What it is and how to get out of dermatillomania
It is called dermatillomania and is a compulsive disorder characterised by the habit of constantly pinching and ‘tormenting’ the skin, sometimes consciously, sometimes unconsciously as a sort of nervous tic
But what are the causes? What are the risks? And what can be done about it?
When dermatillomania occurs
Dermatillomania strikes particularly during the adolescent period, but can continue, if unresolved, into adulthood.
In some cases, it can also affect older people, especially if they are already suffering from depression.
How dermatillomania manifests itself
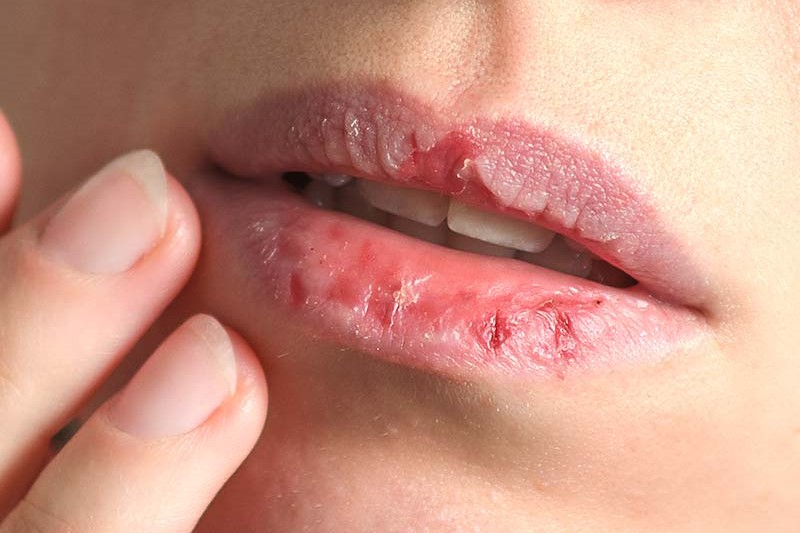
Typical of dermatillomania (from the Greek dèrma – skin, tìllo – to tear and manìa – obsession) is the act of repeatedly pinching or scratching the skin to the point of causing lesions and excoriations.
The area most frequently affected is the face, but ‘pinching’ can affect any part of the body and be done not only with nails and teeth, but also with pins, tweezers or similar instruments.
Sufferers pinch not only pimples or scabs, but also healthy skin.
The causes
The origin of dermatillomania is nervous. Usually skin pimpling is linked to states of anxiety and stress, against which it represents a kind of ‘release valve’.
Besides anxiety, depression can also trigger the instinct to tickle the skin, which in many cases becomes an unconscious habit.
Dermatillomania, the consequences
They can range from small scratches to real scars, infections and obvious marks that disfigure the person, resulting in psychological discomfort and difficulty showing oneself in public and having normal social relationships.
Treatment
Treatment of the disorder is primarily psychological.
It can be very useful to consult a specialist, psychologist or psychotherapist, who can identify the behavioural causes that trigger the problem and direct the person towards a psychotherapeutic course during which they can learn to manage stress and anxiety situations and maintain self-control.
Obviously, if lesions, scars or infections are present, it is important to contact the dermatologist who, on the basis of the person’s skin condition, will be able to suggest the most suitable topical pharmacological therapy.
The synergy between psychologist and dermatologist, as for other skin pathologies in which a psychological component is present, is of fundamental importance in order to deal with the disorder and its consequences in a complete and effective manner and avoid its chronicisation.
Read Also:
Emergency Live Even More…Live: Download The New Free App Of Your Newspaper For IOS And Android
Trichotillomania, Or The Compulsive Habit Of Pulling Out Hair And Hairs
Impulse Control Disorders: Kleptomania
Impulse Control Disorders: Ludopathy, Or Gambling Disorder
Facebook, Social Media Addiction And Narcissistic Personality Traits
Nomophobia, An Unrecognised Mental Disorder: Smartphone Addiction
The Panic Attack And Its Characteristics
Psychosis Is Not Psychopathy: Differences In Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Management Of Mental Disorders In Italy: What Are ASOs And TSOs, And How Do Responders Act?
Yale Medicine: Why Telehealth For Mental Health Care Is Working
Eco-Anxiety: The Effects Of Climate Change On Mental Health
Firefighters / Pyromania And Obsession With Fire: Profile And Diagnosis Of Those With This Disorder
Pyromania: ICD-11 Classification, Causes, Symptoms, Characteristics, Risks, Treatment, Medication



