Skin diseases: how to treat psoriasis?
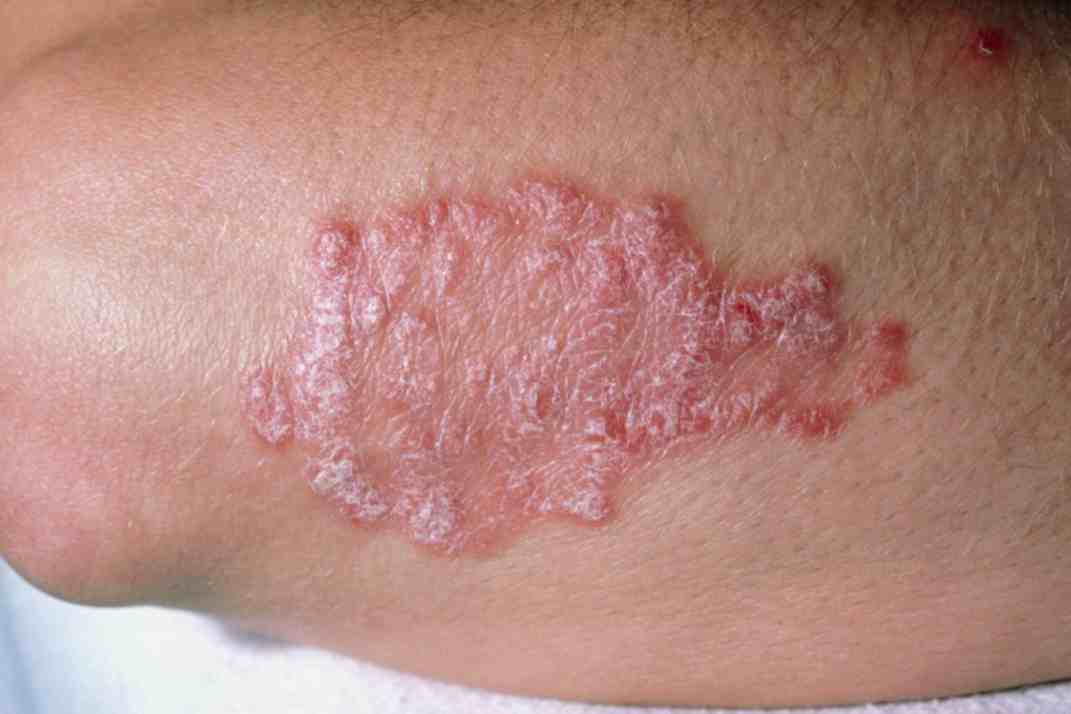
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that presents with extremely varied clinical forms in terms of location and severity of symptoms, so it presupposes treatment tailored to the individual clinical situation
How to treat psoriasis
There is no single treatment to counter psoriasis but several treatment options that the dermatologist determines based on the extent, severity of manifestations, and individual response of the person.
In general, however, all treatments are geared toward containing the active phase of inflammation and avoiding worsening of the condition, as it is not possible to completely recover from psoriasis.
Precisely because of its chronic nature, psoriasis therefore requires constant and regular treatment, and to date the most effective ones include:
- Local topical treatment
- Systemic oral therapy or by injection
- Phototherapy with ultraviolet rays
- Biologic drugs
Topical drugs against psoriasis
Traditional topical therapy is generally used in mild forms of psoriasis and acts directly on the skin with application of ointments, lotions, creams, ointments, and gels to shrink and make the spots disappear.
The dermatologist, depending on the patient’s condition, may choose a drug based on cortisone, tar, vitamin D, glycerin, glycolic acid to counteract the inflammatory action and moisturize the skin.
The treatment of skin lesions will surely result in the patient having a more positive attitude toward his disease.
Traditional systemic treatments for psoriasis
Drugs for systemic use are reserved for more severe forms of psoriasis, for which topical treatments are not satisfactory.
We are talking about drugs to be taken orally or through injections for the purpose of fighting inflammation and immune system malfunction.
They are generally based on methotrexate, retinoids, and cyclosporine and are accompanied by mild side effects such as nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Phototherapy for the treatment of psoriasis
Phototherapy is a very effective therapeutic method against psoriasis as it facilitates clinical improvement simply by reproducing the effect of sun exposure on the skin.
Usually this treatment is combined with traditional topical and systemic therapies with appreciable results especially in the most common variants of the disease (plaque psoriasis).
In fact, the action of ultraviolet rays allows the body to regulate the formation of keratinocytes, which is the protein responsible for the formation of the typical plaques.
Biologic drugs for the treatment of psoriasis
The use of biologic drugs is usually reserved for cases of particularly severe and persistent psoriasis after other treatments.
This is a major therapeutic innovation, as these drugs (anti-TNF type, monoclonal antibodies) have a direct action on inflammatory cells by exerting an immunosuppressive effect, that is, blocking the mechanisms underlying the disease.
They have no particular side effects and significantly improve the condition of patients with severe and distressing forms of psoriasis.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Autoimmune Diseases: Care And Treatment Of Vitiligo
Epidermolysis Bullosa And Skin Cancers: Diagnosis And Treatment
SkinNeutrAll®: Checkmate For Skin-Damaging And Flammable Substances
Healing Wounds And Perfusion Oximeter, New Skin-Like Sensor Can Map Blood-Oxygen Levels
Psoriasis, An Ageless Skin Disease
Psoriasis: It Gets Worse In Winter, But It’s Not Just The Cold That’s To Blame
Childhood Psoriasis: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Treat It
Topical Treatments For Psoriasis: Recommended Over-The-Counter And Prescription Options
What Are The Different Types Of Psoriasis?
Phototherapy For The Treatment Of Psoriasis: What It Is And When It Is Needed


