What is Esophagogastroduodenoscopy?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic test that allows internal observation of the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum, detecting both benign and malignant changes
In the course of the test, it is also possible to take biopsies, i.e. small tissue samples from the affected organs; the samples are then analysed in the laboratory in order to obtain a targeted diagnosis.
This is the case, for example, in patients with coeliac disease: this test confirms the diagnosis.
What is oesophagogastroduodenoscopy used for?
Thanks to this test, it is possible to look inside the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum and check their condition.
In fact, oesophagogastroduodenoscopy makes it possible to ascertain or rule out the presence of abnormalities or changes in the upper digestive tract, such as stenosis, Zenker’s diverticulum, oesophagitis, ulcers, gastritis, celiac disease and tumours.
It also allows early detection of precancerous lesions, especially in at-risk individuals (e.g. patients with Barrett’s oesophagus or atrophic gastritis).
Who can perform oesophagogastroduodenoscopy?
The test is prescribed by a specialist, as in the case of patients with suspected coeliac disease or in patients with symptoms that may suggest the presence of an alteration in the upper gastrointestinal tract (pyrosis, regurgitation, dysphagia, piceous stools, vomiting, epigastralgia, etc.).
Is oesophagogastroduodenoscopy painful and/or dangerous?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is not at all painful, but it is nevertheless invasive and therefore carries with it the risk of possible complications.
However, these are rare (less than 0.05%). Perforation occurs with a maximum frequency of 0.03% and is generally linked to the presence of particular anatomical conditions (oesophageal or duodenal stenosis, Zenker’s diverticulum, neoplasm).
Some patients may present with cardio-respiratory complications related to the use of sedatives, or complications due to heart or lung disease.
How does oesophagogastroduodenoscopy work?
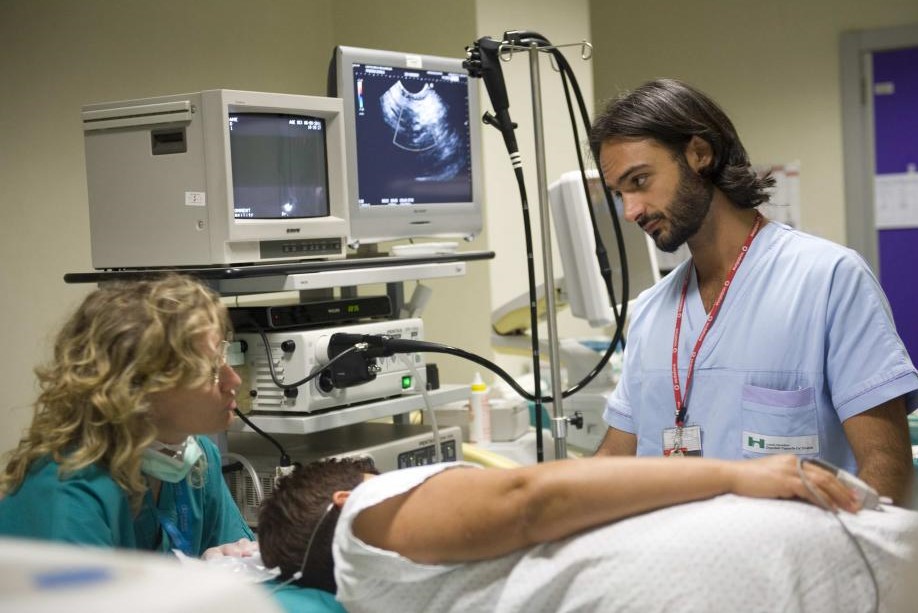
Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed in the outpatient clinic and the patient, after an interview with the doctor to collect anamnestic data, will be asked to lie on the couch on his left side.
The doctor will then proceed to insert, through the patient’s mouth, a thin, flexible tubular instrument (called an endoscope), equipped with a camera on its top.
The endoscope is advanced through the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum and the doctor observes the images obtained directly on a monitor.
Once in the vicinity of the area of interest, the doctor can perform the biopsy, i.e. the taking of small tissue samples that will be examined under a microscope to arrive at a specific diagnosis.
This procedure is not at all painful.
The test is usually of short duration (about 5 minutes) and is usually performed with conscious sedation (benzodiazepines), but technically it can also be performed without sedation; only in special cases is deep sedation managed by the anaesthetist necessary.
If sedation is performed, the patient should preferably be accompanied home and is not allowed to drive for the twelve hours following the test or make any important decisions.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD Test): How It Is Performed
Symptoms And Remedies Of A Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Cough
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Indigestion Or Dyspepsia, What To Do? The New Guidelines
Dyspepsia: What It Is, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Functional Dyspepsia: Symptoms, Tests And Treatment
Straight Leg Raise: The New Manoeuvre To Diagnose Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroenterology: Endoscopic Treatment For Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux
Oesophagitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Asthma, The Disease That Takes Your Breath Away
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Causes, Symptoms, Tests For Diagnosis And Treatment
Global Strategy For Asthma Management And Prevention
Paediatrics: ‘Asthma May Have ‘Protective’ Action Against Covid’
Esophageal Achalasia, The Treatment Is Endoscopic
Oesophageal Achalasia: Symptoms And How To Treat It
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis: What It Is, What The Symptoms Are And How To Treat It
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Causes, Symptoms, Tests For Diagnosis And Treatment
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A Benign Condition To Keep Under Control


