Maneuver and positive or negative Murphy's sign: what are they and what do they indicate?
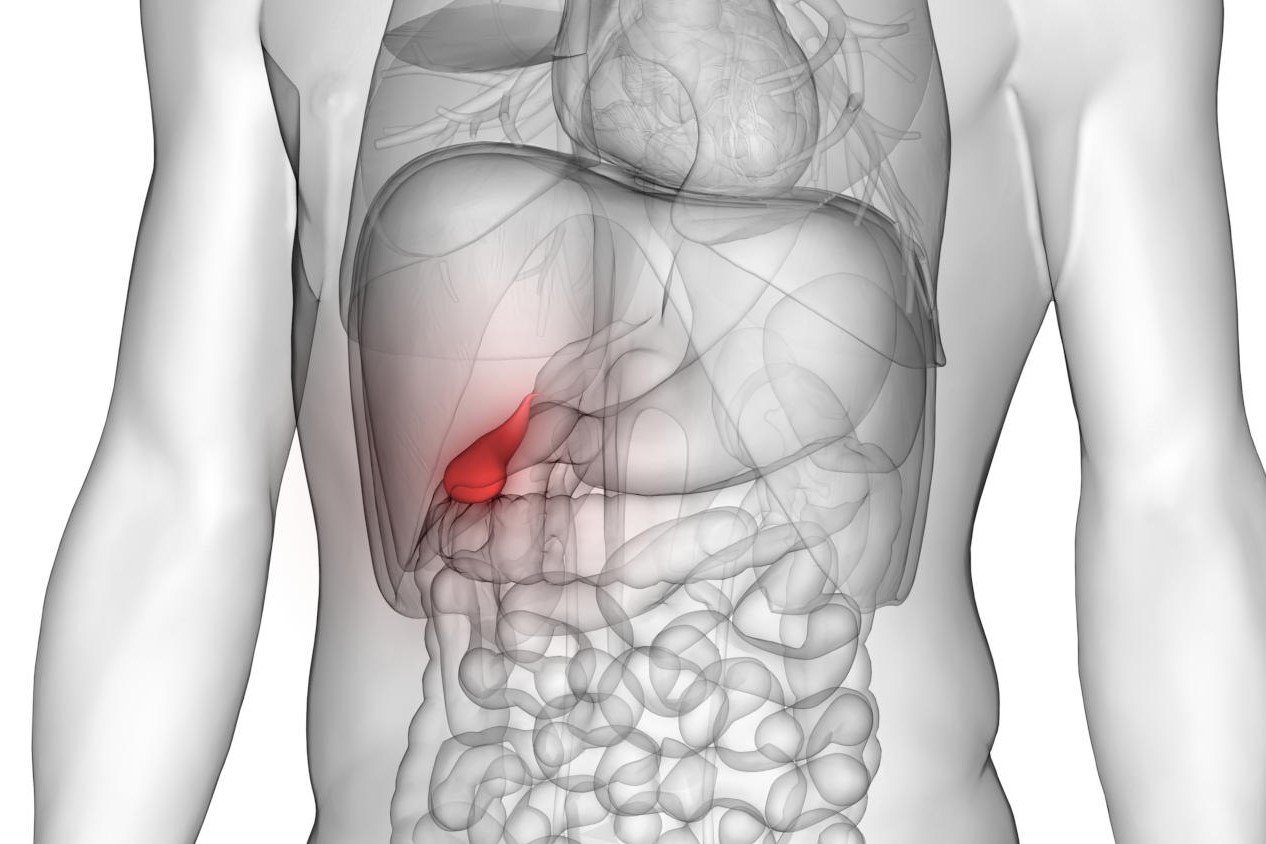
Murphy’s maneuver is a maneuver used by the doctor in semiotics to investigate the presence of pain that originates in the gallbladder (also called gall bladder)
Its name originates from the famous American surgeon John Benjamin Murphy.
How is the Murphy maneuver performed?
- The patient lies in a supine position (with the stomach facing upwards);
- the doctor stands on the patient’s right side;
- the doctor places his right hand flat on the right upper quadrant of the abdomen;
- the doctor presses the tips of the index and middle fingers on the gallbladder point (located under the right tenth rib, at the level of its anterior end);
- the patient is made to inhale deeply, always compressing the cystic point: in this way the gallbladder is pushed down and forward by the diaphragm until it touches the anterior wall of the abdomen.
- if the touch of the organ by the two fingers will exacerbate the pain, so that the patient will abruptly stop inhaling, Murphy’s sign is positive, indicating the probable presence of cholecystitis or calculi, otherwise Murphy’s sign it is negative.
What does positive Murphy’s sign mean?
As just mentioned, the positive Murphy’s sign indicates the probable presence of cholecystitis or calculi.
The pathology for which the positivity of the Murphy maneuver is most frequently observed is acute cholecystitis, i.e. acute inflammation of the gallbladder; if, on the other hand, there is chronic cholecystitis or calculi, the sign will be more nuanced or greater pressure will have to be exerted to obtain a frank positivity.
Is Murphy’s sign enough to make a diagnosis?
No. As often happens in semiotics, the positive Murphy’s sign represents an indication of diagnosis and is NOT sufficient on its own to make any precise diagnosis: the latter must in fact be investigated by continuing with diagnostic laboratory tests (haematochemical tests) and diagnostics for images (ultrasound, RX…) which can avoid false positives and negatives.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Gallstones: Causes And Symptoms
Treatment And Therapy Of Gallstones
Kidney Stones: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Kidney Stones: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Acute Pancreatitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Palpation In The Objective Examination: What Is It And What Is It For?
Acute Abdomen: Causes And Cures
Abdominal Health Emergencies, Warning Signs And Symptoms
Abdominal Ultrasound: How To Prepare For The Exam?
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
Positive Or Negative Psoas Maneuver And Sign: What It Is And What It Indicates
Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck): What It Is And When It Is Performed
Assessment Of Abdominal Trauma: Inspection, Auscultation And Palpation Of The Patient
Acute Abdomen: Meaning, History, Diagnosis And Treatment
Abdominal Trauma: A General Overview Of Management And Trauma Areas
Abdominal Distension (Distended Abdomen): What It Is And What It Is Caused By
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Symptoms, Evaluation And Treatment
Hypothermia Emergencies: How To Intervene On The Patient
Emergencies, How To Prepare Your First Aid Kit
Seizures In The Neonate: An Emergency That Needs To Be Addressed
Abdominal Pain Emergencies: How US Rescuers Intervene
First Aid, When Is It An Emergency? Some Information For Citizens
Acute Abdomen: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Exploratory Laparotomy, Therapies


