Kidney function: what is azotemia?
Azotemia refers to the concentration of urea in the blood. Urea is a waste product of the liver resulting from protein metabolism
It is released from the liver into the blood, then filtered by the kidneys and excreted with the urine.
Why measure azotemia?
The test can be useful for checking proper kidney function.
The sample is usually taken in the morning. The doctor will suggest whether it is necessary to be fasting.
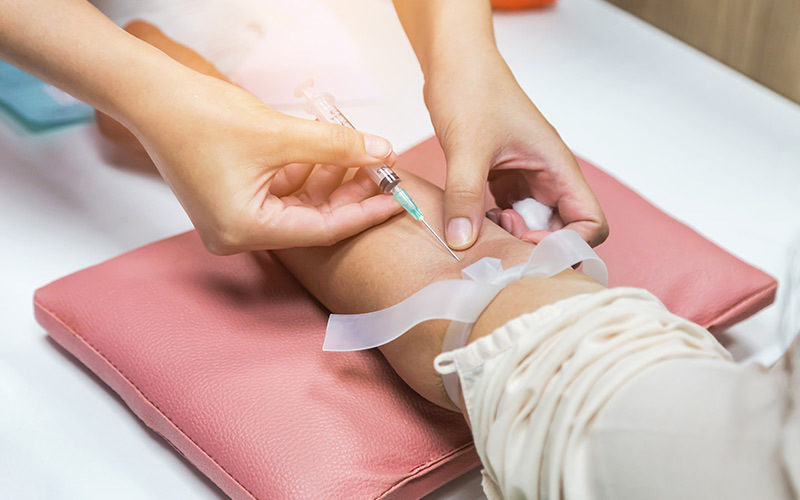
The test is neither dangerous nor painful.
The patient may feel the pinch of the needle entering the arm.
Azotemia, how does the test work?
The test is carried out by means of a simple blood test.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Urine Tests: Glycosuria And Ketonuria Values
Colour Changes In The Urine: When To Consult A Doctor
Paediatric Urinary Calculus: What It Is, How To Treat It
High Leukocytes In The Urine: When To Worry?
The Colour Of Pee: What Does Urine Tell Us About Our Health?
What Is Aspartate Aminotransferase And Why Is It Measured?
Pee Colour: Causes, Diagnosis And When To Worry If Your Urine Is Dark
Haemoglobinuria: What Is The Significance Of The Presence Of Haemoglobin In Urine?
What Is Albumin And Why Is The Test Performed To Quantify Blood Albumin Values?
What Is Cholesterol And Why Is It Tested To Quantify The Level Of (Total) Cholesterol In The Blood?
Gestational Diabetes, What It Is And How To Deal With It
What Is Amylase And Why Is The Test Performed To Measure The Amount Of Amylase In The Blood?
Adverse Drug Reactions: What They Are And How To Manage Adverse Effects
Albumin Replacement In Patients With Severe Sepsis Or Septic Shock
Provocation Tests In Medicine: What Are They, What Are They For, How Do They Take Place?
What Are Cold Agglutinins And Why Is The Test Performed To Quantify Their Values In The Blood?
Why Is Pee Yellow? The Color Of Urine And The Role Of Urobilin
Sugars: What Are They Good For And When Are They Bad For Us?
Urine Test: What It Is Used For And What It Detects
Glycated Haemoglobin: What It Is And Why It Is Important
Haemochrome, What Is It? When Are Red Blood Cell Values Normal?


