High Blood Pressure, when to seek emergency care
Hypertension: High blood pressure increases the risk of heart disease and stroke, two of the leading causes of death in Western countries
Almost 1 in 2 adults suffer from hypertension in western countries.
Most adults with hypertension do not have it under control.
Most adults with hypertension are recommended prescription medication with lifestyle modifications.
It’s important that we share with you to learn about what high blood pressure is, and when you may be having a life-threatening blood pressure complication.
What is High Blood Pressure/Hypertension?
Our heart pumps blood in our entire body.
As it travels, the blood supplies oxygen to the body’s vital organs.
Sometimes, a problem in the body makes it difficult for the heart to pump the blood, for example, when the artery becomes too narrow, etc.
High blood pressure (HBP or hypertension) is when your blood pressure, the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your blood vessels, is consistently too high. It can lead to a variety of health problems, some of which can be life-threatening.
How Do I Know I Have It?
It is a medical condition with negligible physical symptoms, but it can quietly damage different body parts of the patient.
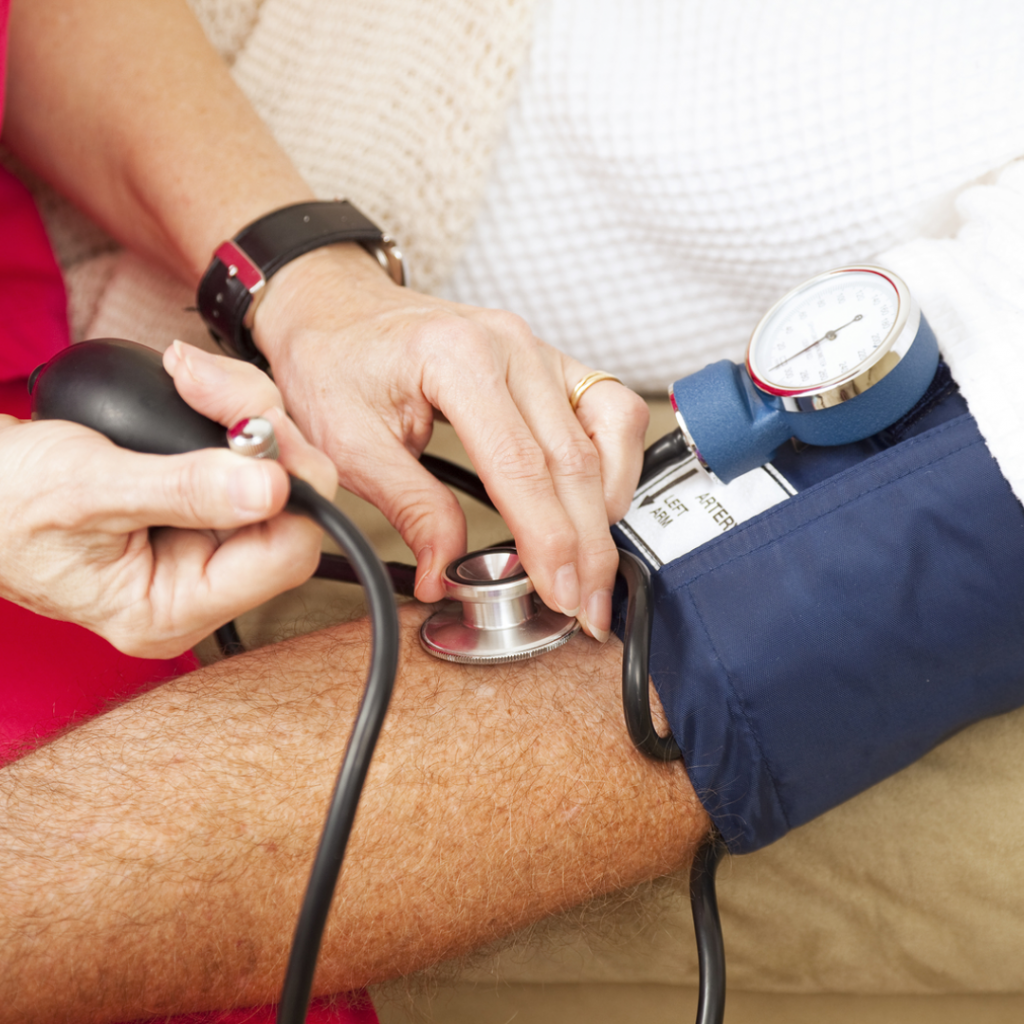
The best way to monitor your heart’s health is to measure your blood pressure levels regularly.
You can do it easily, even at your home.
Blood pressure readings are in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
The top number (systolic) indicates the pressure in the arteries as the heartbeats.
The lower number (diastolic) indicates the pressure as the heart rests between beats.
As long as a person measures their blood pressure correctly, the results are just as reliable as a doctor’s measurement.
What causes extremely high blood pressure?
Specific abnormalities happening in your body can lead to high blood pressure or if a person with born with particular genetic dysfunction.
The likelihood of developing high blood pressure is higher in adults with obesity, diabetes, kidney disease, under or overactive thyroid, lupus, obstructive sleep apnea, amongst others.
Consuming a high-fat diet, carrying excess weight, drinking a lot of alcohol, smoking tobacco, and the use of some medications can also increase the risk.
In some cases, there is no defined cause when doctors diagnose primary hypertension.
No matter the cause, it’s crucial to get help as soon as possible. Seek medical attention if your blood pressure gets above 180 (top) or 110 (bottom).
Doctors must evaluate potential organ damage and reverse the process before it’s too late. (Medical News Today)
What is a hypertensive crisis?
A hypertensive crisis occurs when your blood pressure is so high.
It can inflame your blood vessels and impair the ability of your cardiovascular system to work as it should, putting you at risk for stroke, heart attack, or other severe illness.
There are two stages of a hypertensive crisis: emergency and urgency.
Both require immediate attention as early evaluation of organ function is critical to determine an appropriate course of action.
Hypertensive emergency is when your blood pressure is over 180 (top) or 120 (bottom).
It is a real life-threatening emergency with impending target-organ-damage (TOD) in the heart, brain, kidney, and large blood vessels.
Severe conditions, such as ischemic heart failure, acute renal failure, and aorta rupture, are suspected in such patients.
Emergency admission to an intensive care unit is mandatory for prompt reduction of blood pressure by approximately 20 to 25 percent, depending on alleged conditions.
In urgency hypertensive crisis, your blood pressure is over 180 systolic (the top number) or 110 diastolic (the lower number).
While some patients may hold relatively lower risk, a certain degree of hypertensive urgency can pose an immediate threat.
Thus, it is critical to have clear standards on when to send hypertensive patients to the ER.
These severe symptoms can include:
- Severe chest pain
- Severe headache plus confusion or blurred vision
- Back pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe anxiety
- Shortness of breath
- Vision problems
- Nosebleeds
- Seizures
- Difficulty speaking
- Numbness or weakness
- Unresponsiveness
Stay Prepared!
If you have high blood pressure, track your blood pressure, and medications
If possible, during an emergency, having these logs with you can provide valuable information to the medical team providing treatmen.
Don’t ignore your symptoms.
Call Emergency Number immediately if the person loses consciousness.
Head to the ER when you suspect emergency care is needed, but be sure if you are the one having symptoms, not to drive yourself.
If you know you already have high blood pressure and something changes, it can be a sign that something more serious is happening.
References
“High Blood Pressure.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 7 Apr. 2020, www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/index.htm.
Cdc. “Hypertension Prevalence in the U.S.: Million Hearts®.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 5 Feb. 2020, millionhearts.hhs.gov/data-reports/hypertension-prevalence.html.
Collier, Lorna. “When Is High Blood Pressure an Emergency?” Healthgrades, Healthgrades, 13 Feb. 2020, www.healthgrades.com/right-care/high-blood-pressure/when-is-high-blood-pressure-an-emergency.
Caporuscio, Jessica. Are There Symptoms for High Blood Pressure? Medical News Today, 16 Dec. 2019, www.medicalnewstoday.com/.
Kanai, Kuniyoshi. “When to Send Your Hypertensive Patient to the ER.” Optometry Times, 26 Sept. 2018, www.optometrytimes.com/hypertension/when-send-your-hypertensive-patient-er.
Felman, Adam. “What to Know about High Blood Pressure.” Medical News Today, 13 Nov. 2019, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/159283#what-is-high-bp/articles/327320.
“What Is High Blood Pressure?” heart.org, www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure/what-is-high-blood-pressure.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Holter Blood Pressure: Everything You Need To Know About This Test
Blood Pressure Emergencies: Some Information For Citizens
Alpha-Blockers, Drugs For The Treatment Of High Blood Pressure
Twenty-Four-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring: What Does It Consist Of?
Full Dynamic Electrocardiogram According To Holter: What Is It?
Hypertension: Symptoms, Risk Factors And Prevention
Organ Complications Of Hypertension
How To Conduct Antihypertensive Treatment? An Overview Of Drugs
Blood Pressure: What It Is And How To Measure It
Aetiological Classification Of Hypertension
Classification Of Hypertension According To Organ Damage
Essential Hypertension: Pharmacological Associations In Antihypertensive Therapy
Treatment Of High Blood Pressure
Heart Failure: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
The Thousand Faces Of Vascular Disease
Blood Pressure: When Is It High And When Is It Normal?
First Aid, When Is It An Emergency? Some Information For Citizens
Hypothermia Emergencies: How To Intervene On The Patient
Emergencies, How To Prepare Your First Aid Kit
Seizures In The Neonate: An Emergency That Needs To Be Addressed
Epileptic Aura: The Phase Before A Seizure
Seizures In Children: Types, Causes And Treatments Of Seizures
Spinal Immobilisation Of The Patient: When Should The Spine Board Be Put Aside?
First Aid And Medical Intervention In Epileptic Seizures: Convulsive Emergencies
Airway Management After A Road Accident: An Overview
Ambulance: Common Causes Of EMS Equipment Failures — And How To Avoid Them
Traumatic Injury Emergencies: What Protocol For Trauma Treatment?
Cervical Collar In Trauma Patients In Emergency Medicine: When To Use It, Why It Is Important
What Is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)?
Pathophysiology Of Thoracic Trauma: Injuries To The Heart, Great Vessels And Diaphragm
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Manoeuvres: Management Of The LUCAS Chest Compressor
Chest Trauma: Clinical Aspects, Therapy, Airway And Ventilatory Assistance
Precordial Chest Punch: Meaning, When To Do It, Guidelines
Ambu Bag, Salvation For Patients With Lack Of Breathing
Blind Insertion Airway Devices (BIAD’s)
UK / Emergency Room, Paediatric Intubation: The Procedure With A Child In Serious Condition
How Long Does Brain Activity Last After Cardiac Arrest?
Quick And Dirty Guide To Chest Trauma
Cardiac Arrest: Why Is Airway Management Important During CPR?
Neurogenic Shock: What It Is, How To Diagnose It And How To Treat The Patient
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
6 Facts About Burn Care That Trauma Nurses Should Know
Blast Injuries: How To Intervene On The Patient’s Trauma
What Should Be In A Paediatric First Aid Kit
Ukraine Under Attack, Ministry Of Health Advises Citizens About First Aid For Thermal Burn
Electric Shock First Aid And Treatment
RICE Treatment For Soft Tissue Injuries
How To Carry Out Primary Survey Using The DRABC In First Aid
Heimlich Maneuver: Find Out What It Is And How To Do It
The Patient Complains Of Blurred Vision: What Pathologies Can Be Associated With It?
A Tourniquet Is One Of The Most Important Pieces Of Medical Equipment In Your First Aid Kit
12 Essential Items To Have In Your DIY First Aid Kit
First Aid For Burns: Classification And Treatment
Compensated, Decompensated And Irreversible Shock: What They Are And What They Determine
Burns, First Aid: How To Intervene, What To Do
First Aid, Treatment For Burns And Scalds
Wound Infections: What Causes Them, What Diseases They Are Associated With
Patrick Hardison, The Story Of A Transplanted Face On A Firefighter With Burns
Eye Burns: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Burn Blister: What To Do And What Not To Do
Ukraine: ‘This Is How To Provide First Aid To A Person Injured By Firearms’
Emergency Burn Treatment: Rescuing A Burn Patient


