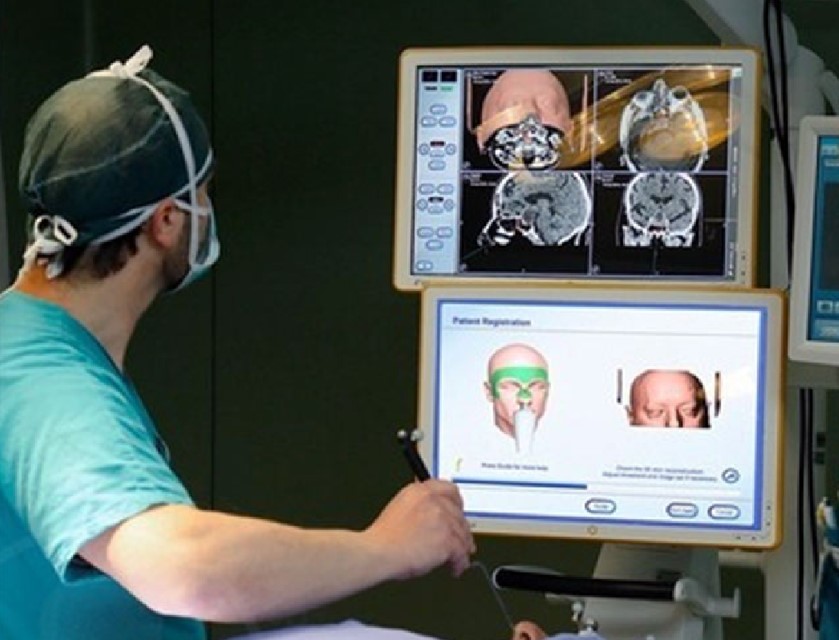
Surgery: neuronavigation and monitoring of brain function
Neuronavigation is a tool that makes it possible to reconstruct and represent in real time the area of the brain affected by surgery
Neuronavigation is a tool that allows three-dimensional reconstruction of digital neuro-anatomical images (CT or MRI) of the brain, synchronising the brain images with the actual shape of the patient and dynamically visualising the relationship between the position of various types of surgical instruments and the surrounding anatomical structures.
Neuronavigation is performed to identify possible access routes to the brain
During an operation, it also makes it possible to make rapid adjustments to the surgical procedure.
Thanks to the continuous evolution of these technologies, neuronavigation is now a widely used tool in neurosurgery.
In the preoperative phase, neuronavigation allows the neurosurgeon to
- Understand the exact anatomical shape of the patient’s brain;
- Understand the three-dimensional relationship of the area of the brain that is to undergo surgery (e.g. the tumour that is to be removed) with neighbouring regions.
- In this way, neuronavigation allows safer planning of complex procedures.
During surgery, the purpose of neuronavigation is to:
- ‘guide’ the neurosurgeon’s hand in using specific instruments in real time;
- Maintain the correct position with respect to specific areas identified as targets;
- Verify, for example during tumour removal, the progress and reach of tissue adjacent to the removed tumour.
- Potentially, all surgical interventions could be conducted with the aid of neuronavigation, thus ensuring that the ‘target’ is reached via the safest route.
However, the main uses of neuronavigation, particularly in paediatric neurosurgery, include:
- Neuro-oncology: localisation and reaching, for removal or biopsy, of neoplasms (tumours) that are small in size or localised in deep places or close to functionally ‘critical’ areas;
- Epilepsy surgery: definition of the area of the cerebral cortex to be removed or the areas of the brain to be disconnected from the epileptogenic area;
- Hydrocephalus: placement of shunt catheters, orientation during endoscopic procedures;
- Functional neurosurgery: planning surgery and reaching specific deep targets.
There are latest-generation systems that combine neuronavigation with robotic arms capable of positioning and moving along predefined pathways.
The end of the robotic arm is equipped with specific holders for different surgical instruments that allow the neurosurgeon to increase the accuracy and safety of delicate minimally invasive procedures.
Application examples of such instruments are:
- The implantation of deep brain recording electrodes in epilepsy surgery;
- The performance of biopsies of deep tumour lesions;
- Neuroendoscopy, especially when conducted in small ventricular spaces;
- The placement of deep brain stimulation electrodes
The performance of pallidotomies in the treatment of movement disorders.
Pallidotomy is a surgical technique that consists of coagulating a specific area of a brain nucleus (the inner pallid globe).
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Cataract: Symptoms, Causes And Intervention
Robotic Surgery: Benefits And Risks
Refractive Surgery: What Is It For, How Is It Performed And What To Do?
Kidney Cancer: Laparoscopic Surgery And The Latest Technologies
Eye For Health: Cataract Surgery With Intraocular Lenses To Correct Visual Defects
Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma


