Lithotomy position: what it is, when it is used and what advantages it brings to patient care
What is the lithotomy position and when is it used: in interventional procedures, it is essential to achieve a correct patient position while maintaining patient comfort and safety
When the patient is in the appropriate position, access to the surgical site is improved and the ability to perform the procedure is enhanced.
To decrease the risk associated with patient positioning, it is important to understand the position, patient risk factors, and environmental risk factors.
This position is one of the common positions used during many surgeries and in childbirth.
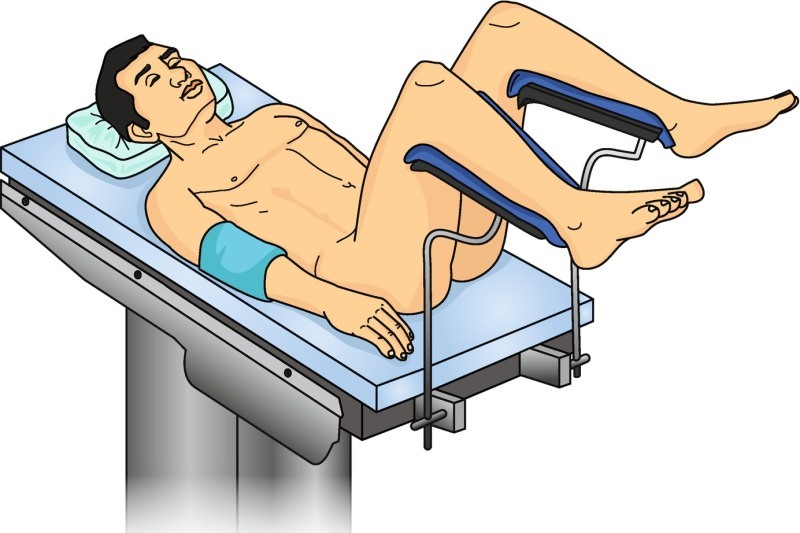
WHAT IS THE LITHOTOMY POSITION?
This position is similar to the supine position of the body when the patient is face-up, arms to the sides, but the legs are separated, raised, and supported in a boot-style leg holder or stirrup-style position.
The most common procedures performed in the Lithotomy position are:
- Gynecological
- Urologic
- Colorectal
- Perineal, or Pelvis Procedures
LITHOTOMY POSITION DURING CHILDBIRTH
This position can be used during childbirth since it provides the doctor with good access to the mother and the baby.
It was used as the standard position for childbirth procedures, but recently, most hospitals have shifted to using birthing beds or chairs.
Studies have shown that Lithotomy Position can cause more pain for the woman in the second or third stage of labor vs other alternative positions like squatting positions.1
LITHOTOMY POSITION DURING SURGERY
This position is used during many operations including, but limited to:
- Urethral Surgery
- Colon Surgery
- Removal of the bladder, and rectal or prostate tumors
- Vaginal, cervical, and uterine surgical procedures
HOW DO YOU PLACE A PATIENT IN A LITHOTOMY POSITION?
The patient is placed on their back face-up and the head is supported by a patient positioning pad.
The legs are elevated at their hips and the knees are bent at a 70 to a 90-degree angle. The legs are supported in padded footrests like leg stirrups.
COMPLICATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH THE LITHOTOMY POSITION
Like other patient positions, this position can be associated with a patient increased risk for some strains or injuries, whether used during childbirth or surgery.
Complications during childbirth
- Increased chance of needing an episiotomy which is cutting the tissue between the vagina and anus, also called the perineum 2
- Increased chance of needing a Caesarian section or forceps
- Increased chance of getting a sphincter injury due to increased pressure3
- Complications during surgery
- Acute Compartment Syndrome when pressure increases within a specific area of your body4
Nerve Injury5: includes two common injuries:
- Peripheral (peroneal) nerve injury increases with the length of surgery. Symptoms include ankle extension, ankle eversion, and foot dorsiflexion.
- lateral femoral nerve injury which leads to lateral thigh pain or meralgia paresthetica.
Other common injuries include hip dislocation, tendon and/or muscle strain, low back strain, Sciatic nerve injury, and pressure injuries
COMMON VARIATIONS OF THE LITHOTOMY POSITION
Thi position can take different variations depending on the type of surgical operation being held.
- Standard Lithotomy (Dorsal) Position
- Low Lithotomy position
- High Lithotomy Position
- Hemi Lithotomy Position
- Exaggerated Lithotomy Position
- Tilted Lithotomy Position
ALTERNATIVE POSITIONS TO THE LITHOTOMY POSITION DURING CHILDBIRTH
With risk factors associated with this position during childbirth, alternative positions have been adopted and proven to be less risky for women’s health.
Some of these alternatives are:
- Standing
- On hands and knees/ leaning forward
- Squatting
- Sitting
- Lying on side
Modified Dorsal Lithotomy Position
The modified dorsal lithotomy position is excellent for radical pelvic operations.
The use of modified Krauss arm supports as stirrups, along with pneumatic devices that intermittently compress the legs, significantly reduces postoperative morbidity in patients who undergo operations in this position.
Lithotomy Position vs. Supine Position
The two positions share similarities in the positioning of the back and head; the patient lays flat facing up and the arms placed to the sides.
In this positioning, the legs are separated and raised. In Supine positioning, the legs stay flat with no separation.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this position is a common position used in childbirth and surgeries to allow access to the proximal lower extremity or genitoperineal region.
It comes with risks that can make it dangerous in some cases.
Other positions can be considered as alternatives for Lithotomy sometimes to avoid complications.
References:
1 Comparative study on the influence of three delivery positions on pain intensity during the second stage of labor. 2016 Jul-Aug; 21(4): 372–378
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4979260/
2https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4877173/
3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4600206/
4Karmaniolou I, et al. (2010). Compartment syndrome as a complication of the lithotomy position
caribbean.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0043-31442010000600017
5 Kuponiyi O, et al. (2014). Nerve injuries associated with gynecological surgery.
DOI: 10.1111/tog.12064
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Trendelenburg (Anti-Shock) Position: What It Is And When It Is Recommended
Prone, Supine, Lateral Decubitus: Meaning, Position And Injuries
Stretchers In The UK: Which Are The Most Used?
Does The Recovery Position In First Aid Actually Work?
Reverse Trendelenburg Position: What It Is And When It Is Recommended
How Is Triage Carried Out In The Emergency Department? The START And CESIRA Methods
Medical Corner – Management Of Tachycardiac Arrhythmias In Pregnancy
Stretcher: What Are The Most Used Types In Bangladesh?
The Ultimate Guide To The Trendelenburg Position


