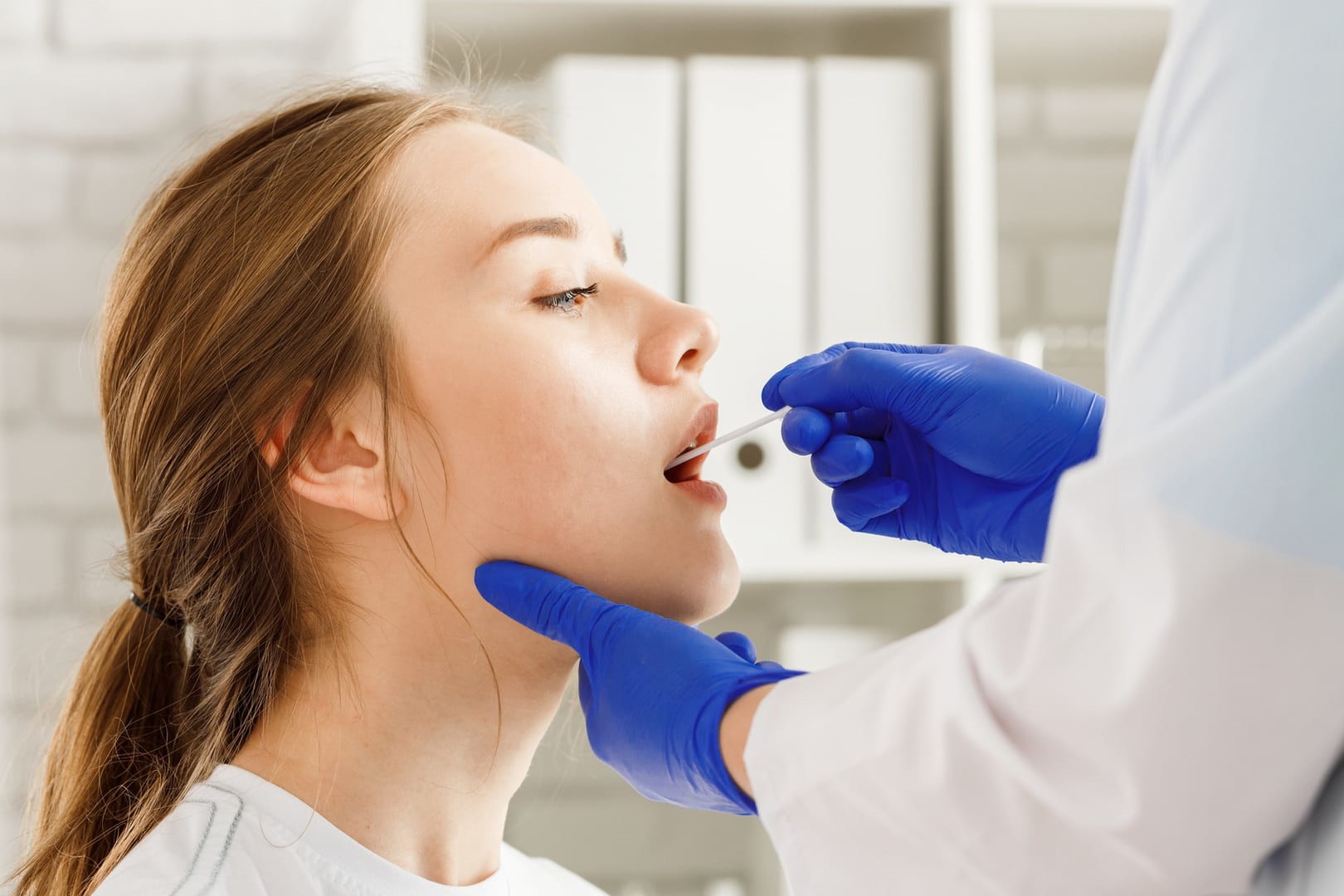
Pharyngeal swab: when is it necessary?
Pharyngeal swab the most indicated examination for the diagnosis of bacterial pharyngitis
It is the microbiological examination of the pharyngeal cavity and is the most indicated procedure for diagnosing bacterial pharyngitis.
The latter are mainly caused by a bacterium called Streptococcus pyogenes.
What does a pharyngeal swab consist of?
It is performed with a swab consisting of a cotton swab stick (similar to a cotton swab, but longer) that is inserted into the mouth and gently rubbed over the back of the oral cavity (the pharynx) and the surface of the tonsils (if they have not been removed due to previous infections).
The stick containing the pharyngeal secretions is then placed in a suitable container to be sent to the laboratory.
With the pharyngeal swab, either the rapid test or the culture can be performed.
This is an easy-to-use test, usually performed at most blood collection centres, or even in paediatricians’ offices, which enables a result to be obtained in a few minutes.
The test detects the possible presence of certain typical streptococcal molecules, using easy-to-perform methods similar to those used in pregnancy tests.
Pharyngeal swab culture is the most reliable tool for diagnosing acute pharyngotonsillitis
The secretion obtained with the swab is placed in suitable culture media: if present, the bacteria grow after 24-48 hours and can be identified to give them a ‘name and surname’ (e.g. the Streptococcus pyogenes mentioned above, or other germs).
Furthermore, with culture it is possible to test the sensitivity of bacteria to various antibiotics, called an antibiogram, in order to give the most appropriate and effective antibiotic therapy.
For optimal results, it is very important to perform the pharyngeal swab before starting antibiotic therapy.
The rapid test is simple to perform, and if positive it is usually reliable and indicates the presence of streptococcus.
On the other hand, if negative (it is not very sensitive), it does not exclude that streptococcus is still present; furthermore, the rapid test does not recognise germs other than streptococcus pyogenes.
Therefore, in the case of a negative rapid test despite the presence of inflammatory symptoms of the pharynx, culture is recommended.
It should be made clear that the presence of the germ in the pharynx is not necessarily indicative of disease, as the germ can ‘lodge’ in the pharynx without giving symptoms.
In this case, one speaks of a ‘healthy carrier’, who can still transmit the germ to other people.
On the other hand, in the case of the presence of symptoms (sore throat, cough, fever, difficulty swallowing, etc.), a positive swab is indicative of the presence of the germ in the pharyngitis or pharyngotonsillitis in progress.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Symptoms Of Emergencies In Children: Fever
Paediatric Seasonal Illnesses: Acute Infectious Rhinitis
Pediatrics: What To Do In Case Of High Fever In Children?
Seasonal Illnesses: What To Eat When You Have Flu?
Plaques In The Throat: How To Recognise Them
Tonsillitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Sore Throat: How To Diagnose Strep Throat?
Sore Throat: When Is It Caused By Streptococcus?
Pharyngotonsillitis: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Flu Vaccine For Children? Paediatricians: ‘Do It Now, Epidemic Already Started’
Paediatrics / Recurrent Fever: Let’s Talk About Autoinflammatory Diseases
Q Fever: What It Is, How To Diagnose It And How To Treat It
Respiratory Allergies: Symptoms And Treatment
RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) Surge Serves As Reminder For Proper Airway Management In Children
Acute And Chronic Sinusitis: Symptoms And Remedies
Symptoms And Remedies Of Allergic Rhinitis
Respiratory Or Food Allergies: What Is The Prick Test And What Is It For?
Anaphylactic Shock: What It Is And How To Deal With It
Sinusitis: How To Recognise That Headache Coming From The Nose
Sinusitis: How To Recognise And Treat It
Flu Vaccine For Children? Paediatricians: ‘Do It Now, Epidemic Already Started’
Rhinitis, Inflammation Of The Nasal Mucous Membranes


