Heart Valve Alteration: Mitral Valve Prolapse Syndrome
Mitral valve prolapse syndrome is a condition characterised by the alteration of one of the heart valves, the mitral valve
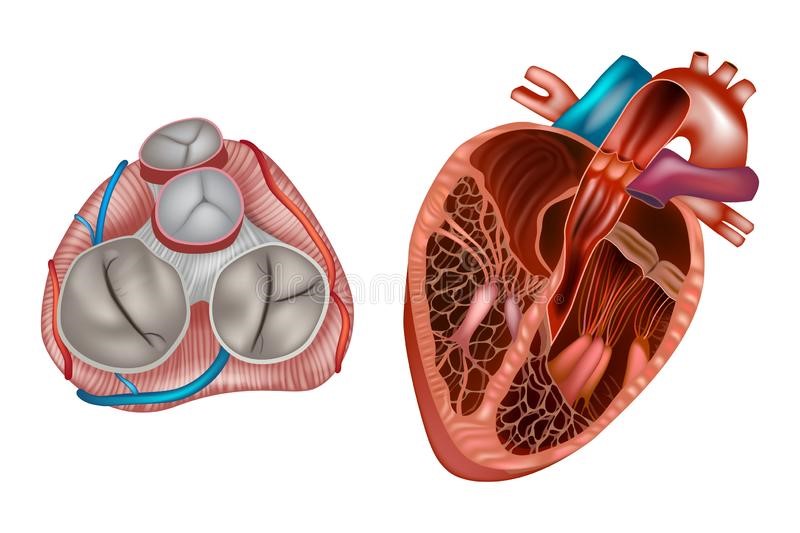
When the heart is functioning properly, the mitral valve will close completely during contraction of the left ventricle, preventing blood from flowing back into the left atrium.
In those suffering from mitral prolapse, one or both valve leaflets will flutter into the left atrium when the left ventricle contracts, preventing the valve from closing.
What is mitral valve prolapse syndrome?
Normally, the mitral valve consists of two thin movable leaflets anchored by chordae tendineae to the papillary muscles that contract together with the left ventricle where they are located and prevent the mitral leaflets from flaring in the left atrium.
The edges of the flaps separate when the valve opens, allowing blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle; they come together again when the valve closes, preventing blood from flowing back.
Mitral valve prolapse is the flaring into the left atrium of one or both mitral valve leaflets when the left ventricle contracts.
This valve defect occurs in approximately 6% of the population, and women are most affected.
The causes of mitral valve prolapse syndrome
Mitral valve prolapse will be in the primary form when there is connective tissue disease at the origin, and there will be exuberance of tissue in the valve leaflets.
There will be secondary forms when the prolapse is caused by problems affecting the heart, including: ischaemic heart disease, endocarditis, interatrial defect, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, tumour forms.
Symptoms of mitral valve prolapse
In most cases, mitral valve prolapse syndrome will be asymptomatic; symptoms will include prolonged retrosternal pain, heart palpitation and syncope.
Mitral valve prolapse prevention
Preventing mitral valve prolapse syndrome is not possible, but it is possible to reduce the likelihood of developing related complications; certain pharmacological treatments must be followed.
Diagnosis
Being an asymptomatic valvulopathy, the diagnosis is occasional and will be suggested by cardiac auscultation, a click will be detected followed by a heart murmur.
An ECG will then be performed, which will usually be normal but may show arrhythmias.
With the echocardiogram it will be possible to visualise the movements of the mitral leaflets allowing an accurate assessment of the extent of the prolapse and its mechanisms.
The dynamic ECG according to Holter, will be indicated in subjects reporting palpitations for the evaluation of possible arrhythmias.
Exercise testing is indicated in subjects suffering from syncope and experiencing chest pain.
THE RADIO OF RESCUERS AROUND THE WORLD? IT’S RADIOEMS: VISIT ITS BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Treatments
Normally, mitral valve prolapse will be asymptomatic and therefore no treatment will be required.
However, it will be advisable to undergo clinical and echocardiographic checks.
If arrhythmias are present, it may be necessary to take anti-arrhythmic drugs and/or beta-blockers.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
What Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Is And How It Is Treated
Heart Rate Disorders: Bradyarrhythmia
Bradyarrhythmias: What They Are, How To Diagnose Them And How To Treat Them
Heart, Bradycardia: What It Is, What It Involves And How To Treat It
What Is Bradycardia And How To Treat It
Interventricular Septal Defect: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, And Treatment
Supraventricular Tachycardia: Definition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Prognosis
Ventricular Aneurysm: How To Recognise It?
Atrial Fibrillation: Classification, Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
EMS: Pediatric SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia) Vs Sinus Tachycardia
Atrioventricular (AV) Block: The Different Types And Patient Management
Pathologies Of The Left Ventricle: Dilated Cardiomyopathy
A Successful CPR Saves On A Patient With Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation: Symptoms To Watch Out For
Atrial Fibrillation: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Difference Between Spontaneous, Electrical And Pharmacological Cardioversion
‘D’ For Deads, ‘C’ For Cardioversion! – Defibrillation And Fibrillation In Paediatric Patients
Inflammations Of The Heart: What Are The Causes Of Pericarditis?
Do You Have Episodes Of Sudden Tachycardia? You May Suffer From Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
Knowing Thrombosis To Intervene On The Blood Clot
Patient Procedures: What Is External Electrical Cardioversion?
Increasing The Workforce Of EMS, Training Laypeople In Using AED
Heart Attack: Characteristics, Causes And Treatment Of Myocardial Infarction
Altered Heart Rate: Palpitations
Heart: What Is A Heart Attack And How Do We Intervene?
Do You Have Heart Palpitations? Here Is What They Are And What They Indicate
Palpitations: What Causes Them And What To Do
Cardiac Arrest: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Intervene
Electrocardiogram (ECG): What It Is For, When It Is Needed
What Are The Risks Of WPW (Wolff-Parkinson-White) Syndrome
Heart Failure: Symptoms And Possible Treatments
What Is Heart Failure And How Can It Be Recognised?
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Quickly Finding – And Treating – The Cause Of A Stroke May Prevent More: New Guidelines
Atrial Fibrillation: Symptoms To Watch Out For
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: What It Is And How To Treat It
Do You Have Episodes Of Sudden Tachycardia? You May Suffer From Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW)
What Is Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy (Broken Heart Syndrome)?
Heart Disease: What Is Cardiomyopathy?
Inflammations Of The Heart: Myocarditis, Infective Endocarditis And Pericarditis
Heart Murmurs: What It Is And When To Be Concerned
Broken Heart Syndrome Is On The Rise: We Know Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Heart Attack, Some Information For Citizens: What Is The Difference With Cardiac Arrest?
Heart Attack, Prediction And Prevention Thanks To Retinal Vessels And Artificial Intelligence
Full Dynamic Electrocardiogram According To Holter: What Is It?
In-Depth Analysis Of The Heart: Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CARDIO – MRI)
Palpitations: What They Are, What Are The Symptoms And What Pathologies They Can Indicate
Cardiac Asthma: What It Is And What It Is A Symptom Of
Cardiac Rhythm Restoration Procedures: Electrical Cardioversion
Abnormal Electrical Activity Of The Heart: Ventricular Fibrillation
Gastro-Cardiac Syndrome (Or Roemheld Syndrome): Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Atrial Fibrillation


