Work-related musculoskeletal disorders: we can all be affected
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders: carpal tunnel, tennis elbow, herniated discs – we have all heard of them, but perhaps without knowing exactly what they are
These disorders, which are widespread in Italy and throughout the world, are illnesses that affect the musculoskeletal system and represent one of the most important causes of incapacity and absence from work due to illness: in fact, these pathologies appear, above all, in workers between the ages of 30 and 60.
What are the causes of musculoskeletal disorders?
These are disorders whose cause is multifactorial.
Both occupational and non-occupational factors contribute to their onset.
Professional factors that are most involved are: manual handling of loads, repetitive movements (especially when carried out at high frequency and speed), the use of force in carrying out one’s job, incorrect postures due also to inadequate positioning of work tools, vibrations and the absence/inadequate rest periods.
While extra-professional/individual factors include gender, age, hormonal status, previous traumas and fractures, the presence of systemic and degenerative diseases, endocrine-metabolic disorders, sports and hobbies practised.
What impact do musculoskeletal disorders have on health?
Prolonged exposure to these risk factors leads to a gradual development of biomechanical overload disorders, which typically manifest themselves with pain and limitation in movement (functional impotence) of the affected district; these symptoms and signs may affect all components of the musculoskeletal system: bones, muscles, tendons, nerves.
What is the impact on work activity?
In industrialised countries, these disorders have a negative impact on workers’ quality of life. According to INAIL, in fact, more than 70 per cent of the occupational disease complaints made each year in our country relate to a musculoskeletal disorder (and the trend is gradually increasing).
Can musculoskeletal disorders be prevented?
In order to prevent work-related musculoskeletal disorders, it is essential to provide information and training on the risks associated with different work activities, as well as to promote good practices in occupational safety and ergonomics that improve production processes in terms of hygiene and safety.
Are there parties most affected?
Depending on the type of work and activity, different body districts from the spine to the knee, from the wrist to the hip can be affected by Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders (-WMSDs).
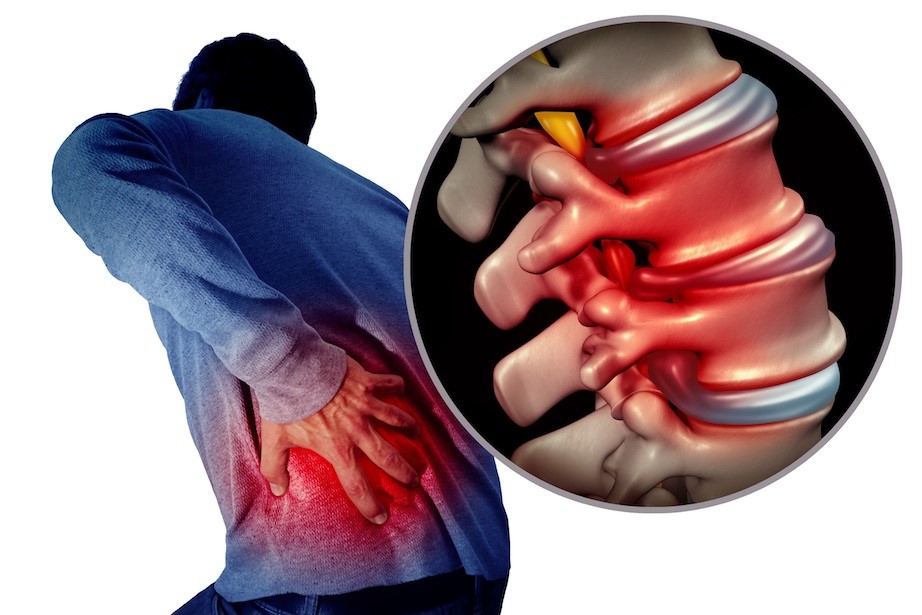
Lumbar spine
Lumbar disc hernia
It is a disease of the spine caused by the leakage of the nucleus pulposus contained in the vertebral disc (central, gelatinous part) due to weakening/rupture of the disc, which leads to subsequent compression and inflammation of the spinal nerves
Symptoms
Lower back pain that may radiate to the buttock, thigh, leg, foot. Paresthesias (altered perception of sensation) and strength deficit may also be present
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, CT scan, MRI
Shoulder
Rotator cuff tendinopathy
The ‘rotator cuff’ refers to a set of muscles and tendons in the shoulder that allow almost all movements of the joint: excessive and repetitive use can lead to its inflammation and damage (degenerative disease on an inflammatory basis)
Symptoms
Pain that is accentuated with movement, felt in the anterior and superior areas of the shoulder. Limitation of upper limb movements and strength deficit
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI
Calcific tendinitis (periarthritis) (Duplay’s disease)
Inflammation of the rotator cuff complex characterised by the formation of calcium deposits (calcifications) in the tendons of the shoulder
Symptoms
Pain in the shoulder radiating to the upper arm during shoulder rotation and abduction movements, which may also occur at rest. Functional impotence (inability to perform a movement/function)
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, ultrasound, MRI
Elbow musculoskeletal disorders
Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow) and lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
Inflammation and damage (degenerative disease on an inflammatory basis) of the tendons of the flexor muscles of the forearm at the point of insertion at the elbow.
Symptoms
Depending on the tendons involved, pain occurs in different areas of the elbow.
In lateral epicondylitis the pain appears in the lateral area of the elbow and increases with extension of the wrist ‘backwards’ (outwards).
While in medial epicondylitis the pain affects the inner elbow area and increases with flexion of the fingers and wrist against resistance (bending of the hand towards the wrist).
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, X-ray, ultrasound
Wrist/hand
Tendonitis and tenosynovitis of the flexor and extensor muscles of the fingers
Inflammation and damage (degenerative disease on an inflammatory basis) of the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles of the fingers
Symptoms
Pain and functional impotence of the wrist and hand (inability to perform a movement/function)
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, ultrasound, MRI
Snapping finger
As a result of the narrowing of the membrane surrounding the finger flexor tendon, difficulty of the finger flexor tendon to bend a finger (degenerative condition on an inflammatory basis)
Symptoms
Difficulty bending a finger or clenching the hand into a fist.
Need to help with the other hand to bend or extend the finger
Diagnosis
Specialist examination
Carpal tunnel syndrome
It is a neurological disorder (neuropathy) that affects the wrist and hand due to nerve compression of the median nerve (peripheral nerve of the upper limbs) at its passage at the wrist: it passes through a channel known as the carpal tunnel, which is formed by the carpal bones of the hand and the transverse carpal ligament
Symptoms
Paresthesia (altered perception of sensitivity to various sensory stimuli (thermal, tactile, painful, vibratory), tingling, numbness and pain in the first three fingers of the hand
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, ultrasound, electromyography
Hip
Coxoarthrosis
Caused by degeneration of articular cartilage.
Also known as arthrosis* of the hip, it is the pathology that most frequently affects this joint and tends to degenerate with age (particularly if it is not detected in the early stages).
Articular cartilage performs a cushioning function and allows the bones to slide against each other, preventing friction and inflammation. [*Disease due to wear and ageing of joints].
Symptoms
Pain on movement that improves with rest.
Difficulty walking and consequent feeling of instability.
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, X-ray, CT scan, MRI
Knee
Medial/lateral meniscopathy
Injury of the menisci, i.e. the ‘shock absorbers’ of the knee joint, fibrous cartilage pads that are essential for the movement of the joint
Symptoms
Intense pain on the inside or outside of the knee. May be associated with swelling and/or joint locking, difficulty in extending the knee
Diagnosis
Specialist examination, MRI
Are some workers at higher risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders?
All jobs that may involve biomechanical overload may result in an increased risk of these disorders.
Depending on the type of job, the affected area may be different.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Arthrosis Of The Knee: An Overview Of Gonarthrosis
Varus Knee: What Is It And How Is It Treated?
Patellar Chondropathy: Definition, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis And Treatment Of Jumper’s Knee
Symptoms And Causes Of Patella Chondropathy
Unicompartmental Prosthesis: The Answer To Gonarthrosis
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Ligaments Injuries: Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Knee Arthrosis (Gonarthrosis): The Various Types Of ‘Customised’ Prosthesis
Rotator Cuff Injuries: New Minimally Invasive Therapies
Knee Ligament Rupture: Symptoms And Causes
MOP Hip Implant: What Is It And What Are The Advantages Of Metal On Polyethylene
Hip Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Complications, And Treatment
Hip Osteoarthritis: What Is Coxarthrosis
Why It Comes And How To Relieve Hip Pain
Hip Arthritis In The Young: Cartilage Degeneration Of The Coxofemoral Joint
Visualizing Pain: Injuries From Whiplash Made Visible With New Scanning Approach
Coxalgia: What Is It And What Is The Surgery To Resolve Hip Pain?
Lumbago: What It Is And How To Treat It
Lumbar Puncture: What Is A LP?
General Or Local A.? Discover The Different Types
Intubation Under A.: How Does It Work?
How Does Loco-Regional Anaesthesia Work?
Are Anaesthesiologists Fundamental For Air Ambulance Medicine?
Epidural For Pain Relief After Surgery
Lumbar Puncture: What Is A Spinal Tap?
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): What It Consists Of, What It Is Used For
What Is Lumbar Stenosis And How To Treat It
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment


