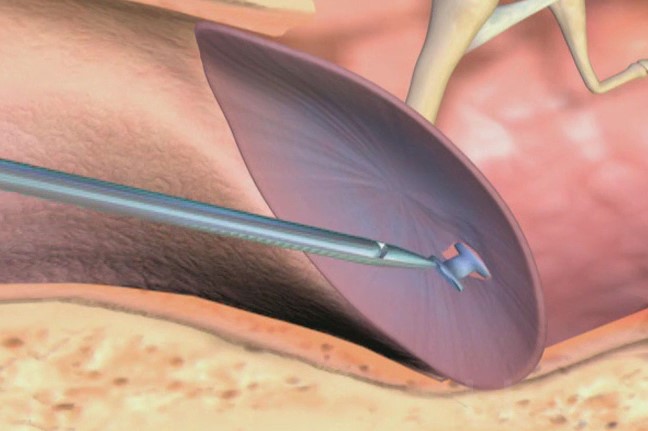
Myringotomy, the incision of the eardrum membrane to remove the mucus that stagnates in the ear
Myringotomy is a surgical procedure that consists of incising the eardrum membrane
Myringotomy is part of ENT surgery:
- Myringocentesis: it is indicated in cases of chronic exudative otitis media involving one or both sides, i.e. chronic persistence of mucus/cartilage in the tympanic cavity, not associated with hearing loss. or associated with minimal hearing loss. It consists of making an incision in the membrane to aspirate mucus through it;
- Transtympanic drainage placement (tympanostomy) on both sides: is indicated in cases of chronic exudative otitis media on one or both sides, associated with significant hearing loss. It consists of making an incision in the membrane and, after suctioning the mucus from the tympanic cavity, applying a drain, i.e. a microscopic silicone tube, through the membrane itself. The tube will remain in place in the months or years following the operation, creating communication between the tympanic cavity and the external environment and allowing good ventilation of the middle ear.
The main indications for transthympanic drainage placement are:
- Chronic exudative otitis media on one or both sides with hearing loss;
- Acute recurrent middle ear otitis media on one or both sides; current indications suggest intervention if at least 4 infections have occurred within 6 months and if, in the interval between infections, fluid stagnates in the ear.
- The most important benefits of transtympanic drainage surgery are:
- A reduction in the recurrence of acute otitis media episodes, with a consequent reduction in the painful symptoms associated with such episodes;
- An improvement in hearing;
- A consequent improvement in language learning;
The procedure is performed by the ENT specialist.
It is performed under general anaesthesia and under an otomicroscopic examination.
Using the operating microscope, the surgeon first inspects the external ear canal, cleaning it of earwax, epidermal material or any other material that prevents the eardrum membrane from being seen.
CHILD HEALTH: LEARN MORE ABOUT MEDICHILD BY VISITING THE BOOTH AT EMERGENCY EXPO
Myringotomy: having framed the tympanic membrane in its entirety, the otorhinolaryngologist makes a 2-3 mm incision in the tympanic membrane using a small scalpel, then sucks the mucus out of the incision
As mentioned above for transtympanic drainage placement, this is followed by the application, through the incision itself, of a ventilation tube (tympanostomy).
Since this is a minimally invasive procedure, it carries no risk of serious complications.
However, the ingress of water into the ear undergoing this procedure, especially in the first few days after the operation, may favour the appearance of otorrhea, i.e. discharge of mucus or pus from the ear.
For this reason, contact of the operated ear with water should be avoided in the week following the surgery, but appropriate precautions should also be taken afterwards when swimming in the sea or swimming pool.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Croup In Children: Meaning, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Mortality
How Are Picornavirus Infections Contracted?
Croup (Laryngotracheitis), The Acute Obstruction Of A Child’s Airways
A. Resistant Bacteria: The Important Discovery Of Australia
Bacterial Infections, Herpetic Whitlow: What Is It And When Do I Need To See A Specialist?
Croup And Epiglottitis: A Guide To The Management Of Respiratory Infection
What Is ‘Hand Foot And Mouth’ Disease And How To Recognise It



