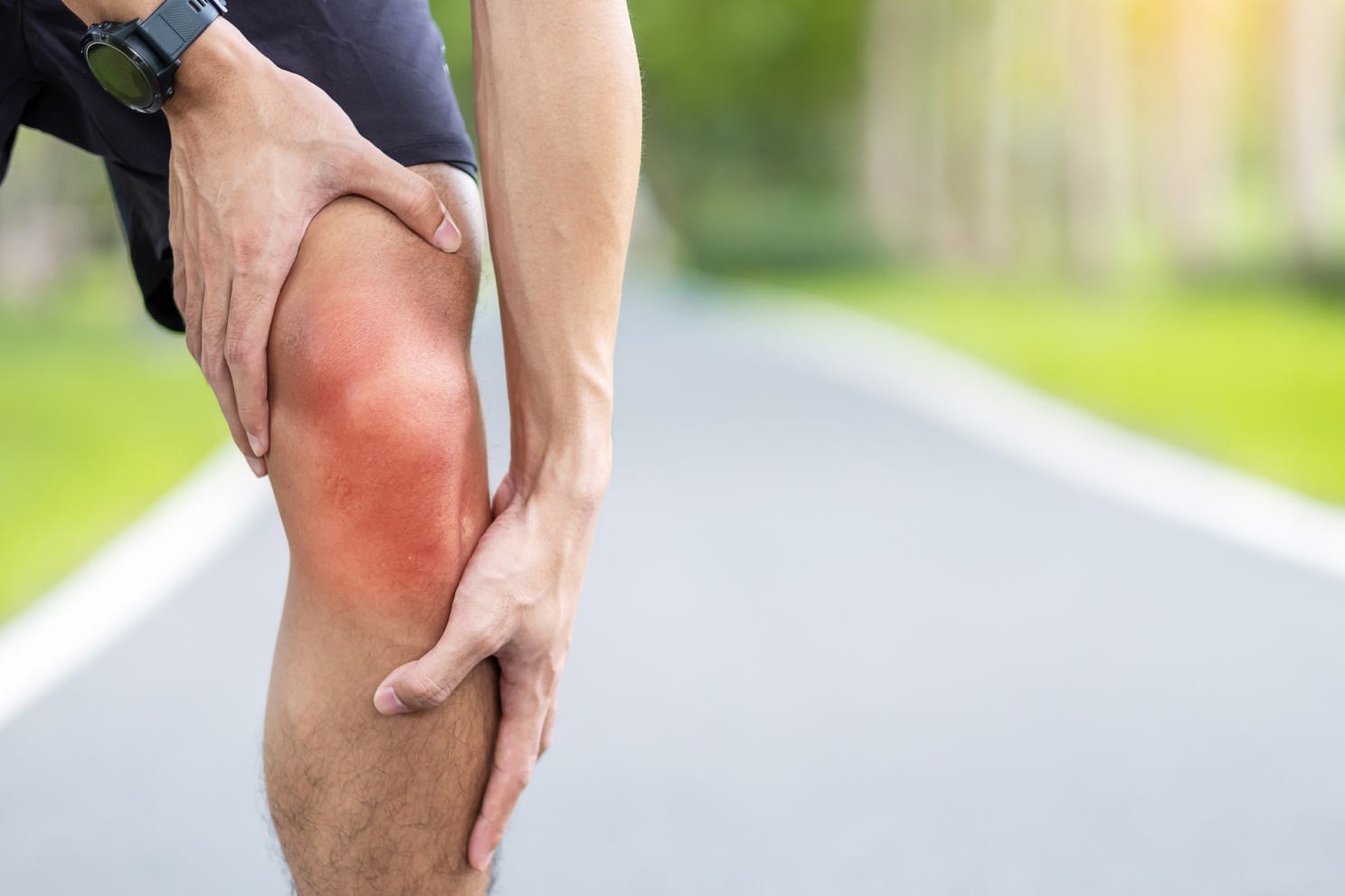
First aid for knee pain and injury
Knee pain or injury is a common complaint: there are several factors that can increase the risk of knee problems, such as obesity (excess weight), lack of flexibility and previous injuries
Osteoarthritis is the leading cause of knee pain, with 1 in 11 people suffering from it at some point.
Knee injuries happen to people of all ages but are more common in adults ages 5 and older
It roots in many causes and can affect different structures of the knee.
Common knee injuries include sprains, strains, tearing of the cartilage that lines the joints, and irritation of the kneecap joints.
Mild injuries typically heal on their own, but it is important for every injury to be checked and evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Chronic and persistent knee pain may require proper medical attention to increase the chances of a full recovery.
First Aid for Knee Pain
Here are some ways you can do to help relieve knee pain.
RICE method
The RICE method is the initial treatment for almost any knee injury. RICE stands for
R – rest, which requires discontinuing any activity that may be causing the pain. For best results, rest the knee for a day or two and limit activities as much as possible.
I – ice or the application of cold packs to the injury to reduce swelling. The cold help to reduce pain and muscle spasm by slowing down the transmission of pain impulses. Apply cold for 1 to 20 minutes several times a day.
C – compression involves wrapping the knee in a bandage or elastic band. It should be applied loosely enough to allow normal blood flow, but tight enough to lessen the swelling.
E – elevation requires placing the leg above heart level to help with the swelling. Place pillows and cushions to support the knee in the elevated position.
The RICE treatment is proven effective in the first 24 to 48 hours after the injury.
Heat Treatment
Applying heat during the recovery stage can help with faster healing.
When applied correctly, the heat can relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation.
Supports and Splints
Immobilising the knee joint is vital in giving first aid care following an injury.
This technique can help lessen the pain and control the swelling.
There are a variety of supports, splints, and bandages available in stores, but old-fashioned techniques using towels, scarves, and other soft pliable materials can be used as an effective wrap.
Preventing Knee Pain
Follow these tips to prevent the occurrence of knee pain.
Take the time to warm up before doing any physical activity and cool down afterwards.
Do some strength training for the leg muscles.
Avoid sudden changes in the intensity of the workout. Give the knees enough time to adjust by starting small and then progressing over time.
Choose the right shoes for activity and replace worn-out footwear regularly. This helps ensure that there is ample support for the entire leg, including the knee.
Wear knee guards, if necessary, when playing sports or engaging in risky activities.
Maintain a healthy weight, because excess weight can increase the chance of developing osteoarthritis.
Consider physical therapy for pain that does not go away.
Conclusion
Knee pain following an injury is a common occurrence, especially in teens and young adult.
A little bit of thought and knowing first aid care can prevent several painful injuries, some of which can take months to recover from.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Wrist Fracture: How To Recognise And Treat It
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnosis And Treatment
Knee Ligament Rupture: Symptoms And Causes
Lateral Knee Pain? Could Be Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Knee Sprains And Meniscal Injuries: How To Treat Them?
Treating Injuries: When Do I Need A Knee Brace?
Everything You Need To Know About Fibromyalgia
Knee Cartilage Damage: What It Is And How To Treat It


