Ruptured brain aneurysm, violent headache among the most frequent symptoms
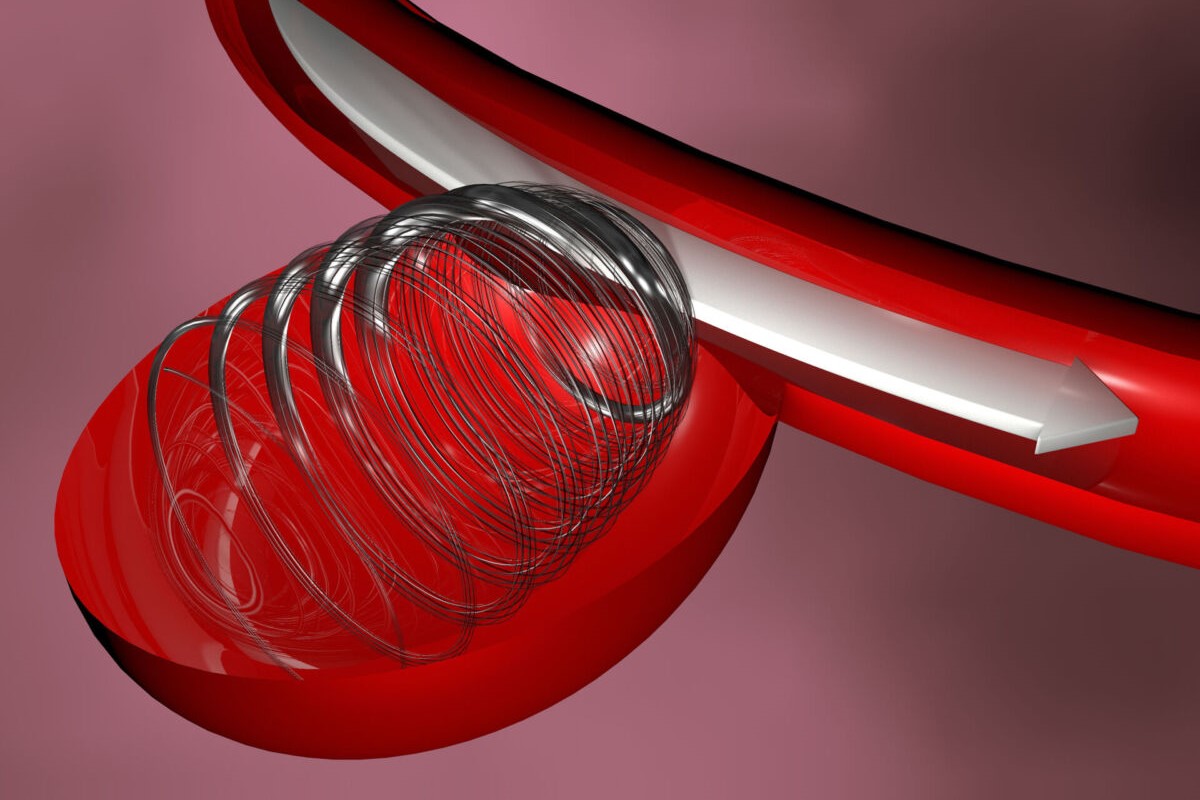
A brain aneurysm can remain hidden in the brain for life or occur suddenly and violently. A cerebral aneurysm is a progressive dilation of an artery that carries blood to the brain, which for congenital reasons is more fragile and slowly collapses under the pressure of the blood, forming a kind of balloon
When the balloon ruptures in the artery, blood invades the spaces surrounding the brain: this is a cerebral aneurysm
Subarachnoid haemorrhage, i.e. a minimal rupture of an aneurysm, is characterised by the appearance of a very violent headache, which patients describe as the most severe headache of their lives, followed by a feeling of neck stiffness; there may also be nausea and vomiting.
If the haemorrhage is more severe, the damage is much greater and there can be up to 40% mortality and two thirds of survivors have permanent damage.
Risk factors for brain aneurysm
Between 2 and 5% of the population are aneurysm carriers, but what are the risk factors?
Smoking, high blood pressure, family history and female sex.
It has also been shown that taking drugs (such as ecstasy or cocaine) greatly increases the risk of having a stroke and therefore of having a haemorrhage.
If a young person with an aneurysm that may never have ruptured in his lifetime takes an ecstasy pill, he may rupture with very serious consequences.
Treatment options for brain aneurysms
Early diagnosis or correct interpretation of the slightest expansion is very important because it allows the aneurysm to be treated before it reaches an extremely serious prognosis.
Depending on the case, the intervention can be carried out by minimally invasive surgery, closing the aneurysm with a metal clip, or endovascularly, introducing a catheter into the arteries, with a stent or coils to facilitate the formation of a thrombus and exclude the aneurysm from the artery.
It is essential to go to a centre that offers both endovascular and microsurgery.
Read Also:
Cerebral Aneurysm: What It Is And How To Treat It
Ruptured Aneurysms: What They Are, How To Treat Them
Pre-Hospital Ultrasound Assessment In Emergencies
Unruptured Brain Aneurysms: How To Diagnose Them, How To Treat Them


