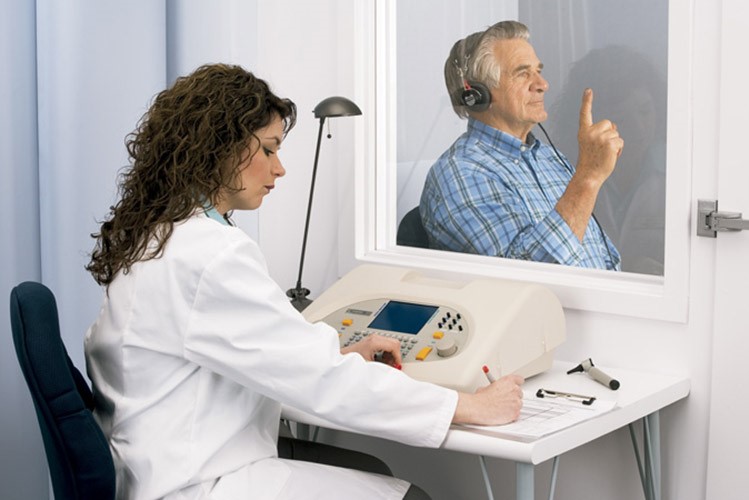
What is an audiometric test and when is it necessary?
The audiometric test is the test of choice to check the functionality of the ear and the ability to hear sounds
Sounds are heard according to intensity (based on volume) and pitch (i.e. the speed of sound vibrations).
Sounds are heard when sound waves reach the auditory nerves, which are located on the inside of both ears, and from there to the brain in the form of electrical impulses.
The intensity of sound is measured in decibels (dB); in general, a sound exceeding 85 dB can cause damage to the tympanic membrane and thus lead to deafness.
Tone is measured in cycles per second (cps) or Hertz (Hz); the human range is between 16 and 16,000 Hz.
How an audiometric test is performed
Air conduction hearing is also ascertained by having the patient wear headphones connected to an audiometer.
A number of sounds of different intensities are transmitted into the headphones, usually to one ear at a time, and the patient must raise a hand or push a button when they hear the sound.
The conduction of sound through the bones of the skull is then checked.
A small vibrator is attached behind the ear (mastoid) and the patient will be asked to signal when they hear a sound that sounds more like a vibration.
The test can take between 5 and 10 minutes, without any risk to the person undergoing it.
The audiometric test is always associated with tympanometry
This is a test that automatically checks whether there are any problems in the middle ear (inflammation, fluid discharge and chronic infections).
The audiometric test allows a more accurate diagnosis of hearing loss.
It is performed by inserting a small rubber plug into the ear bilaterally.
With this the machine, without any discomfort for the patient, measures the amount of air in the middle ear on each side.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Inner Ear Disorders: Meniere’s Syndrome Or Disease
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Paediatrics, What Needs To Be Known About Childhood Otitis
Headaches And Dizziness: It Could Be Vestibular Migraine
Migraine And Tension-Type Headache: How To Distinguish Between Them?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): Symptoms And Liberating Manoeuvres To Cure It
Parotitis: Symptoms, Treatment And Prevention Of Mumps
Acute And Chronic Sinusitis: Symptoms And Remedies
Tinnitus: What It Is, What Diseases It Can Be Associated With And What Are The Remedies
Barotrauma Of The Ear And Nose: What It Is And How To Diagnose It
How To Remove Something From Your Ear
What To Do In Case Of Earache? Here Are The Essential Check-Ups
Perforated Eardrum: What Are The Symptoms Of A Tympanic Perforation?
Earache After Swimming? Could Be ‘Swimming Pool’ Otitis
Swimmer’s Otitis, How Can It Be Prevented?
Deafness: Diagnosis And Treatment
Otitis: External, Medium And Labyrinthitis
The Vestibular Rehabilitation Of Vertiginous Patients
Vestibular Examination: The Test For Balance Disorders


