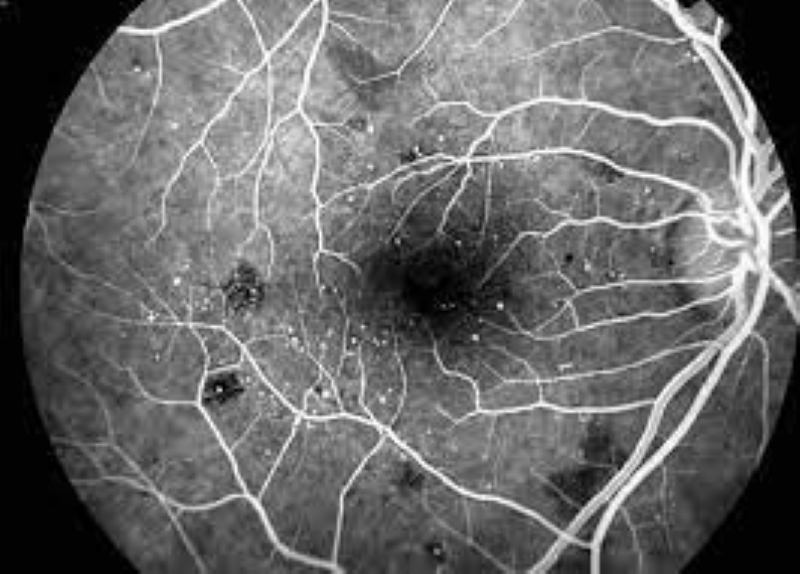
What is retinal fluorangiography?
Retinal fluorangiography: this is a useful test for diagnosing vascular diseases of the eye, including retinopathy, senile degeneration of the macula, vascular occlusions
It is carried out with an optical instrument that does not involve contact with the patient’s eye, but through a simple photograph.
It involves the intravenous injection of a dye, fluorescein, which is spread along blood vessels.
What is retinal fluorangiography used for?
The test allows you to evaluate the blood velocity in the retina and choroid, the presence of abnormalities of the vessel wall and the formation of new vessels.
In the case of vascular anomalies, the permeability of the vascular wall changes with consequent diffusion of the dye from the blood vessel into the surrounding tissue.
The dye can show fluid accumulation within the retina (oedema) or its spread in case of new blood vessel formation induced by diabetes or macular degeneration.
Which patients can have retinal fluorangiography?
All patients can undergo this test.
It is necessary for the patient to report to the doctor in case of previous allergies to contrast media and eye drops.
In such cases, the ophthalmologist will dilate the pupil with eye drops dedicated to the individual case.
In case of suspected allergies to contrast media, the examination can be performed with adequate prophylaxis and assistance during and after the examination by the healthcare personnel.
The examination is carried out by a technician in the presence of the ophthalmologist and a nurse.
It is recommended not to proceed with this test during pregnancy.
Is fluorangiography painful or dangerous?
The exam is not painful.
The patient may report discomfort when the nurse takes the peripheral vein, and may still report sensitivity to light related to flash imaging.
How does retinal fluorangiography work?
The examination is performed by a technician in the presence of the ophthalmologist and a nurse.
The retinograph is used after intravenous administration of the dye.
Frames will be taken at various times after tracer injection.
The patient will be asked to move his gaze in the various directions to make it easier to acquire the images.
Other contextual visualizations of the retinal structures are also possible, through the use of sources of different wavelengths.
The duration of the exam is approximately 10 minutes.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Retinal Detachment: Symptoms And Causes
Electroretinogram: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Symptoms, Causes And Treatment Of Dacryocystitis
Symptoms And Treatment Of Retinitis Pigmentosa
What Is Retinal Fluorangiography And What Are The Risks?
What Is The Fundus Oculi Test?
Red Eyes: What Can Be The Causes Of Conjunctival Hyperemia?
Autoimmune Diseases: The Sand In The Eyes Of Sjögren’s Syndrome
How To Prevent Dry Eyes During Winter: Tips
Corneal Abrasions And Foreign Bodies In The Eye: What To Do? Diagnosis And Treatment
Corneal Keratoconus, Corneal Cross-Linking UVA Treatment
Myopia: What It Is And How To Treat It
Presbyopia: What Are The Symptoms And How To Correct It
Nearsightedness: What It Myopia And How To Correct It
Blepharoptosis: Getting To Know Eyelid Drooping
Lazy Eye: How To Recognise And Treat Amblyopia?
What Is Presbyopia And When Does It Occur?
Presbyopia: An Age-Related Visual Disorder
Blepharoptosis: Getting To Know Eyelid Drooping
Rare Diseases: Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome
Rare Diseases: Septo-Optic Dysplasia
Diseases Of The Cornea: Keratitis
Inflammations Of The Eye: Uveitis
Oncology, An Overview Of Orbital Tumours


