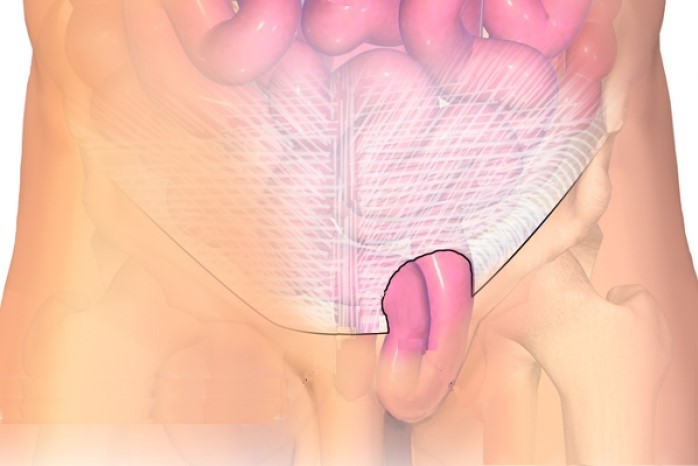
What is inguinal hernia
Let’s talk about inguinal hernia: the term hernia indicates the protrusion of a viscera, or part of it, from the natural cavity that normally contains it
An inguinal hernia is one of the most frequent diseases in the world and predominantly affects men, who suffer from it 7 to 10 times more than women
This difference is linked to anatomical differences related to the inguinal canal, a duct-like anatomical structure that connects the abdomen with the outside by crossing the full thickness of the abdominal wall.
The cause of inguinal hernia can be congenital or acquired
Congenital factors are responsible for the majority of inguinal hernias.
Failure to obliterate the vaginal process is the main factor leading to the development of an indirect inguinal hernia.
Direct hernias, on the other hand, are attributed to stress wear on the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.
Straining to defecate, coughing or lifting weights are factors that can lead to weakening of the inguinal floor.
The hernia may be inguinal, when it engages only the inguinal canal, or inguino-scrotal, when it extends to the scrotum.
It manifests itself with a swelling of the inguinal region, usually following exertion, which reduces spontaneously or with appropriate manoeuvres, in which case it is called a reducible hernia.
When the swelling is not reducible in the abdomen and is very painful, we speak of an irreducible or clogged hernia.
The latter can become choked, a rather rare complication (it appears in about 4 % of cases), causing severe pain, vomiting up to necrosis and intestinal perforation.
For this reason, it requires immediate surgical intervention.
Inguinal hernia can be diagnosed through a specialist examination, sometimes supplemented by a targeted ultrasound of the inguinal region.
There is no medical treatment for inguinal hernia
Most of the restraints that are prescribed only delay the operation without averting the risk of complications.
A groin hernia must be treated surgically.
Surgery is a now standardised procedure that involves the use of prostheses that integrate with the tissues to reinforce the abdominal wall, thus reducing the risk of recurrence.
The operation can be performed with the traditional technique, which involves an incision of about 5-8 cm at the level of the inguinal canal, and can be performed in Day-Surgery generally under local anaesthesia.
Laparoscopic surgery is indicated in cases of a multirecurrent inguinal hernia or in competitive athletes.
Recovery from the operation is a few hours, the patient can walk the same evening and can lead a normal life from the following day.
He requires a restriction to physical exertion for 30 days.
Hernia surgery has now become a routine operation as it is the most performed surgery in the world.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Inguinal Hernia: Symptoms And Treatment
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CHD): What It Is, How To Treat It
What It Is And How To Recognise Abdominal Diastasis
Chronic Pain And Psychotherapy: The ACT Model Is Most Effective
Hiatal Hernia: What It Is And How To Diagnose It
Percutaneous Discectomy For Herniated Discs
What Is That Swelling? Everything You Need To Know About Inguinal Hernia
Symptoms And Causes Of Umbilical Hernia Pain


