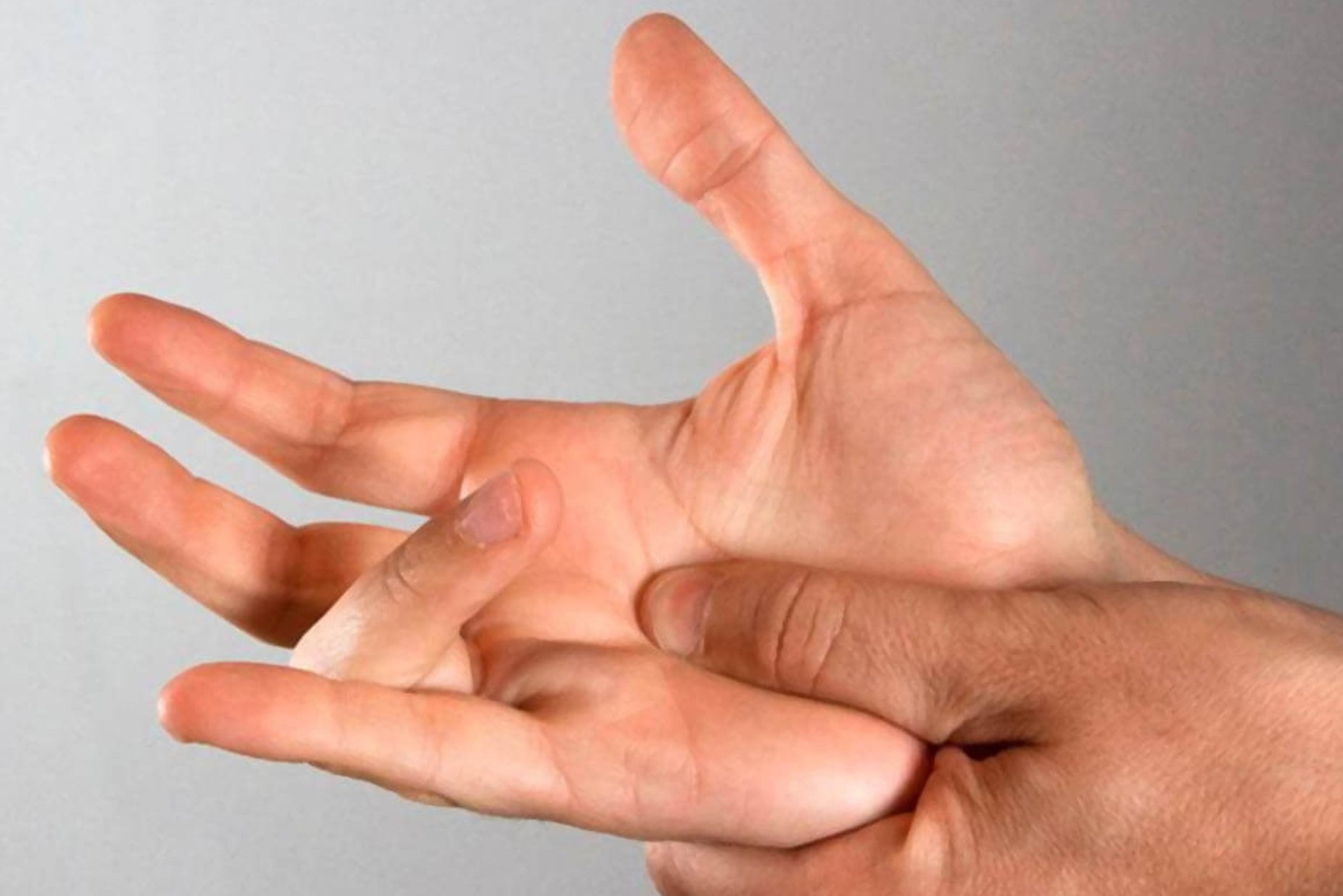
Finger Twitching: why it happens and remedies for tenosynovitis
Finger Twitching: when we wake up in the morning with a finger stuck in flexion, or when we experience the unpleasant sensation of a finger snapping in flexion-extension when we do manual activities, we may be suffering from Notta’s disease, or stenosing tenosynovitis of the flexor tendons, more simply known as “snapping finger”
What is finger twitching?
Snapping finger is a very common form of tendonitis, affecting the flexor tendons of the fingers, the ones that determine the closing of the hand.
These tendons run in an osteo-fibrous channel, called a digital channel (with a bony base and a fibro-elastic channel), which is intended to attach the tendons to the skeleton of the fingers of the hand.
The tendons pass through the digital canal, but when they become inflamed, their volume increases, preventing normal movement.
When the enlarged tendons are forced to pass through the digital canal, a snap is felt.
Causes of finger twitching
This disorder can occur for various reasons:
- Strenuous use of the hand, leading to inflammation, pain and swelling;
- rheumatic pathologies involving the tendons, which can affect all ages of life, with a prevalence between 40 and 60 years of age and especially women;
- systemic diseases such as diabetes, arthritis;
- thyroid-related diseases.
All these conditions lead to water retention with consequent enlargement of the tendons.
Lastly, there is the snap finger in children, which is essentially caused by a congenital narrowing of the digital canal.
The symptoms
Among the symptoms of the trigger finger are obviously
- swelling of the finger
- soreness at the base
- joint limitation with difficulty of movement;
- pain that may extend to the wrist.
In severe cases, the finger may remain in a closed position without being able to extend.
Diagnosis of tenosynovitis, or trigger finger
The diagnosis is made through a clinical examination that proceeds with the palpation of the enlargement of the tendon in the digital canal, often painful at the level of the base of the metacarpophalangeal joint; for more completeness we can carry out an ultrasound scan, which allows us to investigate the structure of the tendon and its movement.
How to treat
The treatment of trigger finger is basically based on the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, especially in the initial or acute phases.
Shock waves
Physical and physiatric therapies are also often used. In recent years, the use of focused shock waves has been very successful in the bloodless treatment of this condition.
Intervention
Unfortunately, when these therapies do not work and the disorder persists, it is necessary to opt for a surgical solution.
The operation involves freeing the two tendons or the thumb tendon (if the latter is affected) by opening the basal trochlea, i.e. the central part of the digital canal.
This is where the conflict between the swollen flexor tendons and the digital canal arises.
Physiotherapy
Obviously, after tendon release surgery, supportive physiatric treatment must always be added, which is basically based on:
- gymnastics;
- kinesis;
- immediate recovery of the sliding function of the two tendons, to avoid adhesion phenomena.
It is important to constantly follow the exercise programme set by the physiotherapist.
Finger-jerk surgery may seem simple and trivial, but it requires great cooperation from the patient.
Read Also:
Healing Wounds And Perfusion Oximeter, New Skin-Like Sensor Can Map Blood-Oxygen Levels
What Is A Lipoma And How To Treat It


