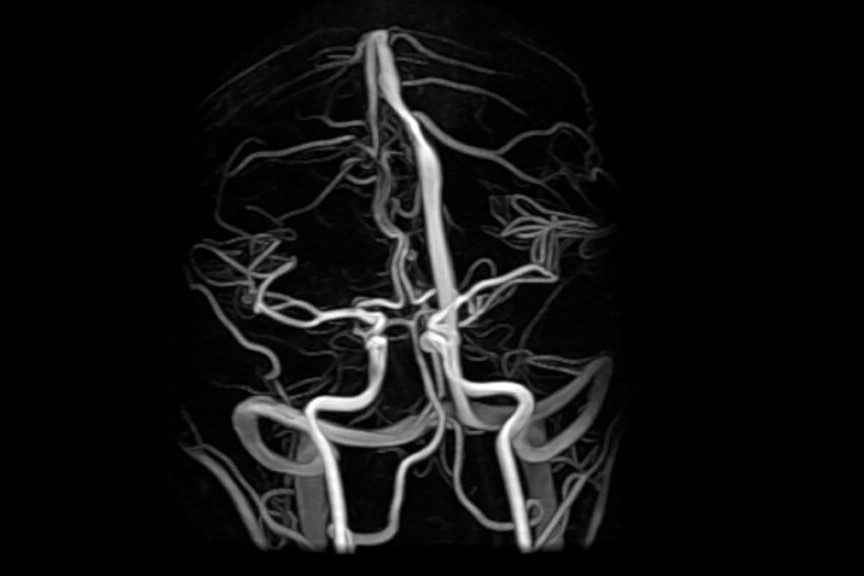
What is magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)?
Magnetic resonance angiography (MR angiography) is a non-invasive method that can make use of several techniques
MRA angiography makes it possible to study blood vessels, especially arterial and less frequently venous ones, in a given body district.
What is MRA angiography used for?
It can be useful to identify and define a vascular alteration due to stenosis, occlusion, aneurysm or malformation.
MR angiography can be performed with or without contrast medium.
In the first case, an intravenous injection of small amounts of paramagnetic contrast medium is performed (contrast bolus technique).
In the second case, specific sequences are used to obtain indications of the speed and direction of blood flow.
Who can perform MRA angiography?
Magnetic resonance angiography is harmless, but in some patients it is contraindicated:
- wearers of pacemakers and cardiac pacemaker clips or vascular, valvular or metallic prostheses
- in the first two months of pregnancy
Is MRA angiography dangerous or painful?
MR angiography is a non-invasive and painless method.
How does MRA angiography work?
It is performed like an MRA test: the patient lies supine on a couch, which is an integral part of the machine.
Depending on the part of the body to be analysed, the couch will move towards the magnetic field; if necessary, a contrast agent will first be injected.
The test can last between 20 and 45 minutes.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): When To Do It?
Medical Thermography: What Is It For?
Rheumatic Diseases: The Role Of Total Body MRI In Diagnosis
Positron Emission Tomography (PET): What It Is, How It Works And What It Is Used For
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT): What It Is And When To Perform It
Instrumental Examinations: What Is The Colour Doppler Echocardiogram?
Coronarography, What Is This Examination?
CT, MRI And PET Scans: What Are They For?
MRI, Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Heart: What Is It And Why Is It Important?
Urethrocistoscopy: What It Is And How Transurethral Cystoscopy Is Performed
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
Surgery: Neuronavigation And Monitoring Of Brain Function
Robotic Surgery: Benefits And Risks
Refractive Surgery: What Is It For, How Is It Performed And What To Do?


