Symptoms and diagnosis: why proctological examination and anorectoscopy are performed
The proctological examination consists of two moments: an interview between patient and proctologist, in which the patient describes all the symptoms for which he or she has decided to consult the specialist, and an external and internal inspection of the anal canal for the diagnosis of presumed anorectal pathologies
Why and when a proctological examination is used
A proctological examination is the quickest and most effective response in the presence of anorectal symptoms (often disabling) such as pain, bleeding, itching, the appearance of swelling, purulent discharge, altered alvus, and enlarged prostate.
It is essential for the diagnosis of hemorrhoidal pathology, fissures, rectal prolapse, rectocele, and other rectal pathologies.
Proctological examination and digital rectal exploration of the prostate is also performed for the prevention of prostatitis and for the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
It is good to perform a proctologic examination as soon as symptoms appear, because these could also be related to cancer pathology, and in general it is useful as a screening examination for the prevention of male cancers.
What the proctological examination consists of and how it is performed
The proctologic examination consists of the collection of a thorough medical history, digital exploration of the anal canal, and anorectoscopy.
The patient who wants to undergo a proctological examination should present after undergoing a small cleansing enema about two hours before the examination.
After the history, the doctor will perform a general examination and rectal exploration: gently inserting a finger into the previously lubricated anus.
Commonly, the patient is made to lie in the fetal position (on the left side with legs flexed) or is made to lie on his knees or in the gynecological position.
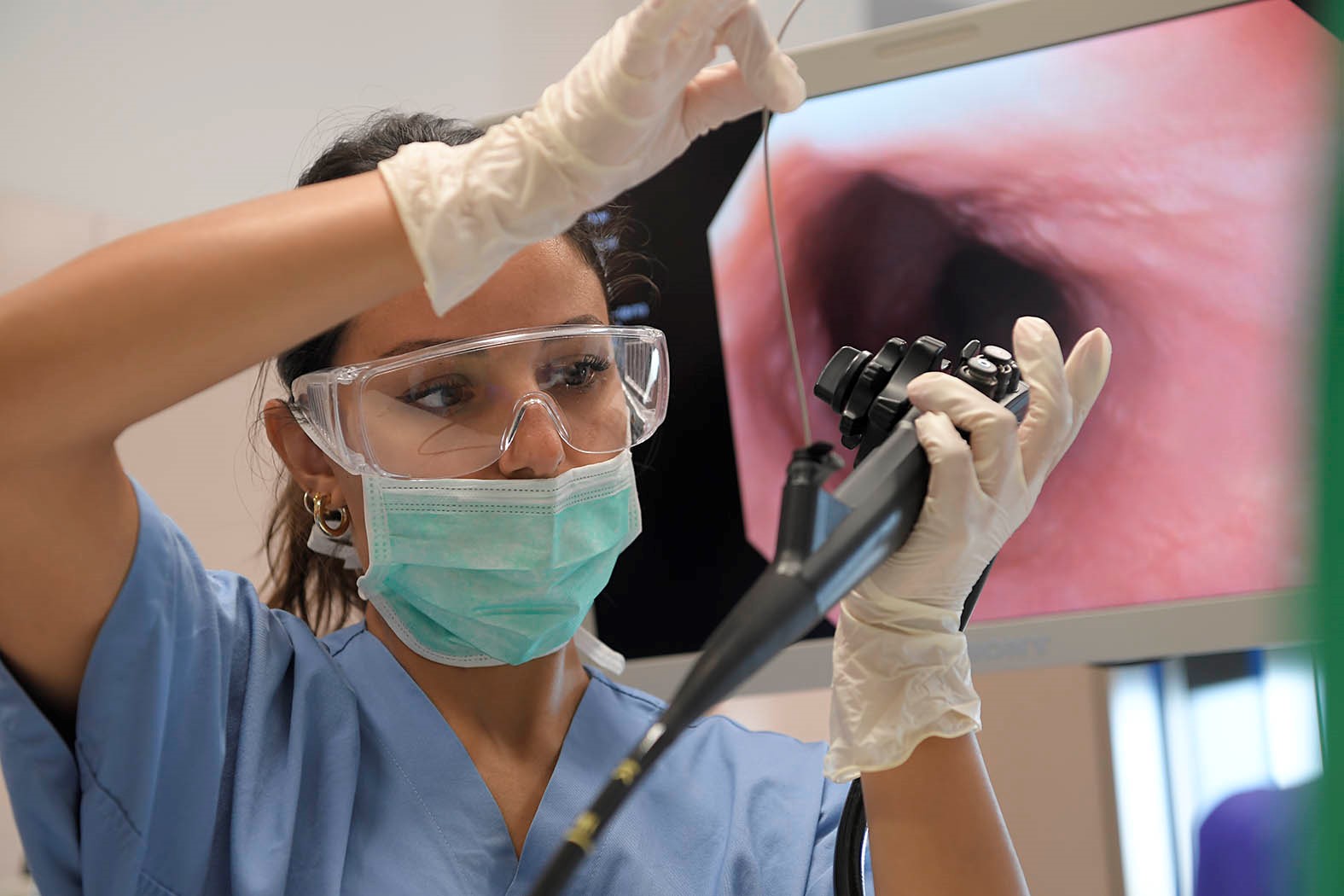
How anorectoscopy is performed
Anorettoscopy (or proctoscopy) is the introduction into the anal canal of a small, disposable, transparent plastic cylinder about 5-6 cm long, called anoscope, which allows a view of the anorectal canal (the diameter of this instrument is little more than that of the finger; therefore, discomfort is minimal and, of course, the examination can be discontinued if not endured by the patient).
Anorectoscopy also represents prevention of rectal cancer, because it allows early diagnosis and treatment of polyps that are still asymptomatic.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Therapies For The Treatment Of Prostatitis
Prostatitis: Symptoms, Causes And Diagnosis
Blood In The Stool: What Causes It And What Diseases It May Be Associated With
Black Stools And Melena: Causes And Treatment In Adults And Infants
Haemorrhoids: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Internal And External Haemorrhoids: Causes, Symptoms And Remedies
Haemorrhoids: The Newest Tests And Treatments To Treat Them
What Is The Difference Between Haemorrhoids And Fissures?
Complications Of Haemorrhoids: Simple And Oedematous External Thrombosis
Faecaloma And Intestinal Obstruction: When To Call The Doctor
Pinworms Infestation: How To Treat A Paediatric Patient With Enterobiasis (Oxyuriasis)
Intestinal Infections: How Is Dientamoeba Fragilis Infection Contracted?
Gastrointestinal Disorders Caused By NSAIDs: What They Are, What Problems They Cause
Intestinal Virus: What To Eat And How To Treat Gastroenteritis
Train With A Mannequin Which Vomits Green Slime!
Pediatric Airway Obstruction Manoeuvre In Case Of Vomit Or Liquids: Yes Or No?
Gastroenteritis: What Is It And How Is Rotavirus Infection Contracted?
Recognising The Different Types Of Vomit According To Colour
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A Benign Condition To Keep Under Control
Colitis And Irritable Bowel Syndrome: What Is The Difference And How To Distinguish Between Them?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Symptoms It Can Manifest Itself With
Experts Call For Changes To The Way IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) Is Diagnosed
What Is Dolichosigma? Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment Of The Condition
Colour Changes In The Urine: When To Consult A Doctor
Acute Hepatitis And Kidney Injury Due To Energy Drink Consuption: Case Report
Bladder Cancer: Symptoms And Risk Factors
Enlarged Prostate: From Diagnosis To Treatment
Male Pathologies: What Is Varicocele And How To Treat It
Continence Care In UK: NHS Guidelines For Best Practice
The Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment Of Bladder Cancer
Fusion Prostate Biopsy: How The Examination Is Performed


