Pityriasis Alba: what it is, how it manifests itself and what is the treatment
Pityriasis Alba is a common skin manifestation in prepubertal age characterised by dry patches that are lighter in colour than the skin, sometimes slightly erythematous (reddened)
To date, the exact causes are not known.
Several disease-causing microorganisms have been considered (Pityrosporum, Streptococcus, Aspergillus, Staphylococcus), but none has been confirmed as a definite cause of pityriasis alba.
Some factors that predispose to pityriasis alba are allergies and inadequate exposure to the sun.
Pityriasis alba is frequently observed in allergic children and is one of the side symptoms of atopic dermatitis
However, it is not an indicator of an allergic phenomenon.
Pityriasis alba may affect one or more children in the same family because they have the same constitution: dry skin or atopic familiarity.
But it is not contagious.
The manifestation generally appears at the end of summer.
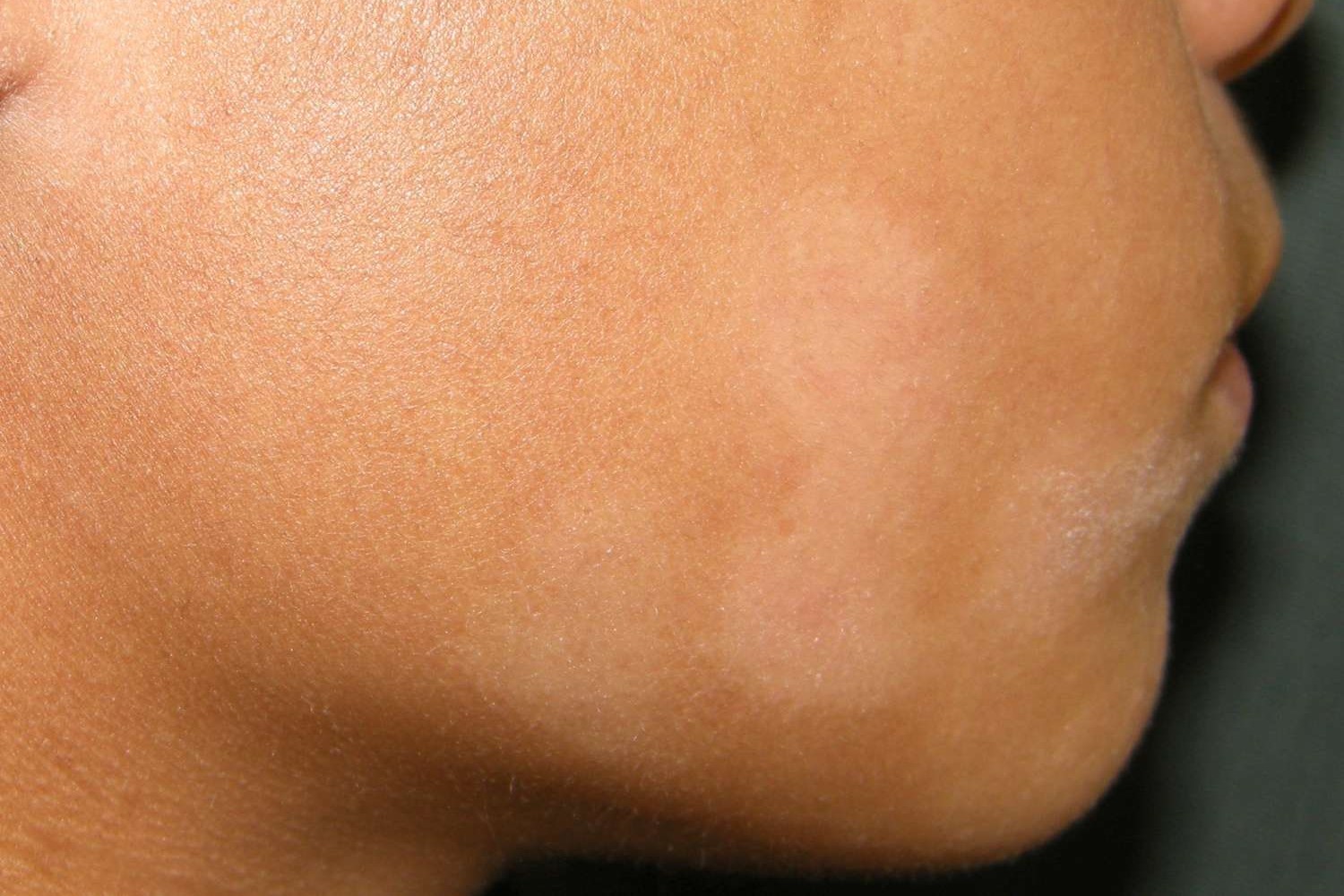
It is characterised by roundish or oval whitish patches localised mainly on the face and arms.
The margins of the patches are blurred, lighter in colour than the surrounding skin, while in the centre the patches are covered with a thin, whitish desquamation.
In some cases, these lesions are erythematous (reddened).
Pityriasis alba is more evident at the end of the summer as exposure to the sun makes the whitish patches more obvious than on tanned skin
The evolution is very slow, chronic-recurrent.
It generally causes no other symptoms or, at most, is slightly itchy.
It is sufficient to use gentle cleansers for body hygiene and constantly apply moisturising/emollient creams.
Effective treatment completely resolves the dryness with the transient persistence of hypopigmented (lighter coloured) and smooth patches for a few weeks and sometimes months.
The use of moisturising creams even during the winter season prevents the recurrence of pityriasis alba during the summer and the persistence of hypopigmented patches during the winter.
In reddened forms, the use of soothing anti-inflammatory creams is indicated.
Sun exposure must follow the appropriate indications for the paediatric age and phototype.
The phototype indicates the amount of melanin produced by the skin.
Dermatologists distinguish 6 categories of phototype: from phototype 1, which indicates people with lighter skin, to phototype 6, which indicates people with darker skin.
Obviously, people with very fair skin (phototype 1) risk sunburn much more than people with phototype 6, i.e. much darker skin.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Atopic Dermatitis: Treatment And Cure
Psoriasis, A Disease That Affects The Mind As Well As The Skin
Allergic Contact Dermatitis And Atopic Dermatitis: The Differences
Adverse Drug Reactions: What They Are And How To Manage Adverse Effects
Symptoms And Remedies Of Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Conjunctivitis: Causes, Symptoms And Prevention
What Is And How To Read The Allergy Patch Test
Eczema Or Cold Dermatitis: Here’s What To Do
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Clinical Manifestations Of Atopic Dermatitis


