Parvovirus B19 on the rise in the USA
The virus is spreading rapidly in all age groups, with a peak among children aged 5-9
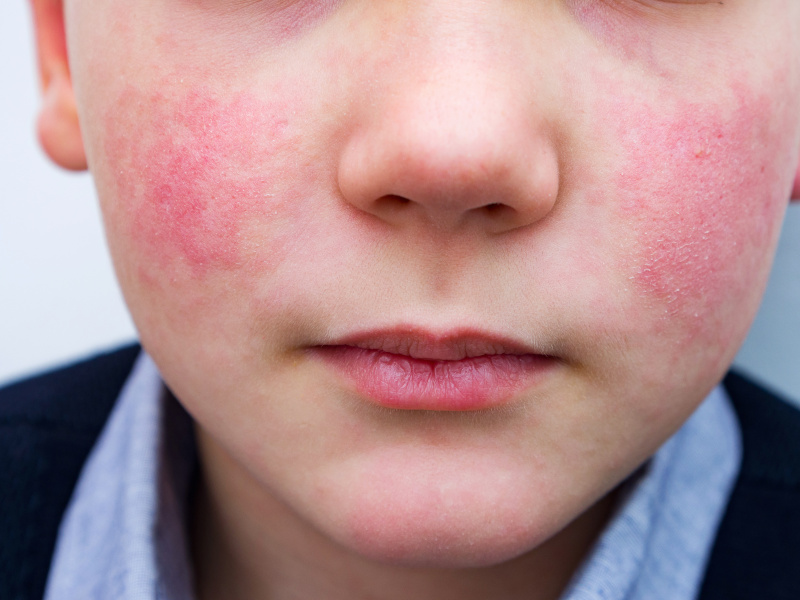
Parvovirus B19, also known as “slap cheek disease” due to the characteristic rash it causes, is on the rise in the United States. According to a recent warning from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the virus is spreading rapidly across all age groups, with a peak among children aged 5-9.
What is Parvovirus B19 and how is it transmitted?
Parvovirus B19 is a highly contagious virus that is transmitted mainly through the respiratory droplets produced by an infected person when he coughs or sneezes. Direct contact with the nasal or oral secretions of an infected person may also facilitate the spread of the virus.
Who is at risk?
Although anyone can get parvovirus B19, some categories of people are particularly at risk:
- Preschool and school-aged children: Children are particularly susceptible to viral infections and often frequent crowded environments such as schools and nurseries, where the virus spreads easily
- Pregnant women: Parvovirus B19 infection during pregnancy can cause serious complications for the fetus, such as anemia and miscarriage
- People with weakened immune system: Cancer patients, transplant patients or HIV patients are more susceptible to parvovirus complications
What are the symptoms?
Many people who are infected have no symptoms or only mild flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headaches and fatigue. However, some individuals may develop a characteristic rash that usually starts on the cheeks and then spreads to the rest of the body.
Complications
In most cases, parvovirus B19 infection resolves spontaneously without leaving long-term consequences. However, in some people, especially pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals, more serious complications may occur, such as:
- Anemia: The infection can cause a decrease in red blood cell production, resulting in anemia
- Miscarriage: In pregnant women, the infection can lead to miscarriage or serious complications for the fetus
- Joint problems: Adults may experience persistent joint pain
Prevention and treatment
There is currently no vaccine or specific treatment against parvovirus B19. Preventive measures are based mainly on the following actions:
- Wash your hands frequently: Washing your hands frequently with soap and water is essential to prevent the spread of the virus
- Cover your mouth and nose: When coughing or sneezing, it is important to cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow
- Avoid contact with infected people: If possible, it is advisable to avoid contact with people who have flu symptoms
Treatment is mainly symptomatic and consists of managing symptoms, such as fever and pain. In some cases, blood transfusions or immunoglobulins may be necessary to treat the complications.


