What is pelvic ultrasound?
Pelvic ultrasound is an investigation that does not involve the use of radiation and is based on the emission of ultrasound, which is considered to cause no harm to the body
It is conducted by spatial focusing according to the various anatomical planes of the organ being tested.
How does pelvic ultrasound work?
During the test, the patient is made to lie on their stomach.
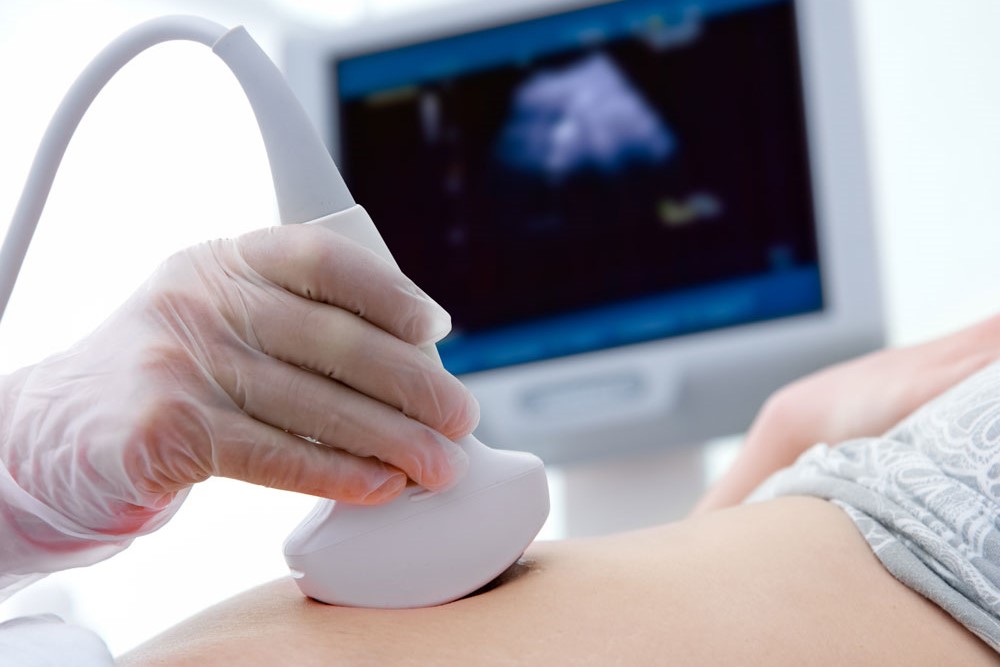
The procedure involves sliding the ultrasound probe – manually operated by the doctor – over the lower abdomen, which has previously been sprinkled with a transparent gel to facilitate the passage of ultrasound from the probe.
For better evaluation, there are endocavitary probes for studying the prostate and female internal genitalia (trans-rectal in men and trans-vaginal in women).
What is pelvic ultrasound used for?
Through pelvic (or lower abdominal) echotomography it is possible to visualise the bladder and prostate in men and the bladder, uterus and ovaries in women.
The objective is to visualise the morphology of these organs and identify any atypical masses or malformations.
Who can have a pelvic ultrasound scan?
Anyone for whom it is necessary to investigate the morphology and obtain information about the affected organs.
Is pelvic ultrasound painful or dangerous?
This test is not painful and involves no risks because it does not use ionising radiation but ultrasound waves, which are harmless to the body.
Read Also
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Abdominal Health Emergencies, Warning Signs And Symptoms
Abdominal Ultrasound: How It Is Performed And What It Is Used For
Diagnostic Tests: What Is Ecoendoscopy?
What Is Ultrasound Of The Complete Abdomen?
What Is The Resting Cardiac Echocolordoppler (Or Echocardiogram)?
Echo- And CT-Guided Biopsy: What It Is And When It Is Needed
Echodoppler: What It Is And When To Perform It
What Is 3D Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
What Is Stress Echocardiography And What Is It Used For?
What Is Echocardiography (Echocardiogram)?
Echocardiogram: What It Is And When It Is Required
What Is Echocolordoppler Of The Supra-Aortic Trunks (Carotids)?
What Is The Loop Recorder? Discovering Home Telemetry
Cardiac Holter, The Characteristics Of The 24-Hour Electrocardiogram
Peripheral Arteriopathy: Symptoms And Diagnosis
Endocavitary Electrophysiological Study: What Does This Examination Consist Of?
Cardiac Catheterisation, What Is This Examination?
Echo Doppler: What It Is And What It Is For
Transesophageal Echocardiogram: What Does It Consist Of?
Venous Thrombosis: From Symptoms To New Drugs
Echotomography Of Carotid Axes



