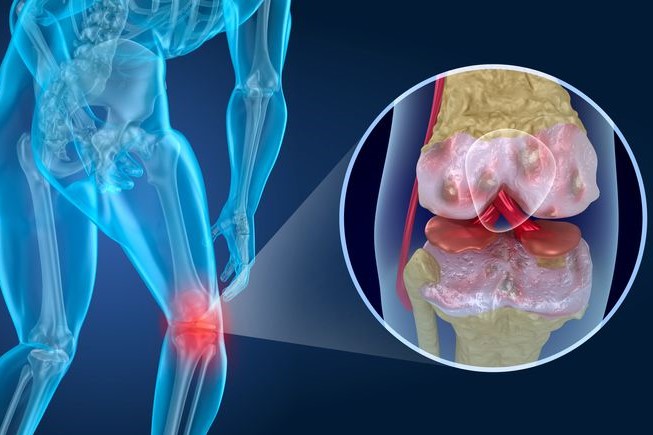
Knee cartilage damage: what it is and how to treat it
Cartilage is the coating that, like enamel, covers and protects our joints, including, of course, the knee joint
Without cartilage, a range of functions, including movement, would not be possible, so it is vital for our well-being to keep the cartilage as healthy as possible.
Cartilage deterioration: the causes
Cartilage can deteriorate as a result of age-related issues as well as other physiological reasons, such as overuse of the joints, too much or too little physical activity, or being overweight, all of which greatly affect joint health and metabolism.
In addition to these risk factors, there are also sudden injuries that can occur at any age.
Previous surgery, especially meniscus removal, is also a frequent cause of cartilage deterioration.
Stiffness and swelling: symptoms of cartilage deterioration
Cartilage is only one element of the whole joint, so the problems affecting it are of a wider nature.
This is why it is essential to treat every aspect of the patient’s pathology, and to follow the patient’s clinical history in a comprehensive manner.
The most common symptoms that indicate possible cartilage deterioration are a feeling of stiffness and swelling in the knee.
This symptom can affect an elderly person suffering from arthrosis as well as a young person who has suffered a sports injury, although the pathology is different.
Biological infiltration: a new treatment option
Except in cases where surgery is necessary to replace the joint, the most common therapies for treating deteriorated cartilage are infiltrations, for example with hyaluronic acid, which helps to lubricate the joint.
But there are also biological infiltrations, which, unlike pharmacological ones, are carried out using concentrates of only minimally modified tissues and cells of the body, such as blood growth factors or so-called stem cells.
Biological infiltrations are not painful and are particularly useful in slowing down the progression of cartilage deterioration, but in the presence of severe arthrosis, when the joint is very compromised, it is necessary to resort to prosthetic surgery.
It is very important, when talking about infiltrations, to refer only to authorised centres, as this therapy should only be carried out by specialists.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Wrist Fracture: How To Recognise And Treat It
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Diagnosis And Treatment
Knee Ligament Rupture: Symptoms And Causes
Lateral Knee Pain? Could Be Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Knee Sprains And Meniscal Injuries: How To Treat Them?
Treating Injuries: When Do I Need A Knee Brace?
Everything You Need To Know About Fibromyalgia


