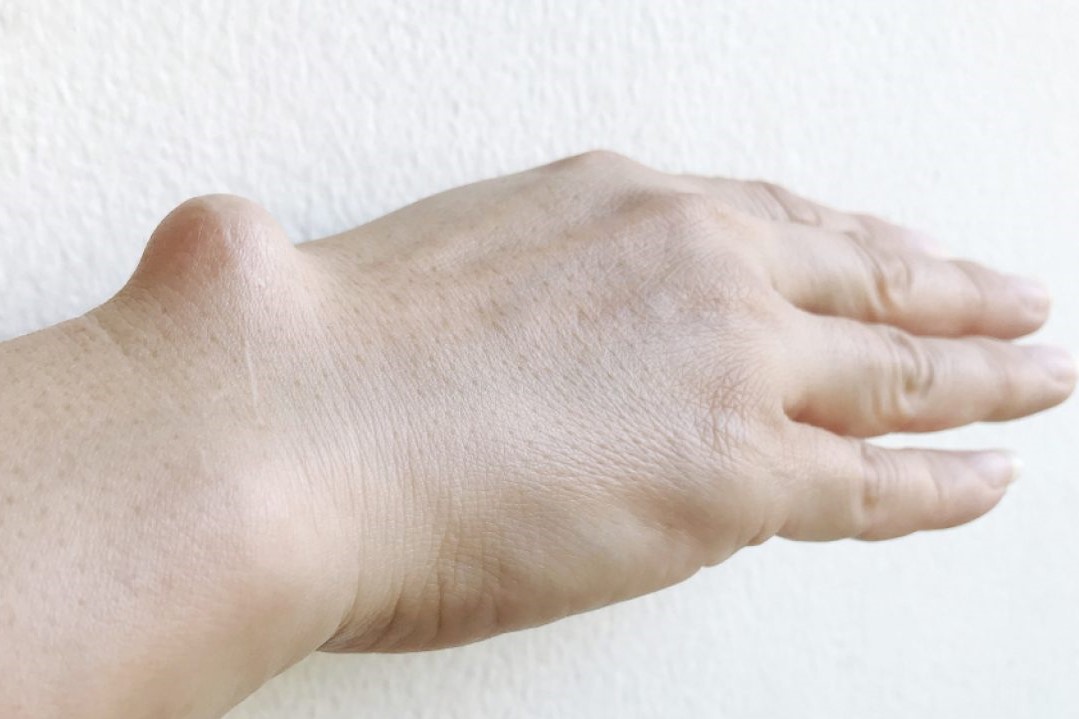
Wrist and hand cysts: what to know and how to treat them
Wrist cysts and hand cysts are benign neoformations. Wrist cysts arise from the wrist joint, while hand cysts arise from the sheaths of both the extensor and flexor tendons of the hand
They can be either large or small, sometimes compromising the functionality of our daily movements. What causes them? How are they treated?
Why do cysts form
The origin of these formations, which are absolutely harmless, can be traced to various factors:
- the person’s predisposition
- a specific trauma (e.g. from over-exertion or certain types of sporting activity);
- certain microtraumas or stresses repeated daily (e.g. certain types of work activity).
It has been demonstrated that sports activities involving frequent use of the hand and wrist, such as volleyball, basketball and handball, are predisposing to the onset of these neoformations: the continuous pressure and stress on the joints (such as extension and flexion of the wrist) can therefore favour the appearance of cysts.
Certain occupational activities are also predisposed to the development of cysts: just think of certain manual jobs that involve significant use of workloads on the wrist, such as those working in construction or workers in general.
Cysts, symptoms: how do they occur?
Most of the time these cysts do not cause any kind of pain or discomfort, and can be left as they are, without intervention.
On the contrary, if they are large enough to create functional discomfort for the patient, or if they hurt, cause discomfort or limit the functionality of the hand or wrist, then there may be a surgical indication for removal.
The reasons why wrist cysts can limit daily or work activities are that they originate deep in the joint, creating a mechanical obstacle to movement.
Another indication is when the size of the cyst is too large or pronounced and, being on the course of the tendon, can lead to friction and subsequent inflammation of the tendon.
In such situations, a surgical solution may be required, always on the advice of your hand specialist.
Diagnosis of a wrist or hand cysts
The diagnosis is essentially clinical because it is based on the patient’s medical history and the assessment of the specialist, in this case the orthopaedic surgeon, i.e. the hand surgeon.
For greater diagnostic accuracy, an ultrasound scan can be used, which is sufficient to identify the type of cyst and its origin.
The removal of cysts
As far as treatment is concerned, as mentioned, if they do not cause any problems, they do not need any kind of treatment. if not, they can be removed.
Some of these, especially wrist cysts, can be removed by arthroscopy, which means less invasive surgery and a quicker recovery.
The operation is carried out in an outpatient setting, with only the arm being put to sleep, and lasts about 15-20 minutes.
The wound is then closed using intradermal aesthetic stitches that self-absorb after about two weeks.
As always, after any surgical treatment, the post-operative rehabilitation protocol, in a few sessions, will allow the patient to recover articulation and manage the scars for a rapid recovery.
From the day after surgery, the patient will already be able to return to normal daily activities, driving a car and playing sports.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Breast Cysts, How To Detect Them
Liver Cysts: When Is Surgery Necessary?
Wrist Cysts: What They Are And How To Treat Them


