Melanoma: What is it and how can it be diagnosed?
Melanoma is a malignant tumour of the skin and mucous membranes that originates from melanocytes, cells that produce melanin and aggregate, resulting in the formation of moles
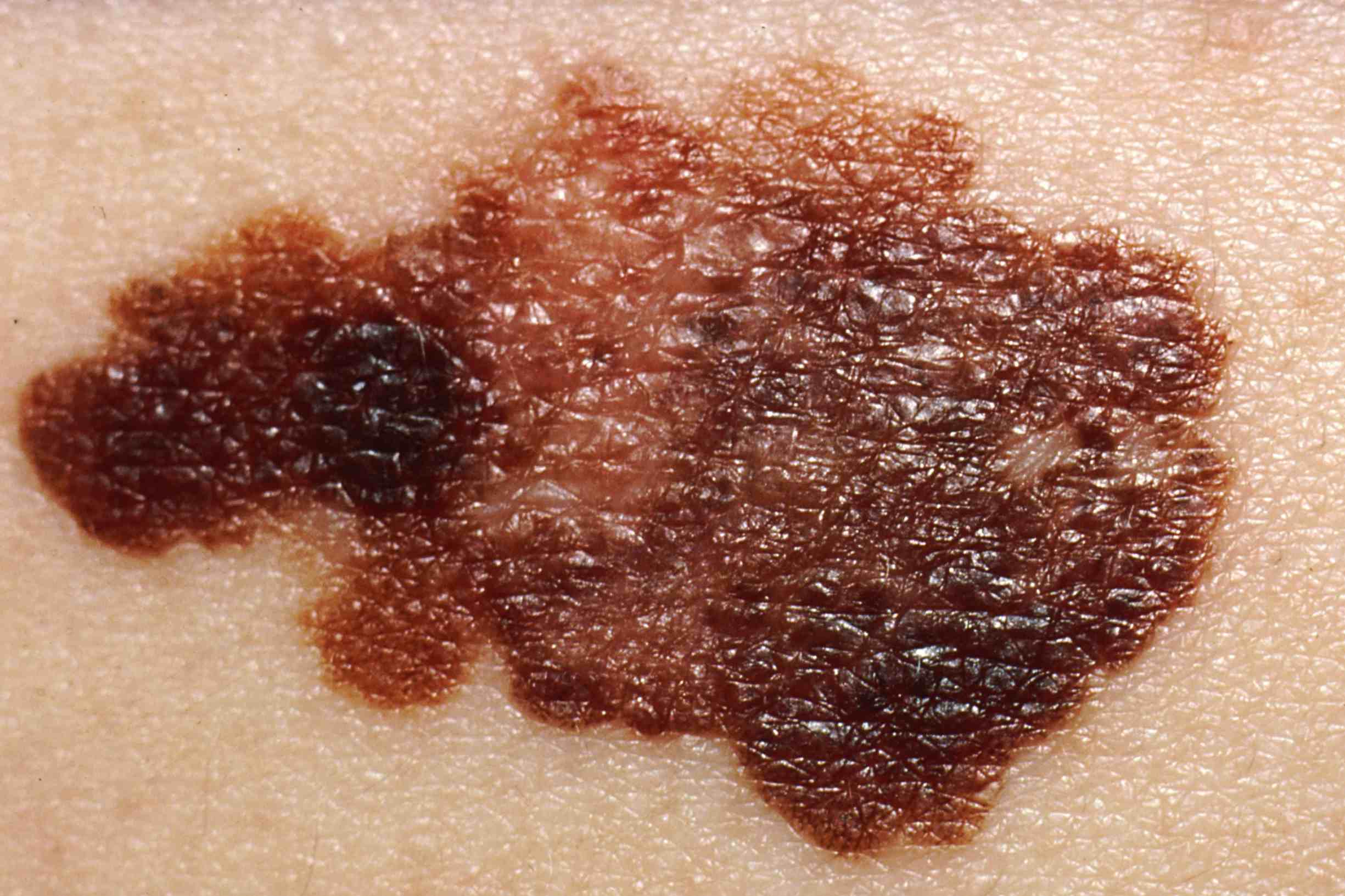
Clinical features of melanoma
Melanoma develops most frequently in body areas most exposed to sunlight and in people with phototype I (fair skin, blue eyes, blond hair).
It can form either from pre-existing nevi (moles) or ex novo.
In the case of plane melanoma the ABCDE rule helps to distinguish a nevus from a melanoma:
Asymmetry: the melanoma is asymmetrical.
Edges: irregular, indented, map-like.
Colour: from black to various shades of brown.
Size: 6 mm or more.
Evolution: the lesion is clearly progressing with changes in morphology.
Age: usually onset in individuals over 15 years of age.
Elevation: appearance of a papule or nodule in the context of the pigmented lesion.
How can melanoma be diagnosed?
The videodermatoscopic test, commonly known as ‘mole mapping’, is a second-level, non-invasive, painless, specialist diagnostic test that consists of studying the microscopic features of nevi and all pigmented skin lesions that are not otherwise appreciable with the naked eye.
Despite health education campaigns, many patients claim that they have never had a dermatological examination to check their moles or that they had never heard of melanoma before diagnosis.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Cherry Angiomas: What They Are And How To Remove Them In Minutes
Cavernous Angiomas: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Lymphoma: 10 Alarm Bells Not To Be Underestimated
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment Of A Heterogeneous Group Of Tumours
CAR-T: An Innovative Therapy For Lymphomas
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: Long-Term Outcomes Described For Childhood ALL Survivors
Lymphangiomas And Lymphatic Malformations: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Melanoma: Prevention And Dermatological Examinations Are Essential Against Skin Cancer
Nail Melanoma: Prevention And Early Diagnosis
Dermatological Examination For Checking Moles: When To Do It
What Is A Tumour And How It Forms
Rare Diseases: New Hope For Erdheim-Chester Disease
How To Recognise And Treat Melanoma
Moles: Knowing Them To Recognise Melanoma
Skin Melanoma: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis And The Latest Treatments
Nevi: What They Are And How To Recognise Melanocytic Moles
Bluish Color Of Baby’s Skin: Could Be Tricuspid Atresia
Skin Diseases: Xeroderma Pigmentosum
Basal Cell Carcinoma, How Can It Be Recognised?
Autoimmune Diseases: Care And Treatment Of Vitiligo
Epidermolysis Bullosa And Skin Cancers: Diagnosis And Treatment
SkinNeutrAll®: Checkmate For Skin-Damaging And Flammable Substances
Healing Wounds And Perfusion Oximeter, New Skin-Like Sensor Can Map Blood-Oxygen Levels
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Psoriasis: It Gets Worse In Winter, But It’s Not Just The Cold That’s To Blame
Childhood Psoriasis: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Treat It
Topical Treatments For Psoriasis: Recommended Over-The-Counter And Prescription Options
What Are The Different Types Of Psoriasis?
Phototherapy For The Treatment Of Psoriasis: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Skin Diseases: How To Treat Psoriasis?
Skin Cancers: Prevention And Care


