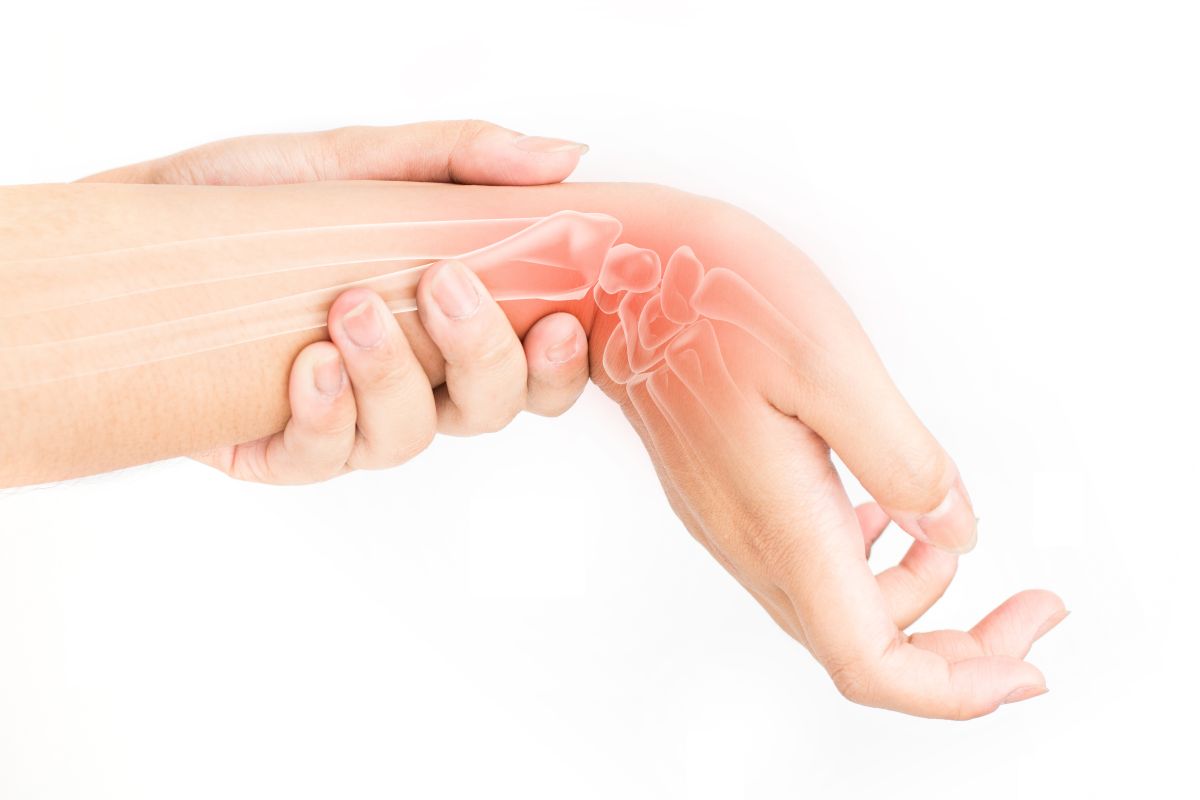
Guyon's canal syndrome, an overview of irritation of the ulnar or cubital nerve of the wrist
Guyon’s syndrome is a pathology characterized by irritation of the ulnar or cubital nerve at the wrist, in the area between the pisiform bone and the unciform process
The cause of the disease is nerve compression which causes reduced sensitivity in some fingers of the hand and difficulty in fine hand movements.
In patients in whom the syndrome is more severe there is a “claw” deformity of the hand caused by the lack of the stimulus that the nerve transmits to some hand muscles.
Guyon’s Syndrome: What is it?
Guyon’s syndrome – or Guyon’s canal – is a debilitating condition affecting the wrist.
The disease affects the tunnel that the ulnar nerve passes through from the forearm to the hand.
This area of the body is called, precisely, Guyon’s canal, it is located in the wrist in a parallel position to the carpal canal, from which it is separated by a wall of a few millimetres.
The canal has a floor made up of the wrist bones and a ceiling made up of the ligament.
At its exit, the ulnar nerve divides into two branches that supply sensation to the little finger and middle of the ring finger, and to most of the muscles in the hand.
In patients suffering from Guyon’s syndrome, the ulnar nerve is compressed, which makes it difficult to pass through the canal.
The causes of compression are various, including thickening of the canal itself and arthritis of the wrist.
The first symptom of Guyon’s syndrome is a tingling sensation affecting the ring and little fingers
Most of the time the onset is nocturnal, but it is often overlooked, for this reason it can worsen over time, causing constant tingling, accompanied by weakness in movements up to paralysis of the last fingers of the hand.
The people most affected by the disease are those who perform manual activities with fixed and repetitive positions and movements.
It is no coincidence that it is considered a professional pathology, which mainly affects goldsmiths and musicians.
The main symptoms of the disease are therefore reduced sensitivity of the hand or the last two fingers, pain and difficulty in moving these same fingers; in the most serious cases, the typical deformity of the syndrome known as “claw hand” appears.
Causes
Guyon’s canal syndrome originates in compression or inflammation of the ulnar nerve in Guyon’s tunnel.
The causes can be trauma, thickening of the canal, arthritis of the wrist, inflammation of the synovial sheaths, cysts, vascular anomalies and neoformations.
Diagnosis
Guyon’s syndrome is a particularly common disease, so there are many therapies and treatments that allow you to solve the problem.
For a complete recovery, however, it is essential to find the most suitable treatment based on the causes of the disease.
It is no coincidence that a visit to a specialist doctor is a key element in this case.
The diagnosis takes place during the visit in which the symptoms and the patient’s history are analyzed.
An ultrasound is then requested, accompanied by an electromyography.
The latter is an examination that is performed by a neurologist and measures the speed with which the electrical stimulus is transported through the ulnar nerve from the brain to the hand and vice versa.
The test also measures the activity of the muscles that receive stimuli from the nerve.
In the area where the emission of the stimulus is hindered, the examination indicates a decrease in speed.
When you feel the first symptoms, such as sudden tingling and loss of sensation in the last two fingers of the hand, it is essential to undergo a preventive visit.
Guyon’s syndrome: the cure
Guyon’s syndrome, as for carpal tunnel syndrome, requires a few cycles of analgesic physiotherapy in the wrist area as a cure.
In any case, it is also possible to intervene with an infiltrative therapy with cortisone or, if the symptoms are more serious, with surgery.
Usually the pathology is treated with electroanalgesia, performed by the physiotherapist and accompanied by therapeutic exercises, manipulation and passive mobilisation.
Surgery to treat Guyon’s syndrome is usually performed in day hospital, lasts about twenty minutes and involves the application of a cast to be worn for ten days in order to limit movement.
After the operation it is important to work gradually, starting with minimal hand effort and carefully bending the fingers.
The complete sensitivity of the limb can only be regained over the course of months, with rehabilitation therapy.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Arthrosis: What It Is And How To Treat It
Septic Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Psoriatic Arthritis: How To Recognize It?
Arthrosis: What It Is And How To Treat It
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Study Of Oral Therapy With Tofacitinib By Gaslini Of Genoa
Arthrosis: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Rheumatic Diseases: Arthritis And Arthrosis, What Are The Differences?
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Joint Pain: Rheumatoid Arthritis Or Arthrosis?
Cervical Arthrosis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Cervicalgia: Why Do We Have Neck Pain?
Psoriatic Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
The Causes Of Acute Low Back Pain
Cervical Stenosis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
Headaches And Dizziness: It Could Be Vestibular Migraine
Migraine And Tension-Type Headache: How To Distinguish Between Them?
First Aid: Distinguishing The Causes Of Dizziness, Knowing The Associated Pathologies
Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), What Is It?
Cervical Dizziness: How To Calm It Down With 7 Exercises
What Is Cervicalgia? The Importance Of Correct Posture At Work Or While Sleeping
Lumbago: What It Is And How To Treat It
Back Pain: The Importance Of Postural Rehabilitation
Cervicalgia, What It Is Caused By And How To Deal With Neck Pain
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Arthrosis Of The Hands: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Arthralgia, How To Cope With Joint Pain
Arthritis: What It Is, What Are The Symptoms And What Are The Differences From Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis, The 3 Basic Symptoms
Rheumatism: What Are They And How Are They Treated?
De Quervain’s Stenosing Tenosynovitis: Symptoms And Treatment Of ‘Mothers’ Disease’ Tendinitis
Finger Twitching: Why It Happens And Remedies For Tenosynovitis
Shoulder Tendonitis: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Tendonitis, The Remedy Is Shock Waves
Pain Between Thumb And Wrist: The Typical Symptom Of De Quervain’s Disease
Pain Management In Rheumatological Diseases: Manifestations And Treatments
Rheumatic Fever: All You Need To Know
De Quervain Syndrome, An Overview Of Stenosing Tenosynovitis


