What is echocardiography (echocardiogram)?
Echocardiography is a method by which the heart and blood flow through the valves are studied using ultrasound
Unlike the radiation used in radiology, ultrasound is harmless, so no precautions are necessary and the test can be performed on any patient countless times (even in pregnant women).
What is echocardiography used for?
Echocardiography makes it possible to obtain information on the contractility of the heart, the morphology of its valves and the flow of blood in its cavities, both at rest and after exercise or taking a drug.
There are various ways of performing it:
- transthoracic echocardiography,
- transesophageal echocardiography (endoscopic),
- 3D echocardiography (three-dimensional).
Who can perform echocardiography?
There are no particular contraindications to echocardiography: anyone can undergo the test.
How does echocardiography work?
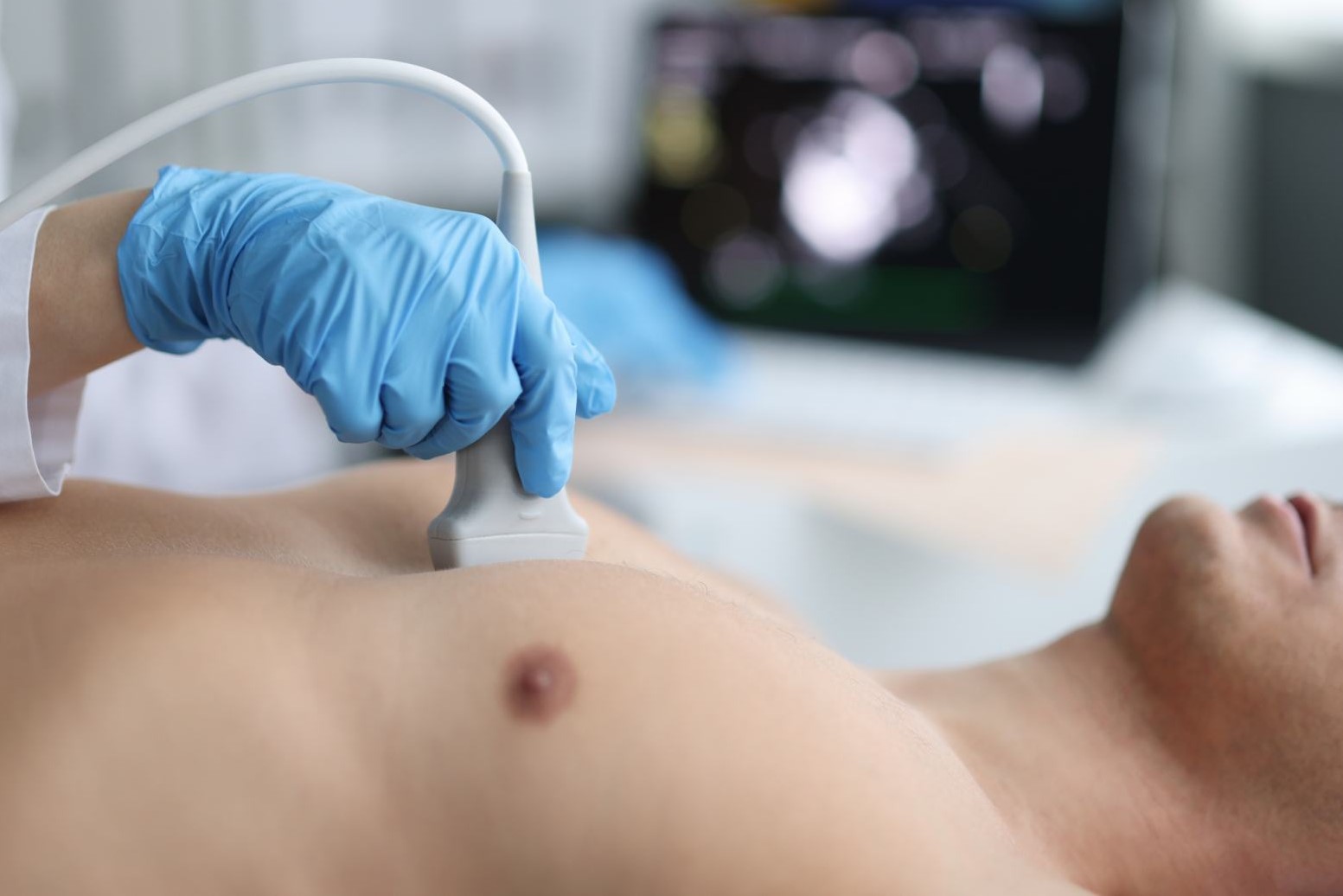
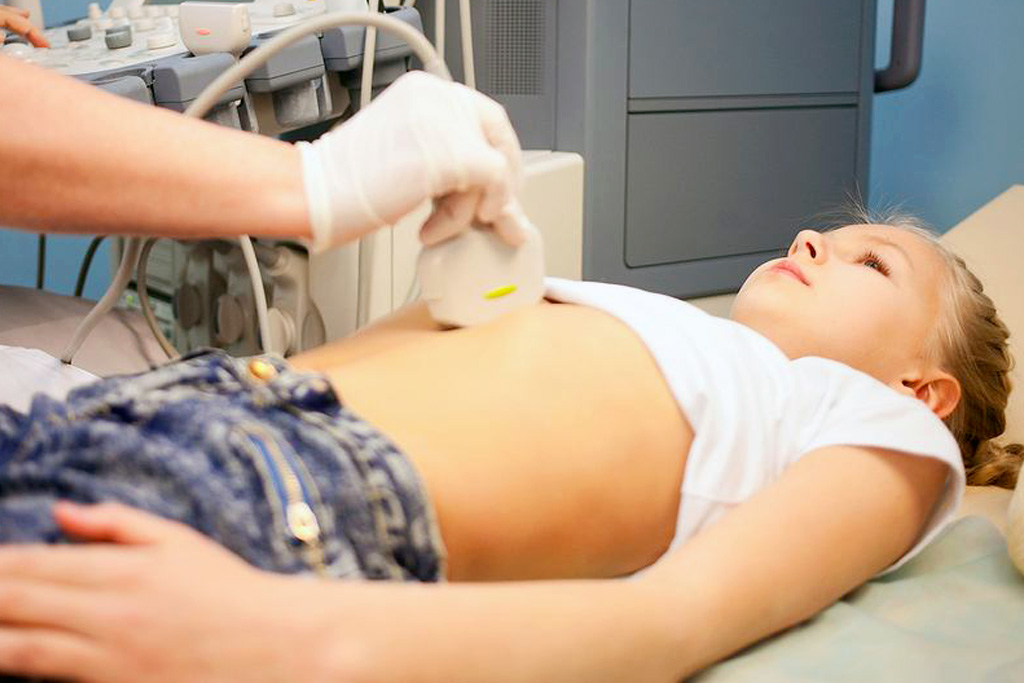
The patient must lie bare-chested on the couch of the sonographer, who will place electrodes on his chest.
Then the sonographer will spread a special gel on the patient’s chest and on the transducer, a probe which, when placed on the chest, emits ultrasound which, reflected and processed by the equipment, makes it possible to visualise the heart and its structures.
The probe is moved over the chest with gentle pressure.
The patient may be asked to remain still or breathe deeply.
At the end of the test, the electrodes will be removed and all that remains is to wipe off the gel left on the chest.
The total duration of the test is approximately 10-15 minutes.
Is echocardiography dangerous or painful?
Echocardiography is neither painful nor dangerous.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Echocardiogram: What It Is And When It Is Required
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
What Is The Loop Recorder? Discovering Home Telemetry
Cardiac Holter, The Characteristics Of The 24-Hour Electrocardiogram
Peripheral Arteriopathy: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Endocavitary Electrophysiological Study: What Does This Examination Consist Of?
Cardiac Catheterisation, What Is This Examination?
Echo Doppler: What It Is And What It Is For
Transesophageal Echocardiogram: What Does It Consist Of?
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Echotomography Of Carotid Axes
Echo- And CT-Guided Biopsy: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Echodoppler: What It Is And When To Perform It