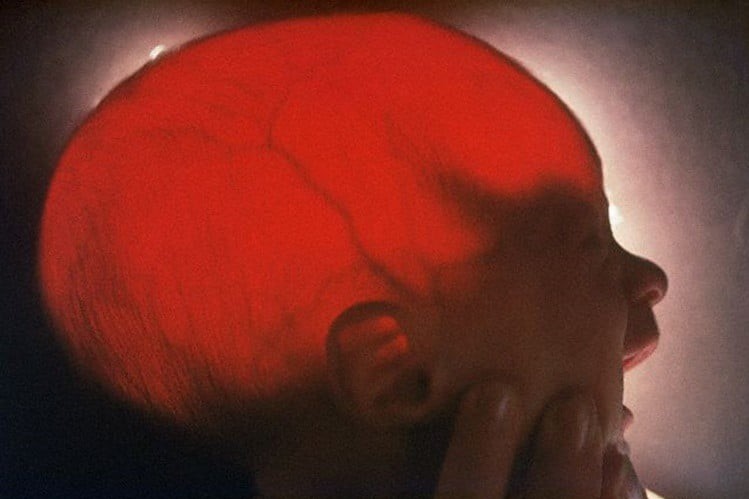
Transillumination of an infant's head for the diagnosis of hydrocephalus
Transillumination is a medical examination performed in a darkened chamber in which a region of the body is illuminated with very bright light so that the underlying structures can be observed in a non-invasive, safe, inexpensive and painless manner
The illuminated areas are very varied, for example: head, scrotum, hand and breast.
In general, however, transillumination is not a reliable method and is therefore – where possible – often combined with other imaging methods such as CT or MRI.
Transillumination and hydroencephalon
In this case, transillumination is performed on the head of a newborn child: as its skeleton is not yet completely calcified, the light from transillumination easily penetrates through the skull, showing various internal structures, such as the obvious blood vessels and their bifurcations.
This technique is useful, for example, in the diagnosis of ‘hydrocephalus’, a condition in which there is an abnormal accumulation of cephalorachidian fluid (CSF) at the level of the cerebral ventricles, which dilate and cause an increase in pressure inside the skull that causes damage to the brain tissue either directly (by compression) or indirectly (by preventing the correct flow of blood).
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Hydrocephalus: Causes, Treatment, Consequences, Life Expectancy
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: What It Is And How To Treat It
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Symptoms And Treatment For Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Our respiratory system: a virtual tour inside our body
Tracheostomy during intubation in COVID-19 patients: a survey on current clinical practice
FDA approves Recarbio to treat hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia
Hydrothorax: Causes, Pathologies, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment


