Liquid Pap test: what it is, how it works and when to do it
The ‘liquid phase’ Pap test allows for greater accuracy and can avoid a second sampling. The specialist explains how it works and what the benefits are
The Pap test is a screening examination carried out in healthy women, with the aim of detecting cervical cancer early on, or abnormalities that may represent a danger for the future.
Since its introduction, cervical cancer has decreased by more than 70%.
Today, thanks to a new testing technique, the ‘liquid phase’ Pap test is able to give more precise and accurate results, with greater diagnostic sensitivity.
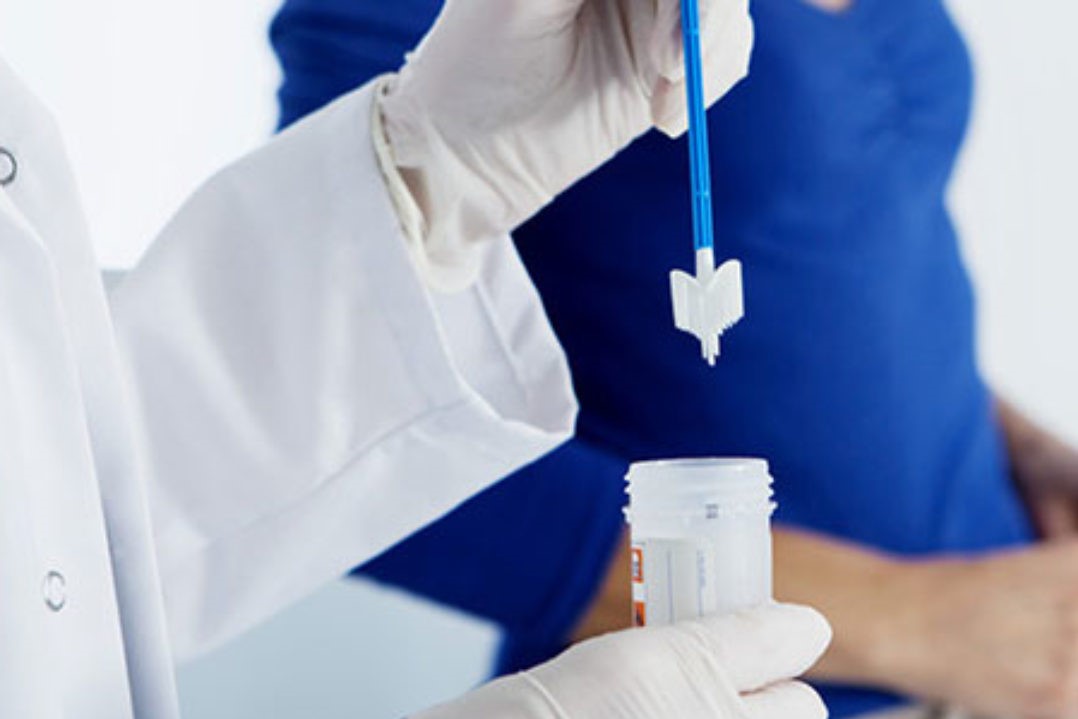
What is the liquid Pap test
The Pap test is a cytological examination performed by means of a quick and painless sampling.
The traditional solid-phase method involves smearing the cells taken from the cervix on a slide and observing them under a microscope to study their characteristics.
Today, a new technique is available, called the ‘liquid phase’ Pap test, which is performed in the same way as the traditional one.
What changes is the preservation of the sample taken.
With this new method, the cells taken from the cervix are placed in a container filled with a fixative liquid that allows them to be preserved for a longer period of time, while retaining more information.
Once the container is sent to the laboratory, the cells are mechanically separated from the non-useful material.
This new procedure allows more representative analysis samples to be obtained, reducing the possibility of inappropriate samples.
In addition to better preservation, in fact, the cells relevant for analysis are the only ones present on the slide to be analysed.
The advantages of the liquid Pap test
The new method of processing and preservation guarantees a more sensitive and accurate diagnosis.
Specifically, compared to the traditional Pap test
- any precancerous lesions that, if left untreated, could give rise to cervical cancer are detected more accurately;
- glandular lesions can be detected;
- diagnostic sensitivity improves;
- cases of uncertain diagnosis, which may unnecessarily alert the patient, are reduced;
- residual cellular material can be used for additional molecular tests, such as HPV DNA or RNA, without the patient having to undergo a second sampling.
When to perform the Pap test
The Pap test cannot be performed during the menstrual period, so the appointment should be scheduled at least 4-5 days after the end of menstruation or 1 week before the next period is expected to start.
How to prepare for the screening examination
Before undergoing the examination, in order not to compromise the outcome, it is necessary to
- discontinue any local therapies (such as ovules, creams or vaginal douches) for at least 4 days beforehand;
- do not have sexual intercourse or take immersion baths (bathtub, pool, sea) in the preceding 24 hours.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Transvaginal Ultrasound: How It Works And Why It Is Important
US CDC Researchers Study: ‘No Increased Risk Of Miscarriage For Pregnant Women With Covid Vaccine’
Pap Test, Or Pap Smear: What It Is And When To Do It


